video slide - CARNES AP BIO | "Nothing in biology makes
... • Have true vascular tissues -- xylem and phloem that allow true “organs” to develop – roots, stems, leaves – Xylem carries water and minerals in a plant ...
... • Have true vascular tissues -- xylem and phloem that allow true “organs” to develop – roots, stems, leaves – Xylem carries water and minerals in a plant ...
Callery pear
... is above about 65°F (and no higher than 80°F for triclopyr) to ensure absorption of the herbicide. To allow ample drying, applications should be made when rain is unlikely for about 12 hours after application and leaves should be dry prior to treatment. Wind speed should be below 8-10 mph to avoid o ...
... is above about 65°F (and no higher than 80°F for triclopyr) to ensure absorption of the herbicide. To allow ample drying, applications should be made when rain is unlikely for about 12 hours after application and leaves should be dry prior to treatment. Wind speed should be below 8-10 mph to avoid o ...
1 Plant Propagation Protocol for Carex rossii ESRM 412 – Native
... Breaking the seed dormancy is necessary, but propagation using seed is less successful. Rhizomes are the best propagation method of Ross ...
... Breaking the seed dormancy is necessary, but propagation using seed is less successful. Rhizomes are the best propagation method of Ross ...
671.pdf
... more salt sensitive asters. However, even within the chenopods, there is a range of salt tolerance (Reimann and Breckle, 1993). These differences may influence the size of the compatible solute pool and thus the amount of potentially resorbable N, masking any trend between NPROF and salt tolerance. N ...
... more salt sensitive asters. However, even within the chenopods, there is a range of salt tolerance (Reimann and Breckle, 1993). These differences may influence the size of the compatible solute pool and thus the amount of potentially resorbable N, masking any trend between NPROF and salt tolerance. N ...
Self Guided Low Boardwalk Tour
... knees, but there is disagreement whether they are for stability or air exchange. 10. Bald Cypresses, Taxodium distichum, like Pond Cypresses are members of the Redwood family. Bald cypress can grow to be 150 feet tall and live hundreds of years. They like faster moving water and more nutrient rich s ...
... knees, but there is disagreement whether they are for stability or air exchange. 10. Bald Cypresses, Taxodium distichum, like Pond Cypresses are members of the Redwood family. Bald cypress can grow to be 150 feet tall and live hundreds of years. They like faster moving water and more nutrient rich s ...
MANGOSTEEN - HomeGrown
... For backyard or small-scale planting, 30 ft spacing is recommended between plants. A well drained soil ensures deep and extensive root development, provided good aeration, and prevents water logging and disease occurrence such as root rot. The pits should be 3x3x3 ft and fill 3/4th of the pit with 1 ...
... For backyard or small-scale planting, 30 ft spacing is recommended between plants. A well drained soil ensures deep and extensive root development, provided good aeration, and prevents water logging and disease occurrence such as root rot. The pits should be 3x3x3 ft and fill 3/4th of the pit with 1 ...
Microclimate - Page Bloomer
... Soil moisture budget – Plants photosynthesise best when both water and oxygen in the soil are non-restricting i.e. there is not too much or too little water, and air is available to the roots for as much of the time as possible. Mulching of the soil can be used to conserve moisture. Shelter generall ...
... Soil moisture budget – Plants photosynthesise best when both water and oxygen in the soil are non-restricting i.e. there is not too much or too little water, and air is available to the roots for as much of the time as possible. Mulching of the soil can be used to conserve moisture. Shelter generall ...
2016 Skrypnіchenko S. V., PhD of Agricultural Sciences, Associate
... However, long-term development is not reflected in the amount of total nitrogen and potassium in the peat soil. The mineralization of peat is also not conducive to the retention of colloidal complex of potassium in non-exchangeable form, and leads to its release and transfer in mobile, available to ...
... However, long-term development is not reflected in the amount of total nitrogen and potassium in the peat soil. The mineralization of peat is also not conducive to the retention of colloidal complex of potassium in non-exchangeable form, and leads to its release and transfer in mobile, available to ...
