The Effects of Atmospheric Turbulence on Simulated
... We are primarily interested in the optical methods of detection to provide direct images of the planets. Two techniques have proven promising in selectively attenuating the direct starlight to provide views of planets: coronagraphy and nulling interferometry [10]. Coronagraphy suppresses starlight b ...
... We are primarily interested in the optical methods of detection to provide direct images of the planets. Two techniques have proven promising in selectively attenuating the direct starlight to provide views of planets: coronagraphy and nulling interferometry [10]. Coronagraphy suppresses starlight b ...
PPT - Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
... Exquisite positional information (5 nrad accuracy) – New capabilities for control – Reduced mission risk ...
... Exquisite positional information (5 nrad accuracy) – New capabilities for control – Reduced mission risk ...
3. Telescopes: The Tools of Astronomy
... • Gamma rays are the most high-energy radiation we can detect. This supernova remnant would be nearly invisible without the Fermi satellite and its gammaray detector. ...
... • Gamma rays are the most high-energy radiation we can detect. This supernova remnant would be nearly invisible without the Fermi satellite and its gammaray detector. ...
Angular measurements
... b. [1] What is the solid angle subtended by a single Hubble telescope pixel? (Assume that the pixel is square.) c. If a polar orbiting satellite flying at an altitude of 800 km had an imaging system that was capable of the same angular resolution: i. [1] What would be the length of a single pixel on ...
... b. [1] What is the solid angle subtended by a single Hubble telescope pixel? (Assume that the pixel is square.) c. If a polar orbiting satellite flying at an altitude of 800 km had an imaging system that was capable of the same angular resolution: i. [1] What would be the length of a single pixel on ...
SGS - SBIG
... stabilization is faulty and the darks taken on separate nights do not subtract well. I have investigated this problem and found that darks on separate nights indeed do not subtract well, but it is not a temperature stabilization problem. It is as if something changes in the CCD slowly over time, and ...
... stabilization is faulty and the darks taken on separate nights do not subtract well. I have investigated this problem and found that darks on separate nights indeed do not subtract well, but it is not a temperature stabilization problem. It is as if something changes in the CCD slowly over time, and ...
copyright 2002 scientific american, inc.
... Space Agency’s X-ray Multi-Mirror satellite found evidence of emission lines from silicon, sulfur, argon and other elements commonly released by supernovae. Although researchers still debate the matter, a growing school of thought holds that the same object can produce, in some cases, both a burst a ...
... Space Agency’s X-ray Multi-Mirror satellite found evidence of emission lines from silicon, sulfur, argon and other elements commonly released by supernovae. Although researchers still debate the matter, a growing school of thought holds that the same object can produce, in some cases, both a burst a ...
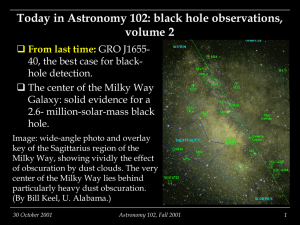
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... The center of the Milky Way is obscured by dust; it cannot be seen at visible through longer X-ray wavelengths. It is bright at infrared and radio wavelengths, and hard (shortwavelength) X rays, which are transmitted through the dust. The name Sagittarius A indicates that it’s the brightest radi ...
... The center of the Milky Way is obscured by dust; it cannot be seen at visible through longer X-ray wavelengths. It is bright at infrared and radio wavelengths, and hard (shortwavelength) X rays, which are transmitted through the dust. The name Sagittarius A indicates that it’s the brightest radi ...
Stellar-Mass Black Holes and Ultraluminous X
... stars, more than 10% of the rest mass energy can be released—a process more efficient at energy release than nuclear fusion. For black holes, the efficiency can be even higher (3), but the presence of an event horizon—from within which no signals can ever be observed in the outside universe—means th ...
... stars, more than 10% of the rest mass energy can be released—a process more efficient at energy release than nuclear fusion. For black holes, the efficiency can be even higher (3), but the presence of an event horizon—from within which no signals can ever be observed in the outside universe—means th ...
CCD Observatory in school - EU-HOU
... However, valuable observations can be made with Internet cameras – webcams. A typical webcam usually costs about €25 and after slight adjustments it can be used for very interesting observations. What criteria should be then taken into account while choosing a particular model? The most important pa ...
... However, valuable observations can be made with Internet cameras – webcams. A typical webcam usually costs about €25 and after slight adjustments it can be used for very interesting observations. What criteria should be then taken into account while choosing a particular model? The most important pa ...
Active mirror technology for large space telescopes
... Mirrors for space applications can benefit from the use of this concept to reduce overall mass, yet maintain performance with the active system. We are now manufacturing a 2-m NGST mirror system demonstrator (NMSD) that will prove out this method for space optics. The NMSD achieves low mass with a 2 ...
