A comparative study of the mammalian amygdala
... guinea pig to the rabbit and to the fox and pig. The only difference is in the size of the basolateral neurons, which increases with the size increase of the brain. Moreover, the intraspecific comparisons revealed that in all the animals studied LA, BL and BM together form a fairly homogenous mass o ...
... guinea pig to the rabbit and to the fox and pig. The only difference is in the size of the basolateral neurons, which increases with the size increase of the brain. Moreover, the intraspecific comparisons revealed that in all the animals studied LA, BL and BM together form a fairly homogenous mass o ...
LTP
... and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased" (Hebb, 1949) • Cells that fire together, wire together ...
... and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased" (Hebb, 1949) • Cells that fire together, wire together ...
--The image of that apple is formed on your retina -
... Very large receptive fields Snail-like conduction velocity low spatial resolution slow temporal resolution project to brain regions responsible for motion perception & the primary visual cortex… Excited by blue/yellow stimuli ...
... Very large receptive fields Snail-like conduction velocity low spatial resolution slow temporal resolution project to brain regions responsible for motion perception & the primary visual cortex… Excited by blue/yellow stimuli ...
Action Potentials
... • EPSP and IPSP travel to the base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...
... • EPSP and IPSP travel to the base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...
Modern neuroscience is based on ideas derived
... that columns could be seen in brilliant clarity and their organization understood, as ocular dominance columns in the primate primary visual cortex, or barrel fields in the rodent somatosensory cortex. Neural tracers replaced the pioneering but difficult and limited ablation-degeneration mapping met ...
... that columns could be seen in brilliant clarity and their organization understood, as ocular dominance columns in the primate primary visual cortex, or barrel fields in the rodent somatosensory cortex. Neural tracers replaced the pioneering but difficult and limited ablation-degeneration mapping met ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic transmission between preganglionic and postg ...
... Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic transmission between preganglionic and postg ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
... the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
Synapse Elimination and Remodeling
... The presence or absence of trophic factors also appears to influence the state of ocular dominance columns. This plasticity (ability for synapses to re-arrange) is only present during a critical period of development because the segregation of synchronous connections and competition can no longer oc ...
... The presence or absence of trophic factors also appears to influence the state of ocular dominance columns. This plasticity (ability for synapses to re-arrange) is only present during a critical period of development because the segregation of synchronous connections and competition can no longer oc ...
Psychology 210
... Graded Potentials Action Potentials are referred to as “________________________________” Either get an action potential or not Inputs that don’t reach threshold: Graded Potentials Can add up across synapses/inputs to reach threshold Saltatory Conduction ________________________________is not perfe ...
... Graded Potentials Action Potentials are referred to as “________________________________” Either get an action potential or not Inputs that don’t reach threshold: Graded Potentials Can add up across synapses/inputs to reach threshold Saltatory Conduction ________________________________is not perfe ...
“Epileptic Neurons” in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
... and severe astrogliosis (6, 9, 36). For all these reasons, research on the mechanisms leading to increased seizure suceptibility in TLE has focused on functional and structural alterations in the hippocampus proper and its most important input and output regions, ie, the entorhinal cortex and the am ...
... and severe astrogliosis (6, 9, 36). For all these reasons, research on the mechanisms leading to increased seizure suceptibility in TLE has focused on functional and structural alterations in the hippocampus proper and its most important input and output regions, ie, the entorhinal cortex and the am ...
Multi-Layer Perceptron
... • Perceptron can only be a linear classifier. • We can have a network of neurons (perceptron-like structures) with an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. • Each layer consists of many neurons and the output of a layer is fed as inputs to all neurons of the next layer. ...
... • Perceptron can only be a linear classifier. • We can have a network of neurons (perceptron-like structures) with an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. • Each layer consists of many neurons and the output of a layer is fed as inputs to all neurons of the next layer. ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological Bases, PP 08b
... In medulla, corticospinal UMN courses through the pyramids (in medulla), crossing at pyramidal (motor) ...
... In medulla, corticospinal UMN courses through the pyramids (in medulla), crossing at pyramidal (motor) ...
lecture #6
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... the goals, commands, and feedback signals associated with movement. There are 40 times more axons project into the cerebellum than exit from it. Second, the output of the cerebellum is sent to the premotor and motor systems of the cerebral cortex and brain stem, systems that control spinal interneur ...
... the goals, commands, and feedback signals associated with movement. There are 40 times more axons project into the cerebellum than exit from it. Second, the output of the cerebellum is sent to the premotor and motor systems of the cerebral cortex and brain stem, systems that control spinal interneur ...
Morphological and Quantitative Study of Neurons in the Gracile
... size and shape; 2) density of dendritic tree and 3) presence or absence of different types of spines and/or appendages on dendrites and/or cell bodies. Type I Neurons: These multipolar or elongated neurons (Figure 2) represented the largest impregnated neuronal type in the Gr. They had very large so ...