NATURAL ORGANIC and BIOLOGICAL FARMING
... charring wood or other biomass by driving off the moisture and volatile gases, leaving mostly carbon. This carbon does 2 main things: it greatly aids soils for plant nutrition, and it holds (sequesters) carbon, creating a negative carbon footprint. ...
... charring wood or other biomass by driving off the moisture and volatile gases, leaving mostly carbon. This carbon does 2 main things: it greatly aids soils for plant nutrition, and it holds (sequesters) carbon, creating a negative carbon footprint. ...
Some ethnomedicines used by the Tai Ahom of Dibrugarh district
... longitude and 22º-28º North latitude. Dibrugarh district is located in the eastern part of Assam and is situated between 27°5׳28′-27º42׳30′ North latitude and 94º30׳46′-95º29׳8′ East longitude, covering an area of 3301 sq. km. The district is surrounded by Dhemaji district of Assam in the No ...
... longitude and 22º-28º North latitude. Dibrugarh district is located in the eastern part of Assam and is situated between 27°5׳28′-27º42׳30′ North latitude and 94º30׳46′-95º29׳8′ East longitude, covering an area of 3301 sq. km. The district is surrounded by Dhemaji district of Assam in the No ...
Starting and Growing Beautiful Summer Bulbs
... which turns the stem to mush. Dry the roots for a day or two. Cleaned roots can be wrapped in newspaper (or layered in peat moss or other packing material if your storage conditions are dry) and stored in paper bags or cardboard boxes, at 45-50ºF. Check periodically to be sure the roots do not dry o ...
... which turns the stem to mush. Dry the roots for a day or two. Cleaned roots can be wrapped in newspaper (or layered in peat moss or other packing material if your storage conditions are dry) and stored in paper bags or cardboard boxes, at 45-50ºF. Check periodically to be sure the roots do not dry o ...
Soil sealing guidelines of the EU - ESDAC
... • Soil sealing occurs when agricultural or other rural land is built on - and soil functions are stopped. • Annual land-take of some 1,000 km² in the EU – the size of Berlin (= 270 ha/day) taken over by urban and infrastructure expansion • In the decade 1990–2000, the sealed area in the EU-15 increa ...
... • Soil sealing occurs when agricultural or other rural land is built on - and soil functions are stopped. • Annual land-take of some 1,000 km² in the EU – the size of Berlin (= 270 ha/day) taken over by urban and infrastructure expansion • In the decade 1990–2000, the sealed area in the EU-15 increa ...
Unit - Test Bank
... a strategy for changing someone’s eating habits how to make a favorite recipe healthier Tips on Internet activities: This section includes activities that refer to specific Web sites. Because of the nature of the Web, these specific sites may change or disappear. Substitute sites will always be ...
... a strategy for changing someone’s eating habits how to make a favorite recipe healthier Tips on Internet activities: This section includes activities that refer to specific Web sites. Because of the nature of the Web, these specific sites may change or disappear. Substitute sites will always be ...
download PDF
... clustering together on plant surfaces as they feed. They have mouthparts that enable them to suck sap from the plant’s leaves, shoots, stems and roots. Adult female mealybugs are wingless and are usually what you see on the plant; adult male mealybugs are very small and gnatlike and have a single pa ...
... clustering together on plant surfaces as they feed. They have mouthparts that enable them to suck sap from the plant’s leaves, shoots, stems and roots. Adult female mealybugs are wingless and are usually what you see on the plant; adult male mealybugs are very small and gnatlike and have a single pa ...
Text – Native prairie wildflowers - University of Minnesota Extension
... Shooting Star (Primrose Family) is commonly planted and makes a fine addition to the Spring wild flower garden. Plant it in moist humus-rich soil in sun or shade. Once established, it can tolerate dry and shady sites. 9 – Shooting Star Flowers are white to lavender and are produced on 18 inch stalks ...
... Shooting Star (Primrose Family) is commonly planted and makes a fine addition to the Spring wild flower garden. Plant it in moist humus-rich soil in sun or shade. Once established, it can tolerate dry and shady sites. 9 – Shooting Star Flowers are white to lavender and are produced on 18 inch stalks ...
