Easy Gardening - Aggie Horticulture
... Rotating crops is very important in disease control. To prevent the buildup of diseases, do not plant melons in the same place more than once every 3 or 4 years. If spots do appear on the leaves and no insects are present, a fungicide may be needed. Ask your county Extension agent about what to use. ...
... Rotating crops is very important in disease control. To prevent the buildup of diseases, do not plant melons in the same place more than once every 3 or 4 years. If spots do appear on the leaves and no insects are present, a fungicide may be needed. Ask your county Extension agent about what to use. ...
Weapon (thorn) automimicry and mimicry of aposematic colorful
... being spiny. A continuous blanket of spiny shrubs and thistles covers large tracts of the land, and other parts are just rich with dozens of such plant species that dominate the vegetation. This dominance clearly indicates the adaptive value of being spiny when grazing pressure is high. It does not ...
... being spiny. A continuous blanket of spiny shrubs and thistles covers large tracts of the land, and other parts are just rich with dozens of such plant species that dominate the vegetation. This dominance clearly indicates the adaptive value of being spiny when grazing pressure is high. It does not ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... living genus of the phylum Arthrophyta. This species forms two kinds of erect stems; one is green and photosynthetic, and the other, which terminates in a spore-producing “cone,” is mostly light brown. ...
... living genus of the phylum Arthrophyta. This species forms two kinds of erect stems; one is green and photosynthetic, and the other, which terminates in a spore-producing “cone,” is mostly light brown. ...
The plant world, life needs `em
... Terrestrial habitats have selected for many adaptations: to hold the body erect, to retain moisture, and to survive and reproduce without being immersed in water. Amazing. These include: Leaves to capture solar energy; Roots to anchor and absorb water and nutrients; Cuticle to minimize water loss; S ...
... Terrestrial habitats have selected for many adaptations: to hold the body erect, to retain moisture, and to survive and reproduce without being immersed in water. Amazing. These include: Leaves to capture solar energy; Roots to anchor and absorb water and nutrients; Cuticle to minimize water loss; S ...
Pennsylvania Field Guide
... Reproduction Primarily through bulblets and tubers Bulblets grow along the leaf stalks Small,cream colored bulblets are easily dislodged from plant by foot traffic and flooding Tubers can be scattered by disturbance Plant also reproduces by seed ...
... Reproduction Primarily through bulblets and tubers Bulblets grow along the leaf stalks Small,cream colored bulblets are easily dislodged from plant by foot traffic and flooding Tubers can be scattered by disturbance Plant also reproduces by seed ...
Word Document - MCHS Science
... crowds itself. To divide mature clumps of perennials, select only vigorous side shoots from the outer part of the clump. Discard the center of the clump. Divide the plant into clumps of three to five shoots each. Be careful not to over-divide; too small a clump will not give much color the first yea ...
... crowds itself. To divide mature clumps of perennials, select only vigorous side shoots from the outer part of the clump. Discard the center of the clump. Divide the plant into clumps of three to five shoots each. Be careful not to over-divide; too small a clump will not give much color the first yea ...
12 Angiosperm Reproduction
... Pollen tube enters through synergid cell, which subsequently dies. Sandaklie-Nikolova et al, 2007. Synergid Cell Death in Arabidopsis Is Triggered following Direct Interaction with the Pollen Tube. Plant Phys 144: 1753. ...
... Pollen tube enters through synergid cell, which subsequently dies. Sandaklie-Nikolova et al, 2007. Synergid Cell Death in Arabidopsis Is Triggered following Direct Interaction with the Pollen Tube. Plant Phys 144: 1753. ...
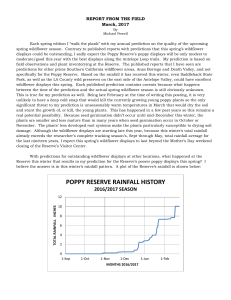
Research March 2017
... starting to bloom, we are seeing very large amount of this species as well. Several seasons ago, there were areas so dense with slender keel fruit plants that they created patches of generalized color similar to poppies and goldfields; the slopes were solid bright yellow. Based on limited observatio ...
