CHAPTER 15 THE CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS
... sensitive to motion. b. The parvocellular (parvo = small) pathway originats in small ganglion cells with small receptive fields. Cells in the parvo pathway are sensitive to color. They are also sensitive to fine ...
... sensitive to motion. b. The parvocellular (parvo = small) pathway originats in small ganglion cells with small receptive fields. Cells in the parvo pathway are sensitive to color. They are also sensitive to fine ...
Preview Sample 2
... respectively located in the frontal and parietal lobes are organized in a medial to lateral fashion by ascending dermatome from the toes to the head. In addition to carrying messages to and from the brain, the spinal cord provides a variety of protective and motor reflexes. The withdrawal reflex is ...
... respectively located in the frontal and parietal lobes are organized in a medial to lateral fashion by ascending dermatome from the toes to the head. In addition to carrying messages to and from the brain, the spinal cord provides a variety of protective and motor reflexes. The withdrawal reflex is ...
Graduate School Systems Neuroscience, MEDS 5371 2011 BASAL
... Subthalamic Nucleus: is a lens-shaped nucleus, between diencephalon and mesencephalon. When lesioned the patient experience uncontrolled whole body movement- hemiballismus. Subthalamic nucleus sends excitatory impulses to Substantia Nigra and Internal Globus Pallidus, both of which are inhibitory t ...
... Subthalamic Nucleus: is a lens-shaped nucleus, between diencephalon and mesencephalon. When lesioned the patient experience uncontrolled whole body movement- hemiballismus. Subthalamic nucleus sends excitatory impulses to Substantia Nigra and Internal Globus Pallidus, both of which are inhibitory t ...
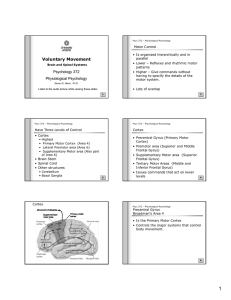
Role of Basal Ganglia in the Regulation of Motor Activities by the
... The onset of voluntary motor activity takes place under the influence of cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia is capable of controlling these motor activities due to the presence of neuronal circuits between the basal ganglia and the motor cortex and supplementary motor area. This neuronal circuit inc ...
... The onset of voluntary motor activity takes place under the influence of cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia is capable of controlling these motor activities due to the presence of neuronal circuits between the basal ganglia and the motor cortex and supplementary motor area. This neuronal circuit inc ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neurons that project to a given muscle <––– B. all of the motor neurons within a single segment of spinal cord C. all of the motor neurons that project to a given limb D. a single motor neuron and all of the muscles it inne ...
... 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neurons that project to a given muscle <––– B. all of the motor neurons within a single segment of spinal cord C. all of the motor neurons that project to a given limb D. a single motor neuron and all of the muscles it inne ...
Cortical inputs to the CA1 field of the monkey hippocampus originate
... transition between areas 36 or TF and area TE appears to have characteristics intermediate between them and we have labeled this area (36 or TF)/TE in Figs. 1 and 2. The injection in experiment M-7-89 was confined to CA 1 of the caudal hippocampus and was focused in stratum lacunosum-moleculare (Fig ...
... transition between areas 36 or TF and area TE appears to have characteristics intermediate between them and we have labeled this area (36 or TF)/TE in Figs. 1 and 2. The injection in experiment M-7-89 was confined to CA 1 of the caudal hippocampus and was focused in stratum lacunosum-moleculare (Fig ...
초록리스트
... ¹ Department of Physiology and Neuroscience Research Institute, Korea University, College of Medicine Seoul 136-705, Republic of Korea ²Center for