... size and shape; 2) density of dendritic tree and 3) presence or absence of different types of spines and/or appendages on dendrites and/or cell bodies. Type I Neurons: These multipolar or elongated neurons (Figure 2) represented the largest impregnated neuronal type in the Gr. They had very large so ...
Cortical inputs to the CA1 field of the monkey hippocampus originate
... A library of 5 experiments with injections of the retrograde tracers Fast blue (FB) or Diamidino yellow (DY) into various fields of the hippocampal formation were available from a previous study [10]. The two tracers were injected on both sides of the brain at different rostrocaudal levels of the hi ...
... A library of 5 experiments with injections of the retrograde tracers Fast blue (FB) or Diamidino yellow (DY) into various fields of the hippocampal formation were available from a previous study [10]. The two tracers were injected on both sides of the brain at different rostrocaudal levels of the hi ...
Radial migration: Retinal neurons hold on for the ride
... overexpressing cells. This finding suggests that signals impinging on the regulation of cortical actin are important for determining whether a neuron detaches from the apical epithelium and migrates in multipolar mode. It will be interesting to define how aPKC controls stability of the apical proces ...
... overexpressing cells. This finding suggests that signals impinging on the regulation of cortical actin are important for determining whether a neuron detaches from the apical epithelium and migrates in multipolar mode. It will be interesting to define how aPKC controls stability of the apical proces ...
Genetics
... them back to the cell body Thin, bushy-like structures that receive information from outside the neuron ...
... them back to the cell body Thin, bushy-like structures that receive information from outside the neuron ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... • Synaptic transmission triggers the opening ligand gated Cl- channels or indirectly through other mechanisms the opening of K+ channels • Cl- flows into the cell • K+ flows out of the cell • Both increase the negative charge within the cell, hyperpolarizes the soma • Brings membrane potential furth ...
... • Synaptic transmission triggers the opening ligand gated Cl- channels or indirectly through other mechanisms the opening of K+ channels • Cl- flows into the cell • K+ flows out of the cell • Both increase the negative charge within the cell, hyperpolarizes the soma • Brings membrane potential furth ...
Eagleman Ch 3. Neurons and Synapses
... In the brain, there are approximately 100 billion neurons, each sending up to a few hundred action potentials per second. The number of spikes per second is used to describe the neuron’s response to a stimulus. ...
... In the brain, there are approximately 100 billion neurons, each sending up to a few hundred action potentials per second. The number of spikes per second is used to describe the neuron’s response to a stimulus. ...
Neurons and action potential
... 5. Using the voltmeter measure the voltage. If the LED is lit threshold has been reached and that neuron can fire an action potential. 6. Keep adding neurotransmitters and measuring the voltage. If the LED gets brighter the connection between the neurons is strengthened. 7. Graph the voltages. ...
... 5. Using the voltmeter measure the voltage. If the LED is lit threshold has been reached and that neuron can fire an action potential. 6. Keep adding neurotransmitters and measuring the voltage. If the LED gets brighter the connection between the neurons is strengthened. 7. Graph the voltages. ...
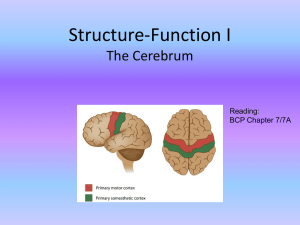
Structure-Function I
... Below the cerebral cortex are a variety of other structures, called subcortical (literally "below the cortex") structures. Collectively, there are three main groups, but not all the nuclei in each group serve the ...
... Below the cerebral cortex are a variety of other structures, called subcortical (literally "below the cortex") structures. Collectively, there are three main groups, but not all the nuclei in each group serve the ...
The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat
... The essentially smooth contours of these dendrites receiving degenerating geniculocortical afferents on their shafts becomes more apparent when their forms are reconstructed from serial thin sections, as shown in Figs. 3-7. At this point it will help to give an indication of how to interpret the fiv ...
... The essentially smooth contours of these dendrites receiving degenerating geniculocortical afferents on their shafts becomes more apparent when their forms are reconstructed from serial thin sections, as shown in Figs. 3-7. At this point it will help to give an indication of how to interpret the fiv ...
Hebbian modification of a hippocampal population
... and 5 indicate the regions used to calculate the areas used for estimating the magnitude of the intracellular and extracellular ripple-related signals. The time scale is 100 ms and the amplitude scale is 0·25 mV in trace 1, 0·16 mV in trace 2, 0·09 mV in traces 3 and 4 and 5·0 mV in trace 5. B, exam ...
... and 5 indicate the regions used to calculate the areas used for estimating the magnitude of the intracellular and extracellular ripple-related signals. The time scale is 100 ms and the amplitude scale is 0·25 mV in trace 1, 0·16 mV in trace 2, 0·09 mV in traces 3 and 4 and 5·0 mV in trace 5. B, exam ...