Basic Concepts - Raymond R. Panko
... Figure 2-10: Internet and Data Link Layers in an Internet • Internet and Transport Layers – An internet is a group of networks connected by routers so that any application on any host on any network can communicate with any application on any other host on any other network – Internet and transport ...
... Figure 2-10: Internet and Data Link Layers in an Internet • Internet and Transport Layers – An internet is a group of networks connected by routers so that any application on any host on any network can communicate with any application on any other host on any other network – Internet and transport ...
Chapter 2
... Figure 2-10: Internet and Data Link Layers in an Internet • Internet and Transport Layers – An internet is a group of networks connected by routers so that any application on any host on any network can communicate with any application on any other host on any other network – Internet and transport ...
... Figure 2-10: Internet and Data Link Layers in an Internet • Internet and Transport Layers – An internet is a group of networks connected by routers so that any application on any host on any network can communicate with any application on any other host on any other network – Internet and transport ...
MPEG-2 TS MULTIPLEXER IN FPGA TECHNOLOGY Podatkovni
... operators’ concept of bundling together various structureindependent services the user can then access /2/, which can be seen from the engineer’s point of view as merging of technologies and processes from multiple industries. It is only in the last decade when convergence has taken places in our ev ...
... operators’ concept of bundling together various structureindependent services the user can then access /2/, which can be seen from the engineer’s point of view as merging of technologies and processes from multiple industries. It is only in the last decade when convergence has taken places in our ev ...
Chapter 24 - William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications
... have scenarios where more appropriately done by application layer ...
... have scenarios where more appropriately done by application layer ...
RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real
... Carry real-time data RTCP: RTP control protocol QoS monitoring and feedback Session control ...
... Carry real-time data RTCP: RTP control protocol QoS monitoring and feedback Session control ...
DSL - Digital Subscriber Line An Overview
... Technical Description Evaluation A View to the Future ...
... Technical Description Evaluation A View to the Future ...
CAN - STI Innsbruck
... n nodes would require O(n2) wires for full meshed networking (up to 100 ECUs in modern cars) Bus topology only requires a single bus with n branches: O(n) Pure CAN does not specify transmission medium Automotive CAN according to ISO 11898-2/3 uses twisted pair with differential voltages on a bus top ...
... n nodes would require O(n2) wires for full meshed networking (up to 100 ECUs in modern cars) Bus topology only requires a single bus with n branches: O(n) Pure CAN does not specify transmission medium Automotive CAN according to ISO 11898-2/3 uses twisted pair with differential voltages on a bus top ...
Bit and Byte Stuffing
... Bit Stuffing • Each frame begins and ends with a special bit pattern called a flag byte [01111110]. • Whenever sender data link layer encounters five consecutive ones in the data stream, it automatically stuffs a 0 bit into the outgoing stream. • When the receiver sees five consecutive incoming one ...
... Bit Stuffing • Each frame begins and ends with a special bit pattern called a flag byte [01111110]. • Whenever sender data link layer encounters five consecutive ones in the data stream, it automatically stuffs a 0 bit into the outgoing stream. • When the receiver sees five consecutive incoming one ...
Automotive CAN Engli..
... controller (and thus in each network node) – one for errors during transmission, one during reception – at the beginning they are reset – if there is an error during transmission, transmission error counter value is increased, the same is tru for reception ...
... controller (and thus in each network node) – one for errors during transmission, one during reception – at the beginning they are reset – if there is an error during transmission, transmission error counter value is increased, the same is tru for reception ...
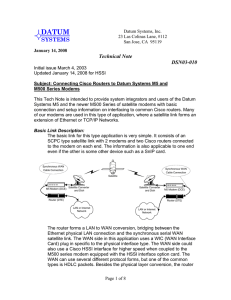
Tech Note - Datum Systems
... link was not correct, then the actual indication would be that the "Link" was down, while if the protocol was not correct then the indication would be that the Link is “Up” and the protocol is “Down”. The M500 series SnIP interface card running Linux can also be used on the other end of a link from ...
