Chapter 10 - Department Of Computer Science
... The third fundamental force of nature strong nuclear force (or just strong force or nuclear force) acts on neutrons The strong nuclear force is a short range force (distance less than 10-14 m) A weak nuclear force also exists – A short range force – Stronger than gravitational force, but very mu ...
... The third fundamental force of nature strong nuclear force (or just strong force or nuclear force) acts on neutrons The strong nuclear force is a short range force (distance less than 10-14 m) A weak nuclear force also exists – A short range force – Stronger than gravitational force, but very mu ...
Atomic
... • The light emitted by an element when its electrons return to a lower energy state can be viewed as a bright line emission spectrum. • The light absorbed by an element when white light is passed through a sample is illustrated by the absorption spectrum. ...
... • The light emitted by an element when its electrons return to a lower energy state can be viewed as a bright line emission spectrum. • The light absorbed by an element when white light is passed through a sample is illustrated by the absorption spectrum. ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
... Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
Fall 2015 Review-2
... ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neutral atom? a. The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of its neutral atom. b. The radius of an anion is identical to the radius of its neutral atom. c. The radius of a cation is greater than ...
... ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neutral atom? a. The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of its neutral atom. b. The radius of an anion is identical to the radius of its neutral atom. c. The radius of a cation is greater than ...
Electron configuration From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... atoms and molecules. For atoms, the notation consists of a sequence of atomic orbital labels (e.g. for phosphorus the sequence 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p) with the number of electrons assigned to each orbital (or set of orbitals sharing the same label) placed as a superscript. For example, hydrogen has one ...
... atoms and molecules. For atoms, the notation consists of a sequence of atomic orbital labels (e.g. for phosphorus the sequence 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p) with the number of electrons assigned to each orbital (or set of orbitals sharing the same label) placed as a superscript. For example, hydrogen has one ...
10B Atoms and Isotopes
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
Chemistry powerpoint notes
... elements in a period have the same number of electron shells. Every element in the top row (the first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, t ...
... elements in a period have the same number of electron shells. Every element in the top row (the first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, t ...
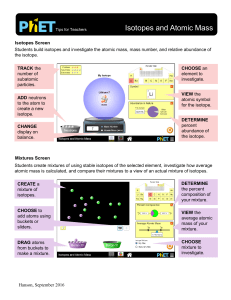
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
Early Atomic Theory and Structure Empedocle (440 BC): all matter
... chemical family: 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 1s2 2s2 2p4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1. 41. In which period and group does an electron first appear in an f orbital? ...
... chemical family: 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 1s2 2s2 2p4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1. 41. In which period and group does an electron first appear in an f orbital? ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Although all atoms of an element have the same number of protons, they don’t all have t ...
... protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Although all atoms of an element have the same number of protons, they don’t all have t ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
ch-4-earth-chemistry
... Chemical formula – a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound. Also, shows the numbers of atoms of each element required to make up a molecule of a compound. ...
... Chemical formula – a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound. Also, shows the numbers of atoms of each element required to make up a molecule of a compound. ...
ELEMENTS AND SYMBOLS
... The number of protons in an atom determines its identity, and is called atomic number (Z). In a neutral atom, the number of protons (+) are equal to the number of electrons (–). Almost all the mass of the atom rests in the nucleus. Therefore the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is cal ...
... The number of protons in an atom determines its identity, and is called atomic number (Z). In a neutral atom, the number of protons (+) are equal to the number of electrons (–). Almost all the mass of the atom rests in the nucleus. Therefore the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is cal ...
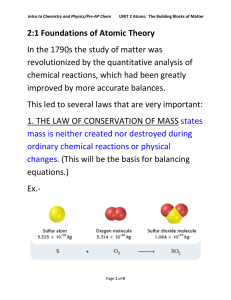
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... of atoms in an element in a sample with a known mass. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons; Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The ...
... of atoms in an element in a sample with a known mass. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons; Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The ...
The Atom Powerpoint 10-16-13
... The ATOMIC MASS NUMBER reported for an element on the PERIODIC TABLE is an AVERAGE of all the different ISOTOPES of that element. ...
... The ATOMIC MASS NUMBER reported for an element on the PERIODIC TABLE is an AVERAGE of all the different ISOTOPES of that element. ...
Electronegativity
... How well an atom can attract a pair of bonding electrons to itself. It is a calculated value and can not actually be measured. How do you think it changes across a period? Down a group? Electronegativity: • Increases across a period • Decreases down a group ...
... How well an atom can attract a pair of bonding electrons to itself. It is a calculated value and can not actually be measured. How do you think it changes across a period? Down a group? Electronegativity: • Increases across a period • Decreases down a group ...
Periodic Table Trends
... • Each element has only one type of atom. • Elements are arranged in columns called groups and rows called periods. ...
... • Each element has only one type of atom. • Elements are arranged in columns called groups and rows called periods. ...
Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Diagrams
... Background Information Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest energy level for an atom. They are the electrons involved with bonding between atoms. Knowing how many valence electrons there are for a specific atom will help you understand the type of bond that forms and what other atoms i ...
... Background Information Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest energy level for an atom. They are the electrons involved with bonding between atoms. Knowing how many valence electrons there are for a specific atom will help you understand the type of bond that forms and what other atoms i ...
Chapter 3 - Industrial ISD
... 1. Date = 400 B.C 2. Discovery = Theorized the smallest unit of an element 3. Importance = gave the term and definition of atom ...
... 1. Date = 400 B.C 2. Discovery = Theorized the smallest unit of an element 3. Importance = gave the term and definition of atom ...
PS-CC-2test - Edquest Science
... 12. As you move across the periodic table the properties of the elements change. The most reactive metals include … A. sodium and lithium B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the ...
... 12. As you move across the periodic table the properties of the elements change. The most reactive metals include … A. sodium and lithium B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the ...
Periodic Table and Electrons
... Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Periods and groups are named by numbering columns and rows. Horizontal rows called periods have predictable properties based on an increasing numb ...
... Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Periods and groups are named by numbering columns and rows. Horizontal rows called periods have predictable properties based on an increasing numb ...
No Slide Title
... Periodic Table 30 • Which group of elements share characteristics of both metals and nonmetals? • What are metalloids or semi-metals? ...
... Periodic Table 30 • Which group of elements share characteristics of both metals and nonmetals? • What are metalloids or semi-metals? ...
Yr11 Chemistry Title Page:TourismContents
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple (whole number) ratios to form compounds. ...
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple (whole number) ratios to form compounds. ...