Heredity is a major factor in ADHD, binge eating
... "We have shown for the first time that the correlation between ADHD symptoms and binge eating in women depends mainly on a common hereditary susceptibility for the two disorders. Much of the correlation between alcohol dependence and ADHD can also be explained by genetic factors. The remainder of th ...
... "We have shown for the first time that the correlation between ADHD symptoms and binge eating in women depends mainly on a common hereditary susceptibility for the two disorders. Much of the correlation between alcohol dependence and ADHD can also be explained by genetic factors. The remainder of th ...
Part C: Genetics
... Environmental factors combined with genetic inheritance dictate the physical appearance or phenotype of an individual. This can be observed in twin studies. e.g. ...
... Environmental factors combined with genetic inheritance dictate the physical appearance or phenotype of an individual. This can be observed in twin studies. e.g. ...
Chapter 11
... •Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. Any human couple can produce a child with one of about 70 trillion different combinations –independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis –random fertilization of gametes –Crossing-over (exchange of chromosome segments between homologous ch ...
... •Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. Any human couple can produce a child with one of about 70 trillion different combinations –independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis –random fertilization of gametes –Crossing-over (exchange of chromosome segments between homologous ch ...
Quantitative Genetics
... allele or gene in a quantitative trait is small compared to qualitative genes. polygenic trait - a trait that is controlled by many genes each contributing a small affect on the phenotype. examples With a quantitative trait the gene action can be either additive, non-additive, or a combination of th ...
... allele or gene in a quantitative trait is small compared to qualitative genes. polygenic trait - a trait that is controlled by many genes each contributing a small affect on the phenotype. examples With a quantitative trait the gene action can be either additive, non-additive, or a combination of th ...
Developmental Psychology Big Developmental Issues
... • If that zygote successfully attachs to the uterus it becomes an embryo rapidly developing the beginnings of all body systems over the next ~ 7 weeks ...
... • If that zygote successfully attachs to the uterus it becomes an embryo rapidly developing the beginnings of all body systems over the next ~ 7 weeks ...
BIOLOGY CLASS NOTES UNIT 7_Part 2 Other Patterns of
... INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE = When alleles are neither recessive nor dominant Phenotype for heterozygous offspring is in between the homozygous phenotypes ...
... INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE = When alleles are neither recessive nor dominant Phenotype for heterozygous offspring is in between the homozygous phenotypes ...
Facing up to Complex Inheritance Patterns
... Influence of Life Stress on Depression: Moderation by a Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of th ...
... Influence of Life Stress on Depression: Moderation by a Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of th ...
Genetic Red Flags
... endurance events, in one copy of their ACTN3 gene may be equally suited for both endurance and sprint/power events, in neither copy of their ACTN3 gene may have a natural predisposition to sprint/power events. Knowing this information may be helpful, not in eliminating choices for sport activities b ...
... endurance events, in one copy of their ACTN3 gene may be equally suited for both endurance and sprint/power events, in neither copy of their ACTN3 gene may have a natural predisposition to sprint/power events. Knowing this information may be helpful, not in eliminating choices for sport activities b ...
Bio addiction AO2 activity – student copy
... not. Some people are more vulnerable due to their genetic predisposition (such as the A1 variant of the DRD2 gene). This is because the concordance rates (such as those in the study by Shields on smoking) are never 100% for MZ twins. This is problematic as it means that in some cases, having the ‘ad ...
... not. Some people are more vulnerable due to their genetic predisposition (such as the A1 variant of the DRD2 gene). This is because the concordance rates (such as those in the study by Shields on smoking) are never 100% for MZ twins. This is problematic as it means that in some cases, having the ‘ad ...
Study Guide for Genetics Test: Structure of DNA: DNA molecules are
... Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. We get 23 chromosomes from each of our parents. Genes are located on chromosomes and are a “blueprint” or set of instructions for each trait. Each parent donates one allele for each trait to its offspring. The two alleles (versions of a ge ...
... Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. We get 23 chromosomes from each of our parents. Genes are located on chromosomes and are a “blueprint” or set of instructions for each trait. Each parent donates one allele for each trait to its offspring. The two alleles (versions of a ge ...
Document
... 3. A __________________ cross is one where you only deal with one trait. (MM x mm) 4. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of _______ different traits.( MMYy x mmYy) 5.Mendel’s 2nd law is the law of ___________________ __________________. It states that ____________ pairs __________________ ind ...