... link was not correct, then the actual indication would be that the "Link" was down, while if the protocol was not correct then the indication would be that the Link is “Up” and the protocol is “Down”. The M500 series SnIP interface card running Linux can also be used on the other end of a link from ...
IEEE 1722 Media on AVB Networks
... Media Synchronization across a shared LAN • Maintain A/V lip-sync between rendering devices – No loss of sync due to separate transport flows across network – Separate streams can have different delivery times ...
... Media Synchronization across a shared LAN • Maintain A/V lip-sync between rendering devices – No loss of sync due to separate transport flows across network – Separate streams can have different delivery times ...
CECS470
... data or information. – Main cause of transmission errors. – Given as the signal to noise ratio S/N and measured in decibels (dB). • Channel Bandwidth: The size of the range of frequencies that can be transmitted through a channel. Measured in Hertz (Hz). Affected by: – Type and physical characterist ...
... data or information. – Main cause of transmission errors. – Given as the signal to noise ratio S/N and measured in decibels (dB). • Channel Bandwidth: The size of the range of frequencies that can be transmitted through a channel. Measured in Hertz (Hz). Affected by: – Type and physical characterist ...
physical media
... the network media the bits that make up a Data Link layer frame. – This layer accepts a complete frame from the Data Link layer and encodes it as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. – The encoded bits that comprise a frame are received by either an end device or an ...
... the network media the bits that make up a Data Link layer frame. – This layer accepts a complete frame from the Data Link layer and encodes it as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. – The encoded bits that comprise a frame are received by either an end device or an ...
Multimedia Applications
... • RTP is for sending audio/video data streams • RTCP is used for exchanging information between senders/receivers about the streams and users • There are 5 types of RTCP messages: – Sender report: sender periodically sends a report to receivers; includes at least an absolute timestamp so receivers c ...
... • RTP is for sending audio/video data streams • RTCP is used for exchanging information between senders/receivers about the streams and users • There are 5 types of RTCP messages: – Sender report: sender periodically sends a report to receivers; includes at least an absolute timestamp so receivers c ...
Ethernet Data Link Layer Standards
... e) If you know that a system has 64 states, how many bits can it send per clock cycle? f) If you know that a system has 256 states, how many bits can it send per clock cycle? g) In general, to transmit twice as many bits per clock cycle, how much must you increase the number of alternatives? (The an ...
... e) If you know that a system has 64 states, how many bits can it send per clock cycle? f) If you know that a system has 256 states, how many bits can it send per clock cycle? g) In general, to transmit twice as many bits per clock cycle, how much must you increase the number of alternatives? (The an ...
Interconnection Networks
... ° Processor-Memory Bus (design specific) • Short and high speed • Only need to match the memory system - Maximize memory-to-processor bandwidth • Connects directly to the processor ° I/O Bus (industry standard) • Usually is lengthy and slower • Need to match a wide range of I/O devices • Connects to ...
... ° Processor-Memory Bus (design specific) • Short and high speed • Only need to match the memory system - Maximize memory-to-processor bandwidth • Connects directly to the processor ° I/O Bus (industry standard) • Usually is lengthy and slower • Need to match a wide range of I/O devices • Connects to ...
Designing RS-485 Circuits
... output. If that’s not available, any spare output bit will do. Most serial-communications tools, including Visual Basic’s MSComm, support RS-485 communications with RTS controlled in software. The COMM-DRV serialport drivers from WCSC have automatic RTS control built-in. The main reason why RS-485 l ...
... output. If that’s not available, any spare output bit will do. Most serial-communications tools, including Visual Basic’s MSComm, support RS-485 communications with RTS controlled in software. The COMM-DRV serialport drivers from WCSC have automatic RTS control built-in. The main reason why RS-485 l ...
Data Communication and Networking
... Data to be transmitted, data must be transformed in to electromagnetic signals. Electromagnetic signals can be either analog or digital. Accordingly data can be classified as analog and digital data. Analog datarefersto information that is represented in continuouswave forms. For example sound produ ...
... Data to be transmitted, data must be transformed in to electromagnetic signals. Electromagnetic signals can be either analog or digital. Accordingly data can be classified as analog and digital data. Analog datarefersto information that is represented in continuouswave forms. For example sound produ ...