16. Plant Reproduction
... OB51 Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction in plants and describe a way in which a named plant can reproduce asexually OB52 Locate and identify the main parts of the flower: sepals, petals, carpel and stamen OB53 Use a suitable flower to identify the stigma, style, ovary, anther and fi ...
... OB51 Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction in plants and describe a way in which a named plant can reproduce asexually OB52 Locate and identify the main parts of the flower: sepals, petals, carpel and stamen OB53 Use a suitable flower to identify the stigma, style, ovary, anther and fi ...
Mechanisms of soil erosion as affected by climatatic and
... Freezing and thawing Freezing resembles drying – Traditionally frost has been considered to increase aggregate stability in clay soils Cycles: results showing decrease and increase in macroaggregate stability have been reported (water content) Spring: weak structure and high runoff - Soil saturated, ...
... Freezing and thawing Freezing resembles drying – Traditionally frost has been considered to increase aggregate stability in clay soils Cycles: results showing decrease and increase in macroaggregate stability have been reported (water content) Spring: weak structure and high runoff - Soil saturated, ...
PP - Chemistry Courses: About
... vary considerably, but all amino acids are degraded to one of seven metabolites: ...
... vary considerably, but all amino acids are degraded to one of seven metabolites: ...
soil weathering erosion.notebook
... April 27, 1935: Congress declares soil erosion "a national menace“. Farming techniques such as terracing, crop rotation, contour plowing, and ...
... April 27, 1935: Congress declares soil erosion "a national menace“. Farming techniques such as terracing, crop rotation, contour plowing, and ...
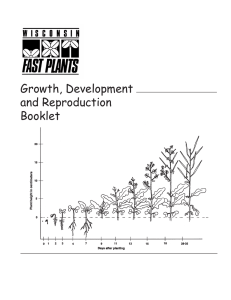
Growth, Development and Reproduction Booklet
... Stems also allow food, water, and minerals to move throughout the plant. Leaves contain many pores (called stomata) on their surfaces, which allow the plant to “breathe” by taking in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and expelling oxygen. A green pigment called chlorophyll makes the leaves appear ...
... Stems also allow food, water, and minerals to move throughout the plant. Leaves contain many pores (called stomata) on their surfaces, which allow the plant to “breathe” by taking in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and expelling oxygen. A green pigment called chlorophyll makes the leaves appear ...
Document
... family member TT12 transports anthocyanins and glycosylated flavan-3ols in the seedcoat (5,6). We have found that another MATE protein, FFT, is necessary for correct accumulation of flavonols in floral tissues. FFT promoter-GUS staining occurs in inflorescence guard cells and, as might be expected f ...
... family member TT12 transports anthocyanins and glycosylated flavan-3ols in the seedcoat (5,6). We have found that another MATE protein, FFT, is necessary for correct accumulation of flavonols in floral tissues. FFT promoter-GUS staining occurs in inflorescence guard cells and, as might be expected f ...
11 emes RESPONSE OF Ornithogalum saundersiae Bak. TO
... which flower buds had not been formed. In this study, O. saundersiae bulbs with a circumference of 14–16 cm were used to secure production of inflorescences. Salinity did not significantly affect the number of O. saundersiae inflorescences derived from a single bulb (tab. 1). Similar results were de ...
... which flower buds had not been formed. In this study, O. saundersiae bulbs with a circumference of 14–16 cm were used to secure production of inflorescences. Salinity did not significantly affect the number of O. saundersiae inflorescences derived from a single bulb (tab. 1). Similar results were de ...
plants as a source of new medicines
... the time to identify candidate new drugs; for example, high throughput screening, combinatorial chemistry and most recently genomics and proteomics. The evidence to date of these increasing the chances of success is limited but that is not to say that in the near future these significant investments ...
... the time to identify candidate new drugs; for example, high throughput screening, combinatorial chemistry and most recently genomics and proteomics. The evidence to date of these increasing the chances of success is limited but that is not to say that in the near future these significant investments ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.