... starting to bloom, we are seeing very large amount of this species as well. Several seasons ago, there were areas so dense with slender keel fruit plants that they created patches of generalized color similar to poppies and goldfields; the slopes were solid bright yellow. Based on limited observatio ...
tips to bio-botany teachers
... characteristics and differences from other disciplines of science such as cytology, genetics, Bio chemistry, phytogeography, numerical taxonomy, molecular biology are taken into consideration. 5. What are the three classes of phanerogams? (1) Dicotyledonae (2) Gymnospermae (3) Monocotyledonae 6. Def ...
... characteristics and differences from other disciplines of science such as cytology, genetics, Bio chemistry, phytogeography, numerical taxonomy, molecular biology are taken into consideration. 5. What are the three classes of phanerogams? (1) Dicotyledonae (2) Gymnospermae (3) Monocotyledonae 6. Def ...
MODEL DESCRIPTION Overall Model Structure SAVANNA is a
... grid-cell area covered by each facet, and summing the products over all facets. The area of land within each grid-cell that is covered by trees or shrubs varies in response to changes in tree and shrub numbers and sizes. As a consequence, direct competitive or facilitative interactions among establi ...
... grid-cell area covered by each facet, and summing the products over all facets. The area of land within each grid-cell that is covered by trees or shrubs varies in response to changes in tree and shrub numbers and sizes. As a consequence, direct competitive or facilitative interactions among establi ...
Final Quick Key.qxd
... If no, are there generally four leaves or more per whorl, and are the leaves finely but conspicuously toothed? (Can you see the serrations ...
... If no, are there generally four leaves or more per whorl, and are the leaves finely but conspicuously toothed? (Can you see the serrations ...
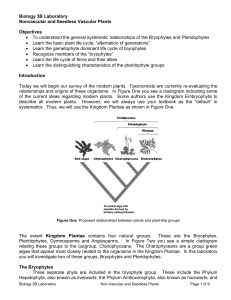
Biology 3B Laboratory Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants
... There are two phyla of non-flowering vascular plants. These include the Pterophyta, or true ferns; and the Lycophyta, or club mosses. In these plants a vascular system connects the leaves, stems and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within ...
... There are two phyla of non-flowering vascular plants. These include the Pterophyta, or true ferns; and the Lycophyta, or club mosses. In these plants a vascular system connects the leaves, stems and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within ...
Plant Problems
... plants that decline or die within first year of being planted • The wrong plant for the site or climate! ...
... plants that decline or die within first year of being planted • The wrong plant for the site or climate! ...
22. Supplementation of the nationally vulnerable
... annually from an underground tuber. It produces a ground-hugging, stemencircling, crowded basal rosette of four ...
... annually from an underground tuber. It produces a ground-hugging, stemencircling, crowded basal rosette of four ...
Care of Flowering Gift Plants In The Home - Extension
... until early spring. Plant the seeds and grow as if you were starting annual flowers or vegetables. Eventually, transplant the seedlings into four- or five-inch pots. Use a low nitrogen fertilizer and fertilize sparingly. Place the pots in a sunny location, but make sure they do not dry out. An occas ...
... until early spring. Plant the seeds and grow as if you were starting annual flowers or vegetables. Eventually, transplant the seedlings into four- or five-inch pots. Use a low nitrogen fertilizer and fertilize sparingly. Place the pots in a sunny location, but make sure they do not dry out. An occas ...
GRADE 6 - Spartanburg School District 2
... grades. In 4th grade (4-2.1), students classified organisms as flowering or nonflowering plants. Students will not revisit this concept in high school, as the focus will be on the cellular level of organisms. It is essential for students to know that organisms in the Plant Kingdom are classified int ...
