5X_Measuring_galaxy_redshifts
... galaxies to be recorded simultaneously. (SALT uses mulitple slits to allow for MOS-Mulit-object spectroscopy) They use optical fibres to isolate light from different galaxies in the focal plane of the telescope. One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal ...
... galaxies to be recorded simultaneously. (SALT uses mulitple slits to allow for MOS-Mulit-object spectroscopy) They use optical fibres to isolate light from different galaxies in the focal plane of the telescope. One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal ...
Science Explorer
... file:///D|/SciExp/generic/0130643777/ch8/ch8_s1_1.html (1 of 3)10/21/2009 1:33:05 PM ...
... file:///D|/SciExp/generic/0130643777/ch8/ch8_s1_1.html (1 of 3)10/21/2009 1:33:05 PM ...
Research Powerpoint - University of Maryland: Department of
... right, comet Lulin, seen with Swift’s Xray (red) and UV (blue) telescopes. Comets glow in X-ray when the solar wind flows through the neutral gas (as seen here in UV). ...
... right, comet Lulin, seen with Swift’s Xray (red) and UV (blue) telescopes. Comets glow in X-ray when the solar wind flows through the neutral gas (as seen here in UV). ...
Star71 Test report(Astronomy Technology Today)
... I keep my observatory air conditioner thermostat set to 80°F. During the subsequent image runs, I noted the ambient temperature dropped 10° from the end of twilight until I packed it in. The telescope maintained its focus over this temperature range with no corrections required! ...
... I keep my observatory air conditioner thermostat set to 80°F. During the subsequent image runs, I noted the ambient temperature dropped 10° from the end of twilight until I packed it in. The telescope maintained its focus over this temperature range with no corrections required! ...
Observing the Sky
... solar system and the stars in our galaxy are moving at different speeds as they revolve around the Milky Way. In addition, because the stars are at varying distance from the Earth, they appear to move in the sky at different speeds, a phenomenon known as parallax. Thus, a hundred thousand years ago, ...
... solar system and the stars in our galaxy are moving at different speeds as they revolve around the Milky Way. In addition, because the stars are at varying distance from the Earth, they appear to move in the sky at different speeds, a phenomenon known as parallax. Thus, a hundred thousand years ago, ...
Student Project - Ott Planetarium
... portion of the chart. The wavelengths to the left of visible light are too long for our eyes to detect, while those on the right are to short. As the wavelength decreases, the energy level of the wave increases, so X-Rays are higher energy than Infrared waves. The Hubble Space Telescope operates ...
... portion of the chart. The wavelengths to the left of visible light are too long for our eyes to detect, while those on the right are to short. As the wavelength decreases, the energy level of the wave increases, so X-Rays are higher energy than Infrared waves. The Hubble Space Telescope operates ...
The Astronomical Search for Origins
... eAstronomy/activeAstronomy.html • SEEK and FLIR smart phone IR cameras ...
... eAstronomy/activeAstronomy.html • SEEK and FLIR smart phone IR cameras ...
Using Multilayer Optics to Measure X-ray Polarization Herman L. Marshall (MIT CSR)
... • Use C/Ni Multilayer ...
... • Use C/Ni Multilayer ...
60-inch Mirror Successfully Re-aluminized in August
... Palomar Transient Factory Supernova Count on the Rise An exploding star is called a supernova. Astronomers have been systematically hunting them since Fritz Zwicky began his first survey for them with Palomar’s 18-inch Schmidt telescope in 1936. Dr. Zwicky found 120 of them in his lifetime. Modern ...
... Palomar Transient Factory Supernova Count on the Rise An exploding star is called a supernova. Astronomers have been systematically hunting them since Fritz Zwicky began his first survey for them with Palomar’s 18-inch Schmidt telescope in 1936. Dr. Zwicky found 120 of them in his lifetime. Modern ...
Who Invented the Telescope?