... 3. A __________________ cross is one where you only deal with one trait. (MM x mm) 4. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of _______ different traits.( MMYy x mmYy) 5.Mendel’s 2nd law is the law of ___________________ __________________. It states that ____________ pairs __________________ ind ...
Animal Growth and Heredity
... with pea plants to learn how traits were inherited. • Through experimentation, Mendel learned that each parent passes one pair of its factors to an offspring. • He learned that traits can skip a generation. • He also learned that the height of pea plants depended on the factors they inherited from t ...
... with pea plants to learn how traits were inherited. • Through experimentation, Mendel learned that each parent passes one pair of its factors to an offspring. • He learned that traits can skip a generation. • He also learned that the height of pea plants depended on the factors they inherited from t ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH11.QXD
... 13. According to the principle known as LAW OF INDEPENDENDT ASSORTMENT , genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance. 14. DOMINANT ____________ alleles “cover up” the expression of ___RECESSIVE_______ alleles 15. A ___HYBRID___________results in the joining of female ...
... 13. According to the principle known as LAW OF INDEPENDENDT ASSORTMENT , genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance. 14. DOMINANT ____________ alleles “cover up” the expression of ___RECESSIVE_______ alleles 15. A ___HYBRID___________results in the joining of female ...
Pedigree Assignment - It Runs in the Family (recovered) Introduction
... Many human traits have two forms –dominant and recessive. Dominant genes are represented with a capital letter, while recessive genes are represented with the lower case version of the same letter. Examples of single inheritance traits include the ability to roll one’s tongue, the shape of the hairl ...
... Many human traits have two forms –dominant and recessive. Dominant genes are represented with a capital letter, while recessive genes are represented with the lower case version of the same letter. Examples of single inheritance traits include the ability to roll one’s tongue, the shape of the hairl ...
Characteristic passed from parent to offspring
... Trait carried on the X chromosome? Picture of all the human chromosomes arranged in pairs by size? ...
... Trait carried on the X chromosome? Picture of all the human chromosomes arranged in pairs by size? ...
Sociology article - UNC
... gene, called 9R/9R, conferred a “protective effect” against sexual behavior. When the researchers looked at environmental factors affecting the group of adolescents with the 9R/9R gene, however, they found the gene’s influence was negated in two circumstances: when kids attended schools with a stude ...
... gene, called 9R/9R, conferred a “protective effect” against sexual behavior. When the researchers looked at environmental factors affecting the group of adolescents with the 9R/9R gene, however, they found the gene’s influence was negated in two circumstances: when kids attended schools with a stude ...
Chapters 10 and 11 - Cellular Reproduction, Meiosis and Genetics
... 9. Variation in human skin color is a result of many genes = polygenic traits 10. If an organism’s diploid number is 36, its haploid number is 18 11. Gametes are produced by the process of meiosis 12. meiosis results in? 4 different haploid cells 13. How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human ...
... 9. Variation in human skin color is a result of many genes = polygenic traits 10. If an organism’s diploid number is 36, its haploid number is 18 11. Gametes are produced by the process of meiosis 12. meiosis results in? 4 different haploid cells 13. How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human ...
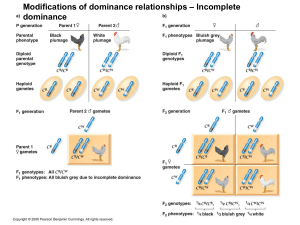
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... In some plants a red pigment, cyanidin, is synthesized from colorless precursor. The addition of a hydroxyl group (OH) to cyanidin molecules causes it to become purple. In a cros between two randomly selected purple plants the following results were obtained: 94 purple 31 red 43 white ...
... In some plants a red pigment, cyanidin, is synthesized from colorless precursor. The addition of a hydroxyl group (OH) to cyanidin molecules causes it to become purple. In a cros between two randomly selected purple plants the following results were obtained: 94 purple 31 red 43 white ...
Mendel`s Laws of Segregation
... traits blended from generation to generation. (Of course, there are exceptions to every rule. We know now that some genes have incomplete dominance. In incomplete dominance, the dominant gene has is not expressed completely, which results in a “mixed” phenotype. ...
... traits blended from generation to generation. (Of course, there are exceptions to every rule. We know now that some genes have incomplete dominance. In incomplete dominance, the dominant gene has is not expressed completely, which results in a “mixed” phenotype. ...
Genetics - Aurora City Schools
... One type of Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration Huntington’s disease – mental deteioration, uncontrollable movements ...
... One type of Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration Huntington’s disease – mental deteioration, uncontrollable movements ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.