... grades. In 4th grade (4-2.1), students classified organisms as flowering or nonflowering plants. Students will not revisit this concept in high school, as the focus will be on the cellular level of organisms. It is essential for students to know that organisms in the Plant Kingdom are classified int ...
plant structure and function
... – Both have thick secondary cell walls – Both are dead at maturity – Chains of tracheids and vessel elements form tubes that make up the vascular tissue called xylem ...
... – Both have thick secondary cell walls – Both are dead at maturity – Chains of tracheids and vessel elements form tubes that make up the vascular tissue called xylem ...
To dwellers in a wood, almost every species of tree has its voice as
... if those species are correctly identified in the first place. However, if your team has limited botanical training or experience, species identification can be extremely challenging. Another approach is to send information about an observed tree to a botanist for later identification. This brief pro ...
... if those species are correctly identified in the first place. However, if your team has limited botanical training or experience, species identification can be extremely challenging. Another approach is to send information about an observed tree to a botanist for later identification. This brief pro ...
Planting Marigold Seeds - National Agriculture in the Classroom
... This lesson will refer to the March pages in Lily’s Garden. Ask the students to explain what is happening in the illustrations. Using the lesson plan provided, the reader will guide class participants through a marigold seed planting activity. Students will discuss what a seed needs to grow: sun, so ...
... This lesson will refer to the March pages in Lily’s Garden. Ask the students to explain what is happening in the illustrations. Using the lesson plan provided, the reader will guide class participants through a marigold seed planting activity. Students will discuss what a seed needs to grow: sun, so ...
roots, stems, and leaves
... – No secondary cell wall – Alive at maturity but lack most organelles – Companion cells – Contain organelles – Control operations of sieve tube members ...
... – No secondary cell wall – Alive at maturity but lack most organelles – Companion cells – Contain organelles – Control operations of sieve tube members ...
File
... Experiments have shown that the important factor determining flowering is the length of night rather than the length of day. Therefore it may help students to remember SDP have a critical long night. That the length of night has to exceed a particular length before there will be flowering. LDP have ...
... Experiments have shown that the important factor determining flowering is the length of night rather than the length of day. Therefore it may help students to remember SDP have a critical long night. That the length of night has to exceed a particular length before there will be flowering. LDP have ...
Course Specifications
... endosperm development, life cycle phase changes, secondary growth, trichome development, miRNA mediated control on development, hormonal control on development, leaf and shoot development, root development. ...
... endosperm development, life cycle phase changes, secondary growth, trichome development, miRNA mediated control on development, hormonal control on development, leaf and shoot development, root development. ...
Globemaster Ornamental Onion
... Globemaster Ornamental Onion will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity extending to 3 feet tall with the flowers, with a spread of 12 inches. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 5 years. As this plant tends to go dormant in summer, i ...
... Globemaster Ornamental Onion will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity extending to 3 feet tall with the flowers, with a spread of 12 inches. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 5 years. As this plant tends to go dormant in summer, i ...
Serrated Tussock - Victorian Serrated Tussock Working Party
... Dense infestations of this weed can pose a serious fire hazard with a recorded burn intensity of up to seven times greater than native grasslands. Seed heads create additional hazards where they build up against housing, sheds, roadsides and fence-lines, particularly in the rural and urban areas of ...
... Dense infestations of this weed can pose a serious fire hazard with a recorded burn intensity of up to seven times greater than native grasslands. Seed heads create additional hazards where they build up against housing, sheds, roadsides and fence-lines, particularly in the rural and urban areas of ...
Daffodil Biology Lab Text - American Daffodil Society
... with blade down on the paper plate and fingers out of the way b. Stem—use scissors to cut through the flower stem in various directions: across, down, diagonal, and compare with each other. What do you see? (channels or openings in the stem, water) c. Line up the stem slices on a paper plate. If not ...
... with blade down on the paper plate and fingers out of the way b. Stem—use scissors to cut through the flower stem in various directions: across, down, diagonal, and compare with each other. What do you see? (channels or openings in the stem, water) c. Line up the stem slices on a paper plate. If not ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.