Met 61: Dynamics
... For typical synoptic scale motions, it turns out that the acceleration is small (~10% or less) compared to the Coriolis, and as we have already seen, the wind is nearly geostrophic. Thus, for geostrophic balance to be valid, the Rossby number must be small (Ro ~ 0.1), or the accelerations of the win ...
... For typical synoptic scale motions, it turns out that the acceleration is small (~10% or less) compared to the Coriolis, and as we have already seen, the wind is nearly geostrophic. Thus, for geostrophic balance to be valid, the Rossby number must be small (Ro ~ 0.1), or the accelerations of the win ...
File - Ms. Quack`s Physics Page
... For the final, you may prepare one side of an 8 ½” by 11” sheet with equations, constants, and anything else you think you may need for the exam. You will turn this in with your final. It would be to your advantage to prepare your card yourself, so that you know where everything is, and what everyth ...
... For the final, you may prepare one side of an 8 ½” by 11” sheet with equations, constants, and anything else you think you may need for the exam. You will turn this in with your final. It would be to your advantage to prepare your card yourself, so that you know where everything is, and what everyth ...
Momentum, Impulse and Recoil
... • The momentum, mv, is the amount gained before the cord begins to stretch. Ft is the impulse the cord supplies to reduce the momentum to zero. • Because the rubber cord stretches for a long time, a large time interval t ensures that a small average force F acts on the jumper. • The cord typically s ...
... • The momentum, mv, is the amount gained before the cord begins to stretch. Ft is the impulse the cord supplies to reduce the momentum to zero. • Because the rubber cord stretches for a long time, a large time interval t ensures that a small average force F acts on the jumper. • The cord typically s ...
Impulse and Momentum
... Impulse and Momentum • Objectives – Compare the system before and after an event in momentum problems – Define the momentum of an object – Determine the impulse given to an object – Recognize that impulse equals the change in momentum of an object ...
... Impulse and Momentum • Objectives – Compare the system before and after an event in momentum problems – Define the momentum of an object – Determine the impulse given to an object – Recognize that impulse equals the change in momentum of an object ...
9-Momentum and impulse
... Impulse does NOT change in a collision Ex: a car colliding with another car Equation: J = F∆t • J = impulse (N*s) • F = force (N) • ∆t = time (s) ...
... Impulse does NOT change in a collision Ex: a car colliding with another car Equation: J = F∆t • J = impulse (N*s) • F = force (N) • ∆t = time (s) ...
10-1 Note 10 Rotational Motion I
... Figure 10-10. How the torque produced by a force is defined. The figure shows a wrench whose jaws fit onto a nut centered at the point O. We assume that the nut-bolt ...
... Figure 10-10. How the torque produced by a force is defined. The figure shows a wrench whose jaws fit onto a nut centered at the point O. We assume that the nut-bolt ...
Circular Motion - Manchester HEP
... The experiment analysed in the tutorial question is now setup and performed. A light gate is used to determine the angular velocity of the disk. The light gate is triggered on and off by a plastic wedge of 10o size that is attached to the disk. Please be careful with this experiment as the plastic p ...
... The experiment analysed in the tutorial question is now setup and performed. A light gate is used to determine the angular velocity of the disk. The light gate is triggered on and off by a plastic wedge of 10o size that is attached to the disk. Please be careful with this experiment as the plastic p ...
In Pursuit of the Unknown : 17 Equations That Changed
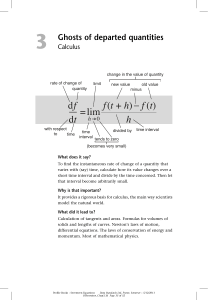
... (‘small difference in x’), and defining dy to be the corresponding small change in y. When a variable y depends on another variable x, the rate of change of y with respect to x is called the derivative of y. Newton wrote the dy . For higher derivative of y by placing a dot above it: ẏ. Leibniz wrot ...
... (‘small difference in x’), and defining dy to be the corresponding small change in y. When a variable y depends on another variable x, the rate of change of y with respect to x is called the derivative of y. Newton wrote the dy . For higher derivative of y by placing a dot above it: ẏ. Leibniz wrot ...