Sharing mHealth Data via Named Data Networking
... constructed to retrieve data for any given time intervals. In cases when the number of samples that an application wishes to store for a given timestamp range exceeds the NDN packet size, the data is further split into named segments.3 Following approaches in past participatory sensing work [2], the ...
... constructed to retrieve data for any given time intervals. In cases when the number of samples that an application wishes to store for a given timestamp range exceeds the NDN packet size, the data is further split into named segments.3 Following approaches in past participatory sensing work [2], the ...
The Internet and Its Uses
... –The transmission of the frame across the media occurs as a stream of bits sent one at a time. –Physical layer represents each bits in the frame as a signal. –Each signal placed onto the media has a specific amount of time to occupy the media. This is referred to as its bit time. •Successful deliver ...
... –The transmission of the frame across the media occurs as a stream of bits sent one at a time. –Physical layer represents each bits in the frame as a signal. –Each signal placed onto the media has a specific amount of time to occupy the media. This is referred to as its bit time. •Successful deliver ...
presentation2
... – data from the upper layers (ie the network layer) is converted by the data link layer into frames – groups raw data bits received via the physical layer into frames, for passing on to the upper layers – may include an error recovery mechanism and also a flow control mechanism, although this may be ...
... – data from the upper layers (ie the network layer) is converted by the data link layer into frames – groups raw data bits received via the physical layer into frames, for passing on to the upper layers – may include an error recovery mechanism and also a flow control mechanism, although this may be ...
Data Link Control
... • One of the most common protocols for point-to-point access • Many Internet users who need to connect their home computer to the server of an Internet service provider use PPP • A point-to-point link protocol is required to control and manage the transfer of data • PPP defines/provides ...
... • One of the most common protocols for point-to-point access • Many Internet users who need to connect their home computer to the server of an Internet service provider use PPP • A point-to-point link protocol is required to control and manage the transfer of data • PPP defines/provides ...
chap11
... • One of the most common protocols for point-to-point access • Many Internet users who need to connect their home computer to the server of an Internet service provider use PPP • A point-to-point link protocol is required to control and manage the transfer of data • PPP defines/provides ...
... • One of the most common protocols for point-to-point access • Many Internet users who need to connect their home computer to the server of an Internet service provider use PPP • A point-to-point link protocol is required to control and manage the transfer of data • PPP defines/provides ...
a Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-269
... Figure 5 shows how MPE operates. The example at the bottom of the diagram indicates how the digital bit stream 10110 is encoded. A transition in the middle of each bit makes it possible to synchronize the sender and receiver. At any instant, it can be in one of three states: transmitting a 0 bit (-0 ...
... Figure 5 shows how MPE operates. The example at the bottom of the diagram indicates how the digital bit stream 10110 is encoded. A transition in the middle of each bit makes it possible to synchronize the sender and receiver. At any instant, it can be in one of three states: transmitting a 0 bit (-0 ...
OSI Model
... TCP is a reliable connection-oriented protocol Allows error-free transmission Incoming byte stream is fragmented into a number of shorter messages and these are passed on to the next layer At the receiving end the TCP reassembles the messages into an output stream TCP also handles flow control – to ...
... TCP is a reliable connection-oriented protocol Allows error-free transmission Incoming byte stream is fragmented into a number of shorter messages and these are passed on to the next layer At the receiving end the TCP reassembles the messages into an output stream TCP also handles flow control – to ...
Low-voltage differential signaling

Low-voltage differential signaling, or LVDS, also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial communications protocol. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. Since LVDS is a physical layer specification only, many data communication standards and applications use it but then add a data link layer as defined in the OSI model on top of it.LVDS was introduced in 1994, and has become popular in products such as LCD-TVs, automotive infotainment systems, industrial cameras and machine vision, notebook and tablet computers, and communications systems. The typical applications are high-speed video, graphics, video camera data transfers, and general purpose computer buses. Early on, the notebook and LCD display vendors commonly used the term LVDS instead of FPD-Link when referring to their application, and the term LVDS has mistakenly become synonymous with Flat Panel Display Link in the video-display engineering vocabulary.