... The British ethnographer and mathematician Thomas Harriot also used a spyglass to observe the moon. Harriot became famous for his travels to the early settlements in Virginia to detail resources there. His August 1609 drawings of the moon predate Galileo's, but were never published. The more he ...
... The British ethnographer and mathematician Thomas Harriot also used a spyglass to observe the moon. Harriot became famous for his travels to the early settlements in Virginia to detail resources there. His August 1609 drawings of the moon predate Galileo's, but were never published. The more he ...
Spectrometer The instrument used in the space telescope
... positioned slits to match the positions of objects in the FOV. • Because of the width of the entrance field, the optics of this spectroscope need to have their aberrations corrected over a much wider FOV than those for normal spectroscopes and this is the reason uses transmission optics. ...
... positioned slits to match the positions of objects in the FOV. • Because of the width of the entrance field, the optics of this spectroscope need to have their aberrations corrected over a much wider FOV than those for normal spectroscopes and this is the reason uses transmission optics. ...
L The James Webb Space Telescope
... Astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, started their first plans for a follow-on instrument in 1989 — a year before the Hubble itself was launched. It should finally make it to the launch pad 24 years later. Although its design and cost have changed a few times ...
... Astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, started their first plans for a follow-on instrument in 1989 — a year before the Hubble itself was launched. It should finally make it to the launch pad 24 years later. Although its design and cost have changed a few times ...
Telescopes
... Light does not go through them and as a result is not dispersed. Most telescopes today are reflecting Multiple mirrors bounce the light around, each time bending it slightly and thus magnifying the image. ...
... Light does not go through them and as a result is not dispersed. Most telescopes today are reflecting Multiple mirrors bounce the light around, each time bending it slightly and thus magnifying the image. ...
Astronomy Today, Chapter 3 Radiation 3
... b. Equitorial: must be aligned with the Earth's axis Images and Detectors 5-2 Telescope Size Intro Light-Gathering Power 10. Describe the powers of the telescope and rank them from most important to least important. a. Light-gathering: bigger telescope see dimmer objects b. Resolving power: accurate ...
... b. Equitorial: must be aligned with the Earth's axis Images and Detectors 5-2 Telescope Size Intro Light-Gathering Power 10. Describe the powers of the telescope and rank them from most important to least important. a. Light-gathering: bigger telescope see dimmer objects b. Resolving power: accurate ...
Research into a Single-Aperture Light Field Camera System to
... Northrop Grumman software then performs the following steps: (1) image refocusing, (2) change detection, (3) range finding, and (4) 3D reconstruction. In Step (1), a series of 2D images are generated from each light field image; as described above, for an optically optimized/matched system the 2D im ...
... Northrop Grumman software then performs the following steps: (1) image refocusing, (2) change detection, (3) range finding, and (4) 3D reconstruction. In Step (1), a series of 2D images are generated from each light field image; as described above, for an optically optimized/matched system the 2D im ...
Glossary of Space Terms
... at least twice a year. Newton was the most important thinker of his day, and he believed that only mirrors would eliminate chromatic abberation and that it could never be done with lenses. The mirror telescopes of the day suffered from poor image quality. This was due to the use of a spherically gro ...
... at least twice a year. Newton was the most important thinker of his day, and he believed that only mirrors would eliminate chromatic abberation and that it could never be done with lenses. The mirror telescopes of the day suffered from poor image quality. This was due to the use of a spherically gro ...
Magnification and Field of View: An Introduction
... Optical systems like telescopes give you an angular field of view, measured in degrees (◦ ), the standard unit of angular measure. For instance, when you hold your thumb finger close to your eye, it appears large, whereas when you hold it at arm’s length it appears much smaller. This is due to a cha ...
... Optical systems like telescopes give you an angular field of view, measured in degrees (◦ ), the standard unit of angular measure. For instance, when you hold your thumb finger close to your eye, it appears large, whereas when you hold it at arm’s length it appears much smaller. This is due to a cha ...
