on Newton Laws of motion File
... the object from moving If F increases, so does ƒs If F decreases, so does ƒs cannot exceed a maximum value. When this max is reached , the frictional force will no longer keep the object in equilibrium and the object will move ...
... the object from moving If F increases, so does ƒs If F decreases, so does ƒs cannot exceed a maximum value. When this max is reached , the frictional force will no longer keep the object in equilibrium and the object will move ...
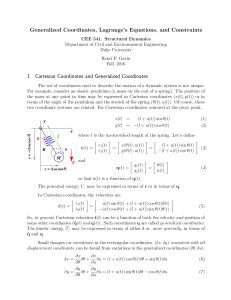
4 Force, Work, and Potential Energy
... limits of the motion. Use Maple to solve for the values of x at these points and show that x min = 0.059 nm and x max = 0.341 nm. Motion in a Potential Well When a particle moves in a potential well, as in the above example, the motion is confined to a finite range of values of x if the energy is su ...
... limits of the motion. Use Maple to solve for the values of x at these points and show that x min = 0.059 nm and x max = 0.341 nm. Motion in a Potential Well When a particle moves in a potential well, as in the above example, the motion is confined to a finite range of values of x if the energy is su ...
on a new approach to motion control of constrained mechanical
... holonomically and nonholonomically constrained mechanical systems when the forces of constraint are ideal. Control of mechanical systems with nonholonomic constraints and control of mechanical systems with kinematics constraints are investigated recently [2], [10], [11]. The last decades have shown ...
... holonomically and nonholonomically constrained mechanical systems when the forces of constraint are ideal. Control of mechanical systems with nonholonomic constraints and control of mechanical systems with kinematics constraints are investigated recently [2], [10], [11]. The last decades have shown ...
Part V
... Ability of force F to cause a rotation or twisting motion depends on 3 factors: 1. The magnitude F of the force. 2. The distance r from point of application to pivot. 3. The angle at which F is applied. ...
... Ability of force F to cause a rotation or twisting motion depends on 3 factors: 1. The magnitude F of the force. 2. The distance r from point of application to pivot. 3. The angle at which F is applied. ...