... Mirrors for space applications can benefit from the use of this concept to reduce overall mass, yet maintain performance with the active system. We are now manufacturing a 2-m NGST mirror system demonstrator (NMSD) that will prove out this method for space optics. The NMSD achieves low mass with a 2 ...
dobsonians - Optical Vision Ltd
... edge of space and that column seldom stays still. Similarly, when viewing over land you are often looking through heat waves radiating from the ground, house, buildings, etc. Your telescope may be able to give very high magnification but what you end up magnifying is all the turbulence between the t ...
... edge of space and that column seldom stays still. Similarly, when viewing over land you are often looking through heat waves radiating from the ground, house, buildings, etc. Your telescope may be able to give very high magnification but what you end up magnifying is all the turbulence between the t ...
Could We Divert a Threatening Asteroid?
... larger than a kilometer (0.6 mile) across. Several tens of thousands of smaller, football-field-size objects approach or cross Earth’s orbit, although at present we have catalogued only a few percent of them. These searches, known as the Spaceguard Survey, were prompted by a growing realization in t ...
... larger than a kilometer (0.6 mile) across. Several tens of thousands of smaller, football-field-size objects approach or cross Earth’s orbit, although at present we have catalogued only a few percent of them. These searches, known as the Spaceguard Survey, were prompted by a growing realization in t ...
Hubble Deep Field Image
... named Hubble Deep Field North (HDFNorth). Same criteria, only now in Southern Hemisphere, within the Tucana ...
... named Hubble Deep Field North (HDFNorth). Same criteria, only now in Southern Hemisphere, within the Tucana ...
The Classical Achromat
... All of these classical achromatic objectives have air spaces between the crown and flint elements. Typically the separation is very small – about the same thickness as a postage stamp (between 0.02 and 0.05 mm). Although the original Fraunhofer doublet was designed with a narrow air gap, like the on ...
... All of these classical achromatic objectives have air spaces between the crown and flint elements. Typically the separation is very small – about the same thickness as a postage stamp (between 0.02 and 0.05 mm). Although the original Fraunhofer doublet was designed with a narrow air gap, like the on ...
- ESA Earth Online
... signal per products and the tangent altitude at which the star is lost. The most interesting analysis presented in the level 1 daily report is the monitoring of the SATU-Y variation along the mission, in fact since Apr 2006 strong oscillation were observed in this parameter and this problem is still ...
... signal per products and the tangent altitude at which the star is lost. The most interesting analysis presented in the level 1 daily report is the monitoring of the SATU-Y variation along the mission, in fact since Apr 2006 strong oscillation were observed in this parameter and this problem is still ...
File - Science Maths Master
... A parallel beam of monochromatic light, incident on a converging lens and parallel to the axis, fills the lens aperture completely. After transmission through the lens the beam falls on a plane surface placed parallel to the plane of the aperture and approximately 1 m away from it. The plane surface ...
... A parallel beam of monochromatic light, incident on a converging lens and parallel to the axis, fills the lens aperture completely. After transmission through the lens the beam falls on a plane surface placed parallel to the plane of the aperture and approximately 1 m away from it. The plane surface ...
Neon and oxygen in low activity stars: towards a coronal unification
... to additionally increase jointly within allowed errors would provide a sufficient opacity increase. Several objections to this solution were raised, especially from solar observers. A reassessment of solar coronal data from the Solar Maximum Mission led to an upper limit of Ne/O = 0.18 ± 0.04 for acti ...
... to additionally increase jointly within allowed errors would provide a sufficient opacity increase. Several objections to this solution were raised, especially from solar observers. A reassessment of solar coronal data from the Solar Maximum Mission led to an upper limit of Ne/O = 0.18 ± 0.04 for acti ...
X-ray binaries
... Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classification is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a so ...
... Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classification is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a so ...
X-ray binaries
... Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classification is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a so ...
... Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classification is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a so ...
The effect of seeing on Stellar Profiles As light passes through the
... The effect of seeing on Stellar Profiles As light passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, the cells refract light by different amounts due to the varying temperatures and pressure within each cell. The effect is to blur a point source such as a star in to a smoothly varying disc. If the image is over ...
... The effect of seeing on Stellar Profiles As light passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, the cells refract light by different amounts due to the varying temperatures and pressure within each cell. The effect is to blur a point source such as a star in to a smoothly varying disc. If the image is over ...
XMM-Newton

The XMM-Newton, also known as the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission and the High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission, is an orbiting X-ray observatory launched by ESA in December 1999 on an Ariane 5 rocket. It is named in honor of Sir Isaac Newton. The telescope was placed in a very eccentric 48 hour elliptical orbit at 40°; at its apogee it is nearly 114,000 kilometres (71,000 mi) from Earth, while the perigee is only 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi).