G & s rasses ucculents
... They are amazingly adapted forms of life, evolved to survive in very adverse environmental conditions. When succulents are mentioned, cacti and sedums come to mind most readily. However, there are at least 34 plant families in which some members fall under this category having thick, fleshy leaves, ...
... They are amazingly adapted forms of life, evolved to survive in very adverse environmental conditions. When succulents are mentioned, cacti and sedums come to mind most readily. However, there are at least 34 plant families in which some members fall under this category having thick, fleshy leaves, ...
San Gabriel Valley Cactus and Succulent Society
... stick it in some potting soil. They propagate readily from leaves (tips are best), rhizomes, roots, etc. They can also be propagated from seeds. In Southern California Sansevieria flower frequently, particularly when grown outdoors. The flowers are extremely fragrant, and can perfume an entire house ...
... stick it in some potting soil. They propagate readily from leaves (tips are best), rhizomes, roots, etc. They can also be propagated from seeds. In Southern California Sansevieria flower frequently, particularly when grown outdoors. The flowers are extremely fragrant, and can perfume an entire house ...
Bio-Botany - Textbooks Online
... Diversity in living organisms There is a great diversity among living organisms found on the planet earth. They differ in their structure, habit, habitat, mode of nutrition, and physiology. The Biodiversity of the earth is enormous. Current estimates suggest that the earth may have anywhere from 10 ...
... Diversity in living organisms There is a great diversity among living organisms found on the planet earth. They differ in their structure, habit, habitat, mode of nutrition, and physiology. The Biodiversity of the earth is enormous. Current estimates suggest that the earth may have anywhere from 10 ...
herbicide moa document - Oklahoma State University
... Specifically, these herbicides bind to the D1 protein in photosystem II. Blocking the electron chain results in the production of free radicals in the chloroplasts, which results in cellular membrane degradation. C. Herbicide Families – Phenyl-carbamate, Pyridazinone, Triazine, Triazinone, and Uraci ...
... Specifically, these herbicides bind to the D1 protein in photosystem II. Blocking the electron chain results in the production of free radicals in the chloroplasts, which results in cellular membrane degradation. C. Herbicide Families – Phenyl-carbamate, Pyridazinone, Triazine, Triazinone, and Uraci ...
Soil type determines how root and rhizosphere traits relate
... and release soil P. In the course of modern plant breeding some of those adaptive traits have been lost (Wissuwa et al. 2009). Therefore, there is a need to develop future crops with superior root traits for a better acquisition of P from soils (Lynch 2007). The acknowledged root traits enabling soi ...
... and release soil P. In the course of modern plant breeding some of those adaptive traits have been lost (Wissuwa et al. 2009). Therefore, there is a need to develop future crops with superior root traits for a better acquisition of P from soils (Lynch 2007). The acknowledged root traits enabling soi ...
Novel Expression Pattern of Cytosolic Gln
... bands representing GS subunits. The mass of the major polypeptide band (43 kD) was slightly larger than the predicted monomer from the translated amino acid sequence of DgGS1-1 (39 kD). This major nodule polypeptide band corresponded to the single band observed in the root extracts (Fig. 4) and fall ...
... bands representing GS subunits. The mass of the major polypeptide band (43 kD) was slightly larger than the predicted monomer from the translated amino acid sequence of DgGS1-1 (39 kD). This major nodule polypeptide band corresponded to the single band observed in the root extracts (Fig. 4) and fall ...
Soil erosion study by using RUSLE model.
... L.V. Cam / VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 191-198 ...
... L.V. Cam / VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 191-198 ...
Sep – Oct 2008 - Bromeliad Society of Queensland
... me for the very tall plants climbing many of the trees. There were occasional plants with in orescences!at!various!stages!of!development,!but!those!with!open! owers!were!rare! and!on!many!of!them!the! owers!were!too! high to see well. Still, with P. nigra, there doesnt!need!to!be!many! owers!to!mai ...
... me for the very tall plants climbing many of the trees. There were occasional plants with in orescences!at!various!stages!of!development,!but!those!with!open! owers!were!rare! and!on!many!of!them!the! owers!were!too! high to see well. Still, with P. nigra, there doesnt!need!to!be!many! owers!to!mai ...
effect of wheat residue incorporation along with n starter dose on
... with N starter dose (0, 30kg N ha-1, 60kg N ha-1 and 90kg N ha-1) on rice (supper basmati) production and soil health at Soil Salinity Research Institute( SSRI) Farm, Pindi Bhattian, district Hafizabad under saline sodic soils (ECe=5.32 dS m 1 , pH=8.52 and SAR=18.38) during 2009 .Treatments were ar ...
... with N starter dose (0, 30kg N ha-1, 60kg N ha-1 and 90kg N ha-1) on rice (supper basmati) production and soil health at Soil Salinity Research Institute( SSRI) Farm, Pindi Bhattian, district Hafizabad under saline sodic soils (ECe=5.32 dS m 1 , pH=8.52 and SAR=18.38) during 2009 .Treatments were ar ...
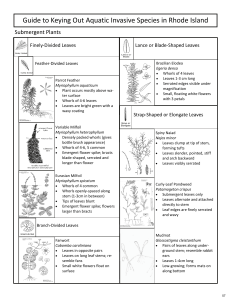
RIDEM Guide to Keying Out Plants
... ground stem; resemble rabbit ears • Leaves 1‐4cm long • Low‐growing; forms mats on along bottom ...
... ground stem; resemble rabbit ears • Leaves 1‐4cm long • Low‐growing; forms mats on along bottom ...
Comparative studies on the digestive enzymes in the gut of
... earthworms. Enzyme activity in earthworms is regionally specialized and influenced by physiological state, age and microorganisms. Digestive enzymes like cellulase, xylanase, acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphates were found to be more in the gut of E. fetida as compared to E. eugeniae. While the ...
... earthworms. Enzyme activity in earthworms is regionally specialized and influenced by physiological state, age and microorganisms. Digestive enzymes like cellulase, xylanase, acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphates were found to be more in the gut of E. fetida as compared to E. eugeniae. While the ...
To investigate the effects that varying levels of forage relative to
... the level of dietary forage and concentrate, we conducted an experiment to determine the effects of differing intakes of dry matter on the nutritional and nitrogen efficiency in growing dairy heifers (Zanton and Heinrichs, 2004; Zanton and Heinrichs, 2005b). Organic matter digestibility was linearly ...
... the level of dietary forage and concentrate, we conducted an experiment to determine the effects of differing intakes of dry matter on the nutritional and nitrogen efficiency in growing dairy heifers (Zanton and Heinrichs, 2004; Zanton and Heinrichs, 2005b). Organic matter digestibility was linearly ...
- Wiley Online Library
... (0.65 Å, coordination number CN = 6) can form a complex with two or three oxygen atoms of different phosphate groups in a phosphate ester more strongly than a divalent calcium ion (0.99 Å, CN=6) (Yamagata et al., 1995). Ozawa et al. (2004) have shown that phosphorylation of AMP into ADP and ATP ca ...
... (0.65 Å, coordination number CN = 6) can form a complex with two or three oxygen atoms of different phosphate groups in a phosphate ester more strongly than a divalent calcium ion (0.99 Å, CN=6) (Yamagata et al., 1995). Ozawa et al. (2004) have shown that phosphorylation of AMP into ADP and ATP ca ...
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta
... Angiosperms - Flowering Plants Angiosperms focus of the course • comprise the phylum Magnoliophyta • vast majority of plant diversity What are the non-angiosperm land plants? • DNA evidence has clarified much but not all of the relatioships of other phyla (= divisions) See first pages of Chpts 1 & 3 ...
... Angiosperms - Flowering Plants Angiosperms focus of the course • comprise the phylum Magnoliophyta • vast majority of plant diversity What are the non-angiosperm land plants? • DNA evidence has clarified much but not all of the relatioships of other phyla (= divisions) See first pages of Chpts 1 & 3 ...
Document
... Sharp toothed leaves are in groups of three Produces many stolons Stems and leaves are very hairy Low maintenance turf ...
... Sharp toothed leaves are in groups of three Produces many stolons Stems and leaves are very hairy Low maintenance turf ...
Biomes Section 3
... conserving water, which allows the plants to live in dry, desert conditions. • Plants called succulents, such as cactuses, have thick, fleshy stems and leaves that conserve water. Their leaves also have a waxy coating to prevent water loss, while sharp spines on the plant keep animals away. • Many p ...
