Auxin biology in roots
... are always affected by various environmental stimuli such as gravity, temperature, and drought. In addition, they sometimes interact with other organisms. Because plants cannot move like animals, they have to critically monitor the surrounding environment and adapt to it by constantly changing their ...
... are always affected by various environmental stimuli such as gravity, temperature, and drought. In addition, they sometimes interact with other organisms. Because plants cannot move like animals, they have to critically monitor the surrounding environment and adapt to it by constantly changing their ...
PDF - CLIMBERS - University of Michigan
... through multiple domestications from Mexico to southern Canada. C. pepo ssp. pepo likely originated in Mexico and C. pepo ssp. ovifera in eastern U.S (9). The oldest archeological records of C. pepo are from Guilá Naquitz cave in Oaxaca, Mexico (from 8,000 to 10,000 years ago), twice as old as other ...
... through multiple domestications from Mexico to southern Canada. C. pepo ssp. pepo likely originated in Mexico and C. pepo ssp. ovifera in eastern U.S (9). The oldest archeological records of C. pepo are from Guilá Naquitz cave in Oaxaca, Mexico (from 8,000 to 10,000 years ago), twice as old as other ...
New Weed ID Guide for Ontario Crops
... Leaves: Everyone knows the “leaves of three, let them be” line, but there are a lot of plants with three leaflets. Focus less on the type of leaf margin and colour, as both vary depending on their environment and the time of year. For example, leaves are generally a copper or reddish colour in the e ...
... Leaves: Everyone knows the “leaves of three, let them be” line, but there are a lot of plants with three leaflets. Focus less on the type of leaf margin and colour, as both vary depending on their environment and the time of year. For example, leaves are generally a copper or reddish colour in the e ...
Medical importance of Cupressus sempervirens
... their traditional use in different parts of the world(1). Plants generally produce many secondary metabolites which were constituted an important source of many pharmaceutical drugs (2). Many previous reviews revealed the wide range of the pharmacological and therapeutic effects of medicinal plants ...
... their traditional use in different parts of the world(1). Plants generally produce many secondary metabolites which were constituted an important source of many pharmaceutical drugs (2). Many previous reviews revealed the wide range of the pharmacological and therapeutic effects of medicinal plants ...
Calotropis Gigantea ISSN: 2348 –0882 ============================================================================= S SARKAR
... thin-walled and isodiametric to circular. Intracellular spaces were present in ground tissue and the stele was crescent-shaped and composed of bicollateral and open vascular bundles. The xylem consisted mostly of vessels and tracheids, and a strip of cambium was present between the xylem and phloem ...
... thin-walled and isodiametric to circular. Intracellular spaces were present in ground tissue and the stele was crescent-shaped and composed of bicollateral and open vascular bundles. The xylem consisted mostly of vessels and tracheids, and a strip of cambium was present between the xylem and phloem ...
LITERATURE PART: Ricinus communis L. and ricin toxin
... into four groups: bulk-forming preparations, stimulants, stool softeners, and osmotic laxatives (Thompson 1980). Castor oil belongs to the group of stimulants and it is a general belief that castor oil stimulates the intestinal motility. Stewart and his group (1975) consider that castor oil does not ...
... into four groups: bulk-forming preparations, stimulants, stool softeners, and osmotic laxatives (Thompson 1980). Castor oil belongs to the group of stimulants and it is a general belief that castor oil stimulates the intestinal motility. Stewart and his group (1975) consider that castor oil does not ...
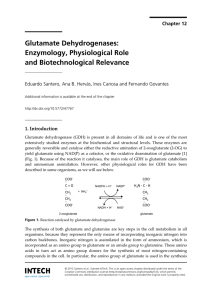
Glutamate Dehydrogenases: Enzymology, Physiological
... specificity are commonly found in higher eukaryotes. However, some dual-GDHs, have also been described in prokaryotes [5, 13-15]. Glutamate dehydrogenases from non-vertebrate animals differ from the GDHs of vertebrates in that they are mono-coenzyme specific and are not regulated by nucleotides [16] ...
... specificity are commonly found in higher eukaryotes. However, some dual-GDHs, have also been described in prokaryotes [5, 13-15]. Glutamate dehydrogenases from non-vertebrate animals differ from the GDHs of vertebrates in that they are mono-coenzyme specific and are not regulated by nucleotides [16] ...
Life Cycle of a Pumpkin
... Pumpkin 4: The yellow powder is pollen. It takes a male and female flower to make a pumpkin. Pumpkin 5: It also takes bees to make pumpkins. They move the pollen from male flowers to female flowers. Pumpkin 1: When a bee visits the male flowers, the pollen sticks to the bee’s body and legs. Pumpkin ...
... Pumpkin 4: The yellow powder is pollen. It takes a male and female flower to make a pumpkin. Pumpkin 5: It also takes bees to make pumpkins. They move the pollen from male flowers to female flowers. Pumpkin 1: When a bee visits the male flowers, the pollen sticks to the bee’s body and legs. Pumpkin ...
MORUS ALBA Review Article BANDNA DEVI, NEHA SHARMA, DINESH KUMAR, KAMAL JEET*
... Pasteurella multocida in mice. It also increased the circulating antibody titre in indirect haemagglutination test. On the other hand, it showed significant increase in the phagocytic index in carbon clearance assay, a significant protection against cyclophosphamide induced neutropenia and increased ...
... Pasteurella multocida in mice. It also increased the circulating antibody titre in indirect haemagglutination test. On the other hand, it showed significant increase in the phagocytic index in carbon clearance assay, a significant protection against cyclophosphamide induced neutropenia and increased ...
about Gladiolus
... the bottoms of the main corm. These are called cormels and these can be separated from the main corm and stored over the winter as well. These cormels can be planted in the garden the following spring and allowed to mature into a full corm over the growing season. Cormels will likely only throw up a ...
... the bottoms of the main corm. These are called cormels and these can be separated from the main corm and stored over the winter as well. These cormels can be planted in the garden the following spring and allowed to mature into a full corm over the growing season. Cormels will likely only throw up a ...
Asparagus weeds management manual: Section 1
... Distinguishing between common and Western Cape bridal creeper Common bridal creeper (Asparagus asparagoides) is one of southern Australia’s worst weeds. It is an aggressive and highly invasive environmental weed that is capable of smothering native ground flora, shrubs and small trees. It forms a th ...
... Distinguishing between common and Western Cape bridal creeper Common bridal creeper (Asparagus asparagoides) is one of southern Australia’s worst weeds. It is an aggressive and highly invasive environmental weed that is capable of smothering native ground flora, shrubs and small trees. It forms a th ...
Pollen tube energetics: respiration, fermentation
... competition among tubes. Through evolution, this has led to rates of cellular elongation unequalled elsewhere in the plant world. For example, in maize, pollen tubes can grow as fast as 1 cm h21 (Mascarenhas 1993). To support this extremely rapid growth, there must be an equally powerful energy tran ...
... competition among tubes. Through evolution, this has led to rates of cellular elongation unequalled elsewhere in the plant world. For example, in maize, pollen tubes can grow as fast as 1 cm h21 (Mascarenhas 1993). To support this extremely rapid growth, there must be an equally powerful energy tran ...
All About Calcium Supplements
... • Different calcium compounds have similar bioavailability (the amount of calcium that the body can use) when supplements are taken with food. The presence of food in the stomach causes the release of acid that is necessary to break down most calcium supplements. When calcium is taken with food, it ...
... • Different calcium compounds have similar bioavailability (the amount of calcium that the body can use) when supplements are taken with food. The presence of food in the stomach causes the release of acid that is necessary to break down most calcium supplements. When calcium is taken with food, it ...
7) The role of cobalt in vitamin B12
... Cofactor: An atom, organic molecule, or molecular group that is necessary for the catalytic activity (see catalysis) of many enzymes. A cofactor may be tightly bound to the protein portion of an enzyme and thus be an integral part of its functional structure, or it may be only loosely associated and ...
... Cofactor: An atom, organic molecule, or molecular group that is necessary for the catalytic activity (see catalysis) of many enzymes. A cofactor may be tightly bound to the protein portion of an enzyme and thus be an integral part of its functional structure, or it may be only loosely associated and ...
Materia Indica, or, Some account of those articles which are
... ages * j but that he had met with a curious fragment of it; in which he was surprized to find an account of the internal structure of the human frame. What> ever may have been done, however, in this way, in former times, it is to be regretted that the custom of (frssecting and examining the dead sub ...