G060325-00
... • 2006: 3rd ASTROD Symposium (July 14-16, Beijing) before COSPAR (July 16-23) in Beijing ...
... • 2006: 3rd ASTROD Symposium (July 14-16, Beijing) before COSPAR (July 16-23) in Beijing ...
astronomy timeline
... Descartes develops concept of inertial motion. Descartes believed that all motion resulted from collision with particles called "corpuscles". In the absence of such collisions, a body remains at rest. An object in motion continues to move in the same direction at the same speed. p. 80-81, F 2.1 ...
... Descartes develops concept of inertial motion. Descartes believed that all motion resulted from collision with particles called "corpuscles". In the absence of such collisions, a body remains at rest. An object in motion continues to move in the same direction at the same speed. p. 80-81, F 2.1 ...
Lecture 7
... The first telescopes, used in the early 1600s, were refractors. Galileo used a small refractor to stunning effect, discovering craters on the Moon, satellites around Jupiter, sunspots, and the phases of Venus and Mercury. Astronomy was revolutionised. Galileo's telescope had a lens 3c ...
... The first telescopes, used in the early 1600s, were refractors. Galileo used a small refractor to stunning effect, discovering craters on the Moon, satellites around Jupiter, sunspots, and the phases of Venus and Mercury. Astronomy was revolutionised. Galileo's telescope had a lens 3c ...
UNIT TWO Astronomical Instruments and Light
... a. there is less air to dim the light. b. the seeing is better. c. CCDs work better when there is less oxygen in the air. d. all of the above e. a and b A _________ has a few million light sensitive diodes in an array about a half inch square. a. photometer b. charge-coupled device c. spectrograph d ...
... a. there is less air to dim the light. b. the seeing is better. c. CCDs work better when there is less oxygen in the air. d. all of the above e. a and b A _________ has a few million light sensitive diodes in an array about a half inch square. a. photometer b. charge-coupled device c. spectrograph d ...
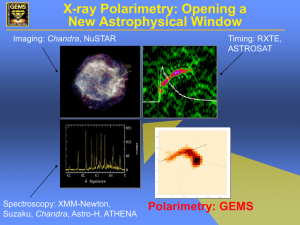
X-ray Polarimetry - XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre
... PF>72% (off pulse) >88% (off pulse plus bridge) Consistent with 77% polarized signal along pulsar rotation axis, maximum ...
... PF>72% (off pulse) >88% (off pulse plus bridge) Consistent with 77% polarized signal along pulsar rotation axis, maximum ...
mission assignment sheets
... interpret the data without assistance. You are simulating an unpiloted mission such as the Magellan mission to Venus (1990). The Magellan spacecraft sent radar waves (microwave radiation) down through the atmosphere to the surface of the Venus where it was then reflected back to the spacecraft. The ...
... interpret the data without assistance. You are simulating an unpiloted mission such as the Magellan mission to Venus (1990). The Magellan spacecraft sent radar waves (microwave radiation) down through the atmosphere to the surface of the Venus where it was then reflected back to the spacecraft. The ...
FourImBII - National University of Singapore
... I first describe the principles of imaging using rays to explain pinhole cameras, waves to explain what a lens does, and Fourier transforms to explain the magic of holograms. Then I describe my own contributions to the analysis and design of computation-based coherent imaging systems at four organiz ...
... I first describe the principles of imaging using rays to explain pinhole cameras, waves to explain what a lens does, and Fourier transforms to explain the magic of holograms. Then I describe my own contributions to the analysis and design of computation-based coherent imaging systems at four organiz ...
XMM-Newton

The XMM-Newton, also known as the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission and the High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission, is an orbiting X-ray observatory launched by ESA in December 1999 on an Ariane 5 rocket. It is named in honor of Sir Isaac Newton. The telescope was placed in a very eccentric 48 hour elliptical orbit at 40°; at its apogee it is nearly 114,000 kilometres (71,000 mi) from Earth, while the perigee is only 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi).