Proteins - RMC Science Home
... Proteins are groups of Amino Acids that are bonded together by a peptide bond. Contain hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen The main function of proteins is to build and maintain tissues. Can also be used for energy but ONLY if carbohydrate and fat stores are depleated. ...
... Proteins are groups of Amino Acids that are bonded together by a peptide bond. Contain hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen The main function of proteins is to build and maintain tissues. Can also be used for energy but ONLY if carbohydrate and fat stores are depleated. ...
10) water soluble vitamins
... Deficiency disease is pernicious anemia • Megaloblasts and macrocytes rather than normal red blood cells • Brain abnormalities and spinal cord degeneration which can be lethal • Pernicious anemia attacks parietal cells and diminishes intrinsic factor and stomach acid ...
... Deficiency disease is pernicious anemia • Megaloblasts and macrocytes rather than normal red blood cells • Brain abnormalities and spinal cord degeneration which can be lethal • Pernicious anemia attacks parietal cells and diminishes intrinsic factor and stomach acid ...
Vitamins - Shanyar
... synthesis vit K and breast milk contains little amounts, these render neonates develop a hemorrhagic disease • In obstructive jaundice ;vit K is not absorbed • Warfarin act by antagonizing vit K action ...
... synthesis vit K and breast milk contains little amounts, these render neonates develop a hemorrhagic disease • In obstructive jaundice ;vit K is not absorbed • Warfarin act by antagonizing vit K action ...
Propagation
... Factors Influencing Rooting Misting – needed in herbaceous cuttings. Need to keep hydrated so will not dry out. Mist the plant then cover with plastic cover. Keeps moisture in. Can also have an automated mist system. 5. Bottom heat – helps force rooting by stimulating the root to grow. ...
... Factors Influencing Rooting Misting – needed in herbaceous cuttings. Need to keep hydrated so will not dry out. Mist the plant then cover with plastic cover. Keeps moisture in. Can also have an automated mist system. 5. Bottom heat – helps force rooting by stimulating the root to grow. ...
Featured Plant of the Month January 2012 Italian Cypress.docx
... writers. This tree is widely cultivated and used as an ornamental in this country. The Arizona Cypress, Cupressus arizonica, is an example of a New World member of the same genus; C. arizonica is native in Texas only in the Chisos Mountains of Big Bend National Park in Brewster County. The leaves of ...
... writers. This tree is widely cultivated and used as an ornamental in this country. The Arizona Cypress, Cupressus arizonica, is an example of a New World member of the same genus; C. arizonica is native in Texas only in the Chisos Mountains of Big Bend National Park in Brewster County. The leaves of ...
Milfoil Look-a-Likes fact sheet – pdf
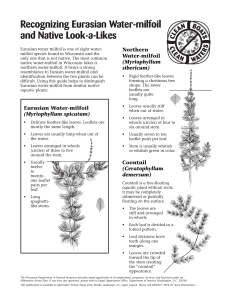
... and Native Look-a-Likes Eurasian water milfoil is one of eight watermilfoil species found in Wisconsin and the only one that is not native. The most common native water-milfoil in Wisconsin lakes is northern water-milfoil. It bears a strong resemblance to Eurasin water-milfoil and identification bet ...
... and Native Look-a-Likes Eurasian water milfoil is one of eight watermilfoil species found in Wisconsin and the only one that is not native. The most common native water-milfoil in Wisconsin lakes is northern water-milfoil. It bears a strong resemblance to Eurasin water-milfoil and identification bet ...
Information - Greyhound Products Direct
... Q. What does it mean to include “chelated” trace-minerals? A. It is widely acknowledged that organic or “chelated” trace-minerals similar to the natural forms contained in common foods, such as copper, zinc and manganese, are absorbed more effectively, with a reduced risk of interaction and interfer ...
... Q. What does it mean to include “chelated” trace-minerals? A. It is widely acknowledged that organic or “chelated” trace-minerals similar to the natural forms contained in common foods, such as copper, zinc and manganese, are absorbed more effectively, with a reduced risk of interaction and interfer ...
1 Nitrogen Oxide Reduction from Air Pollution Using Denitrifying and
... oxides to this form specifically for plant use. However, to maintain plant growth, water must be added periodically. This may cause lithium nitride to ignite (if the amount used is large enough), which, in turn, may cause other nearby combustible materials to burn as well. For these reasons, eithe ...
... oxides to this form specifically for plant use. However, to maintain plant growth, water must be added periodically. This may cause lithium nitride to ignite (if the amount used is large enough), which, in turn, may cause other nearby combustible materials to burn as well. For these reasons, eithe ...
Weathering and Soil Formation *** Practice Test
... spaces through which water can move is ____________. ...
... spaces through which water can move is ____________. ...
Trace minerals
... vitamin B12 molecule but a deficiency of cobalt has not been demonstrated in poultry fed a diet adequate in vitamin B12. Therefore, supplementation with this element is not normally necessary. Diets containing no ingredients of animal origin (which contain vitamin B12) contain no vitamin B12. Theref ...
... vitamin B12 molecule but a deficiency of cobalt has not been demonstrated in poultry fed a diet adequate in vitamin B12. Therefore, supplementation with this element is not normally necessary. Diets containing no ingredients of animal origin (which contain vitamin B12) contain no vitamin B12. Theref ...
Artificial selection, 2
... more obvious than others). Some of this variability is the result of genetic differences among individuals, while some is the result of different environmental conditions. Natural selection is concerned only with variability among individuals that has a genetic basis and can be passed from parent to ...
... more obvious than others). Some of this variability is the result of genetic differences among individuals, while some is the result of different environmental conditions. Natural selection is concerned only with variability among individuals that has a genetic basis and can be passed from parent to ...
Moving onto Land Problems and Solutions
... Characteristics of All Land Plants Life Cycle • Sporic meiosis and Alternation of Generation • Gametophytes are haploid and produce gametes • Sporophytes are diploid, and make haploid spores in sporangia (meiosis) • Spores grow into gametophytes ...
... Characteristics of All Land Plants Life Cycle • Sporic meiosis and Alternation of Generation • Gametophytes are haploid and produce gametes • Sporophytes are diploid, and make haploid spores in sporangia (meiosis) • Spores grow into gametophytes ...
A Plague of Plants - Wildlands Restoration Team
... found on follow-up visits must be carefully removed and disposed of to avoid leaving pieces behind. Since the areas in which this plant is found typically have nutrient-rich soils, rapid regrowth of other vegetation can hinder the job of spotting newly emerging cape ivy until it has grown too large ...
... found on follow-up visits must be carefully removed and disposed of to avoid leaving pieces behind. Since the areas in which this plant is found typically have nutrient-rich soils, rapid regrowth of other vegetation can hinder the job of spotting newly emerging cape ivy until it has grown too large ...
Adansonia gregorii plant notes
... Large, showy, cream, fragrant flowers occur usually during the summer and autumn months. They open early in the evening and are pollinated that night. Each flower lasts for only a day or two before falling. Growing conditions The following information provides guidance for those growing their own bo ...
... Large, showy, cream, fragrant flowers occur usually during the summer and autumn months. They open early in the evening and are pollinated that night. Each flower lasts for only a day or two before falling. Growing conditions The following information provides guidance for those growing their own bo ...
Rozanne Cranesbill
... mid summer, which are most effective when planted in groupings. It's deeply cut lobed palmate leaves are forest green in colour. As an added bonus, the foliage turns a gorgeous indian red in the fall. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: Rozanne Cranesbill is an herbaceou ...
... mid summer, which are most effective when planted in groupings. It's deeply cut lobed palmate leaves are forest green in colour. As an added bonus, the foliage turns a gorgeous indian red in the fall. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: Rozanne Cranesbill is an herbaceou ...
CVBG June Bulletin 2015 - Conejo Valley Botanical Garden
... In fact, many butterfly gardeners plan their garden around Buddleia davidii. There are many different types, so the plant characteristics and color can vary. Butterfly bushes are drought tolerant and easy to grow! -Sandy Krutilek- ...
... In fact, many butterfly gardeners plan their garden around Buddleia davidii. There are many different types, so the plant characteristics and color can vary. Butterfly bushes are drought tolerant and easy to grow! -Sandy Krutilek- ...
Seed Plants
... - 2 sperm cells carry out double fertilization: one fertilizes egg, other fuses w. 2 nuclei in central cell - central cell becomes triploid endosperm (food supply for seed) ...
... - 2 sperm cells carry out double fertilization: one fertilizes egg, other fuses w. 2 nuclei in central cell - central cell becomes triploid endosperm (food supply for seed) ...
Part I: Flower Structure and Function
... Skill: Reflect on background knowledge (what you know and don’t know) to prepare to learn new concepts and skills. Assignment: This assignment has three parts. (1) Fill in the Pre-Assessment Survey form individually. Answer true (T), false (F), or don’t know (DK) for every question. It is fine if yo ...
... Skill: Reflect on background knowledge (what you know and don’t know) to prepare to learn new concepts and skills. Assignment: This assignment has three parts. (1) Fill in the Pre-Assessment Survey form individually. Answer true (T), false (F), or don’t know (DK) for every question. It is fine if yo ...
Growth in Plants
... •The absorption of light by photoreceptors can control the transcription of specific genes. ...
... •The absorption of light by photoreceptors can control the transcription of specific genes. ...
Purple Petticoats Coral Bells
... with the flowers, with a spread of 24 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This perennial does best in partial shade to shade. It p ...
... with the flowers, with a spread of 24 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This perennial does best in partial shade to shade. It p ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.