Suitable Species for Urban Forestry 3a
... Particulate pollutant removal capability of vegetation is greatly affected by its morphological make-up. Plants with modified parts like hairy leaves, twigs and petioles trap particles more easily than smooth-textured plants. Trees with a high ratio of surface area to volume of foliage, such as coni ...
... Particulate pollutant removal capability of vegetation is greatly affected by its morphological make-up. Plants with modified parts like hairy leaves, twigs and petioles trap particles more easily than smooth-textured plants. Trees with a high ratio of surface area to volume of foliage, such as coni ...
Arabella Clematis - Garden Supply Co
... Arabella Clematis features bold nodding powder blue recurved flowers with lemon yellow anthers at the ends of the stems from early summer to early fall. It's pointy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: Arabella Clematis ...
... Arabella Clematis features bold nodding powder blue recurved flowers with lemon yellow anthers at the ends of the stems from early summer to early fall. It's pointy leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. Landscape Attributes: Arabella Clematis ...
Plant Signaling and Behavior
... in mycorrhization has also focused on jasmonates. AM colonization appears to be related to endogenous JA levels. In this respect, Hause et al. observed an induction of genes involved in JA biosynthesis in cells harboring arbuscules in barley roots.38 Similar results were obtained by Isayenkov et al. ...
... in mycorrhization has also focused on jasmonates. AM colonization appears to be related to endogenous JA levels. In this respect, Hause et al. observed an induction of genes involved in JA biosynthesis in cells harboring arbuscules in barley roots.38 Similar results were obtained by Isayenkov et al. ...
Wolf Rocks Trail and Spruce Flats Bog Narrative
... and slippery and every brush against the surrounding vegetation leaves a smear of moisture. Mushrooms cover old stumps and logs and many have pushed up out of the loose soil so rapidly (and recently) that they are still wearing “caps” of brown, dry leaves. The trees on this section of the trail ...
... and slippery and every brush against the surrounding vegetation leaves a smear of moisture. Mushrooms cover old stumps and logs and many have pushed up out of the loose soil so rapidly (and recently) that they are still wearing “caps” of brown, dry leaves. The trees on this section of the trail ...
Cocoplum - Lee County Extension
... has yellow-greenish new growth and creamy white or purple fruits. C. icaco var. pellocarpus is the inland variety. It is marginally salt tolerant. It has light green new growth and dark purple fruit. There are several cocoplum cultivars. ‘Horizontal’ is a cultivar of C. icaco var. icaco. It is highl ...
... has yellow-greenish new growth and creamy white or purple fruits. C. icaco var. pellocarpus is the inland variety. It is marginally salt tolerant. It has light green new growth and dark purple fruit. There are several cocoplum cultivars. ‘Horizontal’ is a cultivar of C. icaco var. icaco. It is highl ...
The Nursery Industry - Protecting Our
... Introduction from the Ministers The nursery and gardening industry has joined with the Australian Government in the fight against invasive garden plants. In championing this initiative, Nursery and Gardening Industry Australia (NGIA) is taking a significant step forward in tackling one of the natio ...
... Introduction from the Ministers The nursery and gardening industry has joined with the Australian Government in the fight against invasive garden plants. In championing this initiative, Nursery and Gardening Industry Australia (NGIA) is taking a significant step forward in tackling one of the natio ...
Soils and the Environment
... Alfisols - soils with a subsurface zone of silicate clay accumulation and >35% base saturation Ultisols - soils with a subsurface zone of silicate clay accumulation and <35% base saturation Oxisols - intensely weathered soils, tropical and subtropical Histosols - organic soils (peak, bog, muck) Geli ...
... Alfisols - soils with a subsurface zone of silicate clay accumulation and >35% base saturation Ultisols - soils with a subsurface zone of silicate clay accumulation and <35% base saturation Oxisols - intensely weathered soils, tropical and subtropical Histosols - organic soils (peak, bog, muck) Geli ...
the carbon grazing story - Australian Rangeland Society
... Carbon takes many different forms after it moves from the atmosphere to the landscape via photosynthesis. These different carbon compounds add to the resilience of the landscape. The resilience of the landscape relies on the resilience of both plants and the soil. Allowing carbon to flow into plants ...
... Carbon takes many different forms after it moves from the atmosphere to the landscape via photosynthesis. These different carbon compounds add to the resilience of the landscape. The resilience of the landscape relies on the resilience of both plants and the soil. Allowing carbon to flow into plants ...
Preliminary Phytochemical, Antimicrobial and Proximate Analysis of
... These findings are consistent with Etuk, et al. [16] who reported that the bark extract of P. gaujava had antidiarrheal activity in vitro. Previous reports have demonstrated the antidiarrheal activity of tannins [17], Flavonoids [18] and saponins [9]. In Table 2, the low moisture content (3.67%) imp ...
... These findings are consistent with Etuk, et al. [16] who reported that the bark extract of P. gaujava had antidiarrheal activity in vitro. Previous reports have demonstrated the antidiarrheal activity of tannins [17], Flavonoids [18] and saponins [9]. In Table 2, the low moisture content (3.67%) imp ...
LifePak Prime®
... healthy food selections and sources, yet our modern lifestyles often make it difficult to consume recommended levels of key nutrients that are essential to our health and well-being. Dietary surveys continue to confirm a sad fact—the overwhelming majority of people do not consume optimal levels of k ...
... healthy food selections and sources, yet our modern lifestyles often make it difficult to consume recommended levels of key nutrients that are essential to our health and well-being. Dietary surveys continue to confirm a sad fact—the overwhelming majority of people do not consume optimal levels of k ...
Basics of Planting Aquatic Plants - University of Maryland Extension
... Partial list of recommended varieties: ...
... Partial list of recommended varieties: ...
No Slide Title
... – called the coelacanths, – were thought to have become extinct at the end of the Cretaceous ...
... – called the coelacanths, – were thought to have become extinct at the end of the Cretaceous ...
Purple Loosestrife sPecies Fact sheet
... Map of purple loosestrife distribution from the USDA PLANTS database (http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=LYSA2). ...
... Map of purple loosestrife distribution from the USDA PLANTS database (http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=LYSA2). ...
The Northeastern Area Invasive Forest Plant Species Project
... Ecological disturbances that kill existing vegetation or disturb the soil can result from natural occurrences such as fire, windstorms, and heavy browsing by deer. Human activities such as logging, road building, and cultivation are also causes of ecological disturbance. Since disturbances free up g ...
... Ecological disturbances that kill existing vegetation or disturb the soil can result from natural occurrences such as fire, windstorms, and heavy browsing by deer. Human activities such as logging, road building, and cultivation are also causes of ecological disturbance. Since disturbances free up g ...
seed plants
... • Annual rings – xylem formed by the vascular cambium during one growth season • Early Spring wood – vessel diameter is large, xylem walls are thinner • Late Summer wood – vessel diameter is ...
... • Annual rings – xylem formed by the vascular cambium during one growth season • Early Spring wood – vessel diameter is large, xylem walls are thinner • Late Summer wood – vessel diameter is ...
Multicellular Primary Producers
... • Diverse group of microbes and multicellular organisms that contain some pigments found in vasculaar plants, chlorphyll a & b and certain carotenoids • Structure of green algae – Most are unicellular or small multicellular filaments, tubes or sheets – Some tropical green algae have a coenocytic tha ...
... • Diverse group of microbes and multicellular organisms that contain some pigments found in vasculaar plants, chlorphyll a & b and certain carotenoids • Structure of green algae – Most are unicellular or small multicellular filaments, tubes or sheets – Some tropical green algae have a coenocytic tha ...
SAMPLE
... Much of the information about the practical uses of the desert plants in this guide comes from research conducted by Bailey and Danin (1981). They report that during their 6-year survey they “encountered no plant that was not useful to the bedouins in one way or another” (p.145). Plants are an impor ...
... Much of the information about the practical uses of the desert plants in this guide comes from research conducted by Bailey and Danin (1981). They report that during their 6-year survey they “encountered no plant that was not useful to the bedouins in one way or another” (p.145). Plants are an impor ...
View/Open - UoN Repository
... rodents, birds, slugs and snails whereas plant pathogens include fungi, ...
... rodents, birds, slugs and snails whereas plant pathogens include fungi, ...
Age States of Plants of Various Growth Forms: A Review
... Living organismsfrombirthto death undergo sequentialphases which are usually of an indivicharacterized bychronologicalage. This sequenceofphasesof development anatomical,physiologicaland dual organismis called ontogeny.Variousmorphological, biochemicalchangestake place in the course of ontogeny,so t ...
... Living organismsfrombirthto death undergo sequentialphases which are usually of an indivicharacterized bychronologicalage. This sequenceofphasesof development anatomical,physiologicaland dual organismis called ontogeny.Variousmorphological, biochemicalchangestake place in the course of ontogeny,so t ...
Science Grade 02 Unit 09 Exemplar Lesson 02: How Do Plants
... 9. Read a story about roots. 10. Have examples of ‘roots’ that students may already know, such as radishes, carrots, turnips, parsnips, or onions. 11. Distribute one root to each table group. (Each table group does not need to have a different root.) Allow students to use a hand lens to observe the ...
... 9. Read a story about roots. 10. Have examples of ‘roots’ that students may already know, such as radishes, carrots, turnips, parsnips, or onions. 11. Distribute one root to each table group. (Each table group does not need to have a different root.) Allow students to use a hand lens to observe the ...
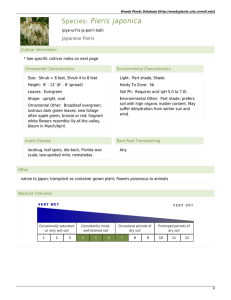
Woody Plants Database
... Environmental Other: Part shade; prefers soil with high organic matter content. May suffer dehydration from winter sun and wind. ...
... Environmental Other: Part shade; prefers soil with high organic matter content. May suffer dehydration from winter sun and wind. ...
Resource - The Stewardship Network
... Invasive plants challenge the goals, resources, and morale of the people whose passion or livelihood is the conservation of biological diversity, natural resource management, or environmental protection. Sometimes called “biological pollution,” invasive plants establish and persist without cultivati ...
... Invasive plants challenge the goals, resources, and morale of the people whose passion or livelihood is the conservation of biological diversity, natural resource management, or environmental protection. Sometimes called “biological pollution,” invasive plants establish and persist without cultivati ...
Wisconsin Nursery and Landscape Association`s 2015 PLANT OF
... Musclewood resembles the muscles of a flexed arm, hence the name. It’s a slow grower and may live up to 100 years, displaying shiny bluish-green leaves that turn a clear yellow or a brilliant scarletorange in the fall. This Wisconsin native is a small and handsome tree with a papery pendulous fruit ...
... Musclewood resembles the muscles of a flexed arm, hence the name. It’s a slow grower and may live up to 100 years, displaying shiny bluish-green leaves that turn a clear yellow or a brilliant scarletorange in the fall. This Wisconsin native is a small and handsome tree with a papery pendulous fruit ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT M.Sc. PLANT SCIENCE
... 2. Classification of Algae: Comparison of systems of classification of F.E. Fritsch and van den Hoek et al. (1995) system. Modern trends in algal classification, DNA barcoding in algae. 3. Reproduction: different types of reproduction, life history patterns, parallelism in evolution, origin of highe ...
... 2. Classification of Algae: Comparison of systems of classification of F.E. Fritsch and van den Hoek et al. (1995) system. Modern trends in algal classification, DNA barcoding in algae. 3. Reproduction: different types of reproduction, life history patterns, parallelism in evolution, origin of highe ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.