Central Force
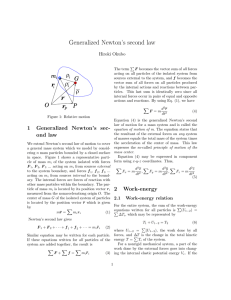
... • If the angular momentum L of mass µ is constant, its magnitude and direction are fixed in space. Hence, by definition of the cross product, if the direction of L is fixed in space, vectors r and p must lie in a plane perpendicular to L. That is, the motion of particle of mass µ is confined to a p ...
... • If the angular momentum L of mass µ is constant, its magnitude and direction are fixed in space. Hence, by definition of the cross product, if the direction of L is fixed in space, vectors r and p must lie in a plane perpendicular to L. That is, the motion of particle of mass µ is confined to a p ...
Final Question
... For the following table, tell whether y varies directly with x. If it does, write a function rule for the relationship shown in the data. ...
... For the following table, tell whether y varies directly with x. If it does, write a function rule for the relationship shown in the data. ...
r -2 - TTU Physics
... L = (½)μ (r2 + r2θ2) - U(r) • The Lagrangian is cyclic in θ The corresponding generalized momentum pθ is conserved: pθ (L/θ) = μr2θ; (L/θ) - (d/dt)[(L/θ)]= 0 pθ = 0, pθ = constant = μr2θ • PHYSICS: pθ = μr2θ = The (magnitude of the) angular momentum about an axis to the plane of the m ...
... L = (½)μ (r2 + r2θ2) - U(r) • The Lagrangian is cyclic in θ The corresponding generalized momentum pθ is conserved: pθ (L/θ) = μr2θ; (L/θ) - (d/dt)[(L/θ)]= 0 pθ = 0, pθ = constant = μr2θ • PHYSICS: pθ = μr2θ = The (magnitude of the) angular momentum about an axis to the plane of the m ...
differential equation
... ( dP / dt ) = k P and any exponential function of the form P(t) = Ce k t. ( dP / dt ) k P if P is small ( dP / dt ) < 0 if P > K. Then we can conclude that ( dP / dt ) = k P ( 1 – ( P / K ). ...
... ( dP / dt ) = k P and any exponential function of the form P(t) = Ce k t. ( dP / dt ) k P if P is small ( dP / dt ) < 0 if P > K. Then we can conclude that ( dP / dt ) = k P ( 1 – ( P / K ). ...
Paper Reference(s)
... Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Orange) ...
... Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Orange) ...
Paper Reference(s)
... Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Orange) ...
... Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Orange) ...
Sec 12.1
... Step 1: Choose a variable to eliminate. Step 2: Multiply one or both equations by an appropriate nonzero constant so that the sum of the coefficients of one of the variables is zero. Step 3: Add the two equations together to obtain an equation in one variable. Step 4: Solve the equation in one varia ...
... Step 1: Choose a variable to eliminate. Step 2: Multiply one or both equations by an appropriate nonzero constant so that the sum of the coefficients of one of the variables is zero. Step 3: Add the two equations together to obtain an equation in one variable. Step 4: Solve the equation in one varia ...
Concepts 1.1
... To solve equations involving absolute ______ bars first make sure that the absolute value bars are isolated to one side. Next _______ branch off into two ________ problems, one set to the original positive number and equations negative Finally solve both _________ one set to the ________. separately ...
... To solve equations involving absolute ______ bars first make sure that the absolute value bars are isolated to one side. Next _______ branch off into two ________ problems, one set to the original positive number and equations negative Finally solve both _________ one set to the ________. separately ...
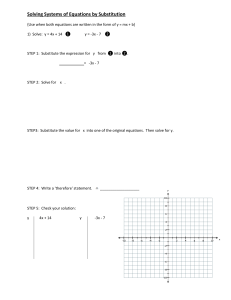
Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both
... Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both equations are written in the form of y = mx + b} 1) Solve: y = 4x + 14 ❶ ...
... Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both equations are written in the form of y = mx + b} 1) Solve: y = 4x + 14 ❶ ...
13.1 - Newton`s Law of Motion
... Newton’s Law of Motion (13.1) Mass and Weight. Mass is a property of matter by which we can compare the response of one body with that of another. It is an absolute quantity since the measurement can be made at any location. Weight of a body is not absolute since it is measured in a gravitational fi ...
... Newton’s Law of Motion (13.1) Mass and Weight. Mass is a property of matter by which we can compare the response of one body with that of another. It is an absolute quantity since the measurement can be made at any location. Weight of a body is not absolute since it is measured in a gravitational fi ...