1 - AzMİU
... m D) E) J m 3. Specify the expression for amplitud value of acceleration at harmonious oscillation of a body ( -is a cyclic frequency, A-is a amplitud of oscillation). A) 2 A B) A C) A 2 D) 2 A 2 E) 3 A 4. Under what conditions is there a resonance ( 0 - is the natural frequency, - ...
... m D) E) J m 3. Specify the expression for amplitud value of acceleration at harmonious oscillation of a body ( -is a cyclic frequency, A-is a amplitud of oscillation). A) 2 A B) A C) A 2 D) 2 A 2 E) 3 A 4. Under what conditions is there a resonance ( 0 - is the natural frequency, - ...
Physics - Belfast Royal Academy
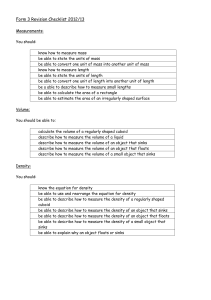
... know that the units of AMPLITUDE and WAVELENGTH are in metres or cm or mm know how to label AMPLITUDE and WAVELENGTH on a wave diagram Electromagnetic Waves You should: know the names of the different waves which form the electromagnetic spectrum be able to arrange the different parts of the electro ...
... know that the units of AMPLITUDE and WAVELENGTH are in metres or cm or mm know how to label AMPLITUDE and WAVELENGTH on a wave diagram Electromagnetic Waves You should: know the names of the different waves which form the electromagnetic spectrum be able to arrange the different parts of the electro ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... will be carried by these fields second thing is, what is the directional dependence of this power flow. So the feature which captures the directional dependence is called the radiation pattern of a dipole or of a antenna in general. So if I take the electric field and if I plot the electric field as ...
... will be carried by these fields second thing is, what is the directional dependence of this power flow. So the feature which captures the directional dependence is called the radiation pattern of a dipole or of a antenna in general. So if I take the electric field and if I plot the electric field as ...
Faraday and the Electromagnetic Theory of Light
... of field and field lines, moving away from the mechanistic explanation of natural phenomena like Newton’s actions-at-a-distance. Faraday’s introduction of the concept of field into physics is perhaps his most important contribution and was described by Einstein as the great change in physics because ...
... of field and field lines, moving away from the mechanistic explanation of natural phenomena like Newton’s actions-at-a-distance. Faraday’s introduction of the concept of field into physics is perhaps his most important contribution and was described by Einstein as the great change in physics because ...
Photonic Devices and Systems (ELEC ENG 4EM4)
... – Field is specified in a limited set of spatial points, not specified in the rest area (– not specified doesn’t necessarily mean that the field is zero) – Specification is given in the form of equations – implicit expressions – These equations must be in the differential or integral form, cannot be ...
... – Field is specified in a limited set of spatial points, not specified in the rest area (– not specified doesn’t necessarily mean that the field is zero) – Specification is given in the form of equations – implicit expressions – These equations must be in the differential or integral form, cannot be ...
An Advanced Review of Thermodynamics of Electromagnetism
... subjected to transfer of heat, electric, magnetic and mechanical energies. However, literature that dealt with the transfer of electric and magnetic energies were involved mainly in momentum conservation while they gave a narrow space to the energy transfer that considers the entropy as an essential ...
... subjected to transfer of heat, electric, magnetic and mechanical energies. However, literature that dealt with the transfer of electric and magnetic energies were involved mainly in momentum conservation while they gave a narrow space to the energy transfer that considers the entropy as an essential ...
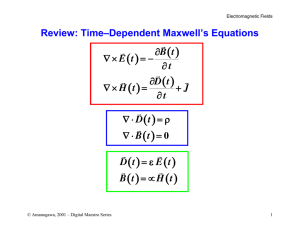
Review: Time–Dependent Maxwell`s Equations D t E t B t H t = ε = µ
... magnetic field H, since there is no current density J. MAGNETOSTATICS – The charge crossing a given crosssection (current) does not vary in time. Therefore, J, H and B are constant. Although charges are moving, the steady current maintains a constant charge density field E is static. ...