... conserving water, which allows the plants to live in dry, desert conditions. • Plants called succulents, such as cactuses, have thick, fleshy stems and leaves that conserve water. Their leaves also have a waxy coating to prevent water loss, while sharp spines on the plant keep animals away. • Many p ...
Monogastric Nutrition
... feed in addition to that offered by the owner to provide a readily available source of meat. While such a husbandry system may still be possible, pigs are now largely kept in purpose-built facilities where feed as well as environment for the pigs can be controlled. Such facilities require a more ela ...
... feed in addition to that offered by the owner to provide a readily available source of meat. While such a husbandry system may still be possible, pigs are now largely kept in purpose-built facilities where feed as well as environment for the pigs can be controlled. Such facilities require a more ela ...
Supplying the Best Tomato, Pepper and Herb
... a lighter color, more fruits per truss and slightly smaller in size, all else is the same as Cherokee Purple. Cherokee Purple was from TN and Indian Stripe was found in AR where the Cherokee had (and still have) a presence. ...
... a lighter color, more fruits per truss and slightly smaller in size, all else is the same as Cherokee Purple. Cherokee Purple was from TN and Indian Stripe was found in AR where the Cherokee had (and still have) a presence. ...
How Can We Master Energy and Information on the Nanoscale to
... and P-CR, fold into distinct subdomains within the cytosolic region, supporting the potential importance of these regions for CESA assembly into plant CSCs. L. Sethaphong, C. H. Haigler, J. D. Kubicki, J. Zimmer, D. Bonetta, S. DeBolt, Y. G. Yingling, "Tertiary model of a plant cellulose synthase", ...
... and P-CR, fold into distinct subdomains within the cytosolic region, supporting the potential importance of these regions for CESA assembly into plant CSCs. L. Sethaphong, C. H. Haigler, J. D. Kubicki, J. Zimmer, D. Bonetta, S. DeBolt, Y. G. Yingling, "Tertiary model of a plant cellulose synthase", ...
invasive exotic plants - Southeast Exotic Pest Plant Council
... species for sunlight and space. It thrives in full sun but also exhibits shade tolerance. In addition, this plant produces an allelopathic chemical that prevents other plants from growing in its vicinity. Roadsides throughout the piedmont and mountains are infested with A. altissima providing the id ...
... species for sunlight and space. It thrives in full sun but also exhibits shade tolerance. In addition, this plant produces an allelopathic chemical that prevents other plants from growing in its vicinity. Roadsides throughout the piedmont and mountains are infested with A. altissima providing the id ...
Koala Pals with Patent-Pending Oligofructose Complex
... What makes Koala Pals better than other children’s multivitamins? Koala Pals multivitamins start with the nutrients doctors recommend most in researchrecommended amounts. We then formulate Koala Pals with patent-pending Oligofructose Complex to help provide maximum solubility and increased antioxida ...
... What makes Koala Pals better than other children’s multivitamins? Koala Pals multivitamins start with the nutrients doctors recommend most in researchrecommended amounts. We then formulate Koala Pals with patent-pending Oligofructose Complex to help provide maximum solubility and increased antioxida ...
Growing Vegetables at Home - UW Learning Store
... throughout the summer for insect protection. These fabrics work best either with a high tunnel system or with a crop that is harvested only once. Remember, you must remove any protective coverings at pollination time for all cross-pollinated crops such as cucumbers, melons and squashes. ...
... throughout the summer for insect protection. These fabrics work best either with a high tunnel system or with a crop that is harvested only once. Remember, you must remove any protective coverings at pollination time for all cross-pollinated crops such as cucumbers, melons and squashes. ...
appendices - Shodhganga
... known as sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the union of ------- ...
... known as sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the union of ------- ...
INVITRO PARTHENIUM HYSTEROPHORUS Research Article
... (BHT) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) are included in various foods, but their safety, however, can be doubted 6,7. For this reason, importance and demand for natural antioxidants has grown over the recent years. These antioxidants occur in all plants and in all parts of the plants8. It is alread ...
... (BHT) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) are included in various foods, but their safety, however, can be doubted 6,7. For this reason, importance and demand for natural antioxidants has grown over the recent years. These antioxidants occur in all plants and in all parts of the plants8. It is alread ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.