... ages * j but that he had met with a curious fragment of it; in which he was surprized to find an account of the internal structure of the human frame. What> ever may have been done, however, in this way, in former times, it is to be regretted that the custom of (frssecting and examining the dead sub ...
Mutagenesis of Plants Overexpressing CONSTANS
... All five lines flowered earlier than did wild-type plants under both long- and short-day conditions (Figure 2 and Table 1). Earlier flowering was apparent both in the time between sowing until floral buds were visible in the center of the rosette and in the fewer leaves formed by the shoot meristem ...
... All five lines flowered earlier than did wild-type plants under both long- and short-day conditions (Figure 2 and Table 1). Earlier flowering was apparent both in the time between sowing until floral buds were visible in the center of the rosette and in the fewer leaves formed by the shoot meristem ...
MF2408 Sericea Lespedeza: History, Characteristics, and
... ation found in a burned pasture. Burning is assumed to enhance establishment, possibly due to more sunlight available to the seed and seedlings and scarification. Seedlings will germinate and survive at low population levels where ground cover and other plant competition is dense. Examples of such ...
... ation found in a burned pasture. Burning is assumed to enhance establishment, possibly due to more sunlight available to the seed and seedlings and scarification. Seedlings will germinate and survive at low population levels where ground cover and other plant competition is dense. Examples of such ...
TEMPERATURE, NITROGEN AND SULFUR FERTILITY
... nothing is known concerning the effects of lower N levels flavor. Furthermore, there have been several reports of N nutrition influencing S metabolism in plants, thus presenting questions of how N availability would affect the biosynthesis of the S-containing flavor compounds in onion (Brunold and S ...
... nothing is known concerning the effects of lower N levels flavor. Furthermore, there have been several reports of N nutrition influencing S metabolism in plants, thus presenting questions of how N availability would affect the biosynthesis of the S-containing flavor compounds in onion (Brunold and S ...
Phar 722 Pharmacy Practice III
... – Zinc does affect glucose metabolism. – Patients with diabetes taking zinc supplements should carefully monitor their blood-glucose levels. ...
... – Zinc does affect glucose metabolism. – Patients with diabetes taking zinc supplements should carefully monitor their blood-glucose levels. ...
Swine Nutrition Guide
... The University of Nebraska and South Dakota State University are solely responsible for the content of this publication. No endorsement of these firms is intended, nor a discredit to any one omitted from the list. This publication is available at:.
...
... The University of Nebraska and South Dakota State University are solely responsible for the content of this publication. No endorsement of these firms is intended, nor a discredit to any one omitted from the list. This publication is available at:
Vitamin D - Mercy Health
... Statin drugs are the most commonly used medications for reducing cholesterol levels. They help prevent cardiovascular disease through their cholesterol reducing effects. Statins are not free from side effects. They are well known to have the ability to induce mus ...
... Statin drugs are the most commonly used medications for reducing cholesterol levels. They help prevent cardiovascular disease through their cholesterol reducing effects. Statins are not free from side effects. They are well known to have the ability to induce mus ...
MF2734 Great Plains Canola Production Handbook
... 10 to 22 months 2 Corn/Sorghum/Cotton 15 months ...
... 10 to 22 months 2 Corn/Sorghum/Cotton 15 months ...
Alpha PMX - Alpha Online
... Instructions for Mixing & Use Alpha PMX is an elemental nutrient formula in powder form that contains a mixture of pure nutrients. The formula is mixed with water and juices. The basic idea behind Alpha PMX is to supply a complete set of nutrients in their pure form. We recognized, of course, that p ...
... Instructions for Mixing & Use Alpha PMX is an elemental nutrient formula in powder form that contains a mixture of pure nutrients. The formula is mixed with water and juices. The basic idea behind Alpha PMX is to supply a complete set of nutrients in their pure form. We recognized, of course, that p ...
A Review on Natural Plant: Aerva lanata
... kaempferol-3-rahmno galactoside, and starch. It also consists of free sugars like fructose, galactose, ...
... kaempferol-3-rahmno galactoside, and starch. It also consists of free sugars like fructose, galactose, ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.