... magnetic field H, since there is no current density J. MAGNETOSTATICS – The charge crossing a given crosssection (current) does not vary in time. Therefore, J, H and B are constant. Although charges are moving, the steady current maintains a constant charge density field E is static. ...
Maxwell equations - Neo
... which the aforementioned researchers already examined mechanics – although time does not enter into classical mechanics on an equal basis with the spacelike coordinates, but as an independent parameter, as opposed to Minkowski’s theory – when the metric of this four-dimensional space of Minkowski do ...
... which the aforementioned researchers already examined mechanics – although time does not enter into classical mechanics on an equal basis with the spacelike coordinates, but as an independent parameter, as opposed to Minkowski’s theory – when the metric of this four-dimensional space of Minkowski do ...
Section 26.1 Interactions of Electric and Magnetic
... Reason: In Thomson’s cathode-ray tube experiment, the electric field, which was produced by charged parallel plates, was oriented perpendicular to the beam. The electric field (of strength E) produced a force equal to qE that acted on the electrons and deflected them upward, toward the positive plat ...
... Reason: In Thomson’s cathode-ray tube experiment, the electric field, which was produced by charged parallel plates, was oriented perpendicular to the beam. The electric field (of strength E) produced a force equal to qE that acted on the electrons and deflected them upward, toward the positive plat ...
PHYS 304 Mod 2009.11.2
... Electrostatics: charges, forces, fields, and potentials Electrostatics: charges, forces, fields, and potentials Dielectrics and conductors: the interaction of materials with Dielectrics and conductors: the interaction of materials with electrostatic charges. electrostatic charges. Electric flux : ca ...
... Electrostatics: charges, forces, fields, and potentials Electrostatics: charges, forces, fields, and potentials Dielectrics and conductors: the interaction of materials with Dielectrics and conductors: the interaction of materials with electrostatic charges. electrostatic charges. Electric flux : ca ...
Electromagnetic radiation
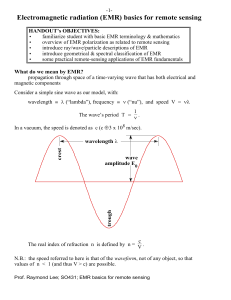
Electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR) is the radiant energy released by certain electromagnetic processes. Visible light is one type of electromagnetic radiation, other familiar forms are invisible electromagnetic radiations such as radio waves, infrared light and X rays.Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields that propagate at the speed of light through a vacuum. The oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. Electromagnetic waves can be characterized by either the frequency or wavelength of their oscillations to form the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.Electromagnetic waves are produced whenever charged particles are accelerated, and these waves can subsequently interact with any charged particles. EM waves carry energy, momentum and angular momentum away from their source particle and can impart those quantities to matter with which they interact. Quanta of EM waves are called photons, which are massless, but they are still affected by gravity. Electromagnetic radiation is associated with those EM waves that are free to propagate themselves (""radiate"") without the continuing influence of the moving charges that produced them, because they have achieved sufficient distance from those charges. Thus, EMR is sometimes referred to as the far field. In this jargon, the near field refers to EM fields near the charges and current that directly produced them, specifically, electromagnetic induction and electrostatic induction phenomena.In the quantum theory of electromagnetism, EMR consists of photons, the elementary particles responsible for all electromagnetic interactions. Quantum effects provide additional sources of EMR, such as the transition of electrons to lower energy levels in an atom and black-body radiation. The energy of an individual photon is quantized and is greater for photons of higher frequency. This relationship is given by Planck's equation E=hν, where E is the energy per photon, ν is the frequency of the photon, and h is Planck's constant. A single gamma ray photon, for example, might carry ~100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light.The effects of EMR upon biological systems (and also to many other chemical systems, under standard conditions) depend both upon the radiation's power and its frequency. For EMR of visible frequencies or lower (i.e., radio, microwave, infrared), the damage done to cells and other materials is determined mainly by power and caused primarily by heating effects from the combined energy transfer of many photons. By contrast, for ultraviolet and higher frequencies (i.e., X-rays and gamma rays), chemical materials and living cells can be further damaged beyond that done by simple heating, since individual photons of such high frequency have enough energy to cause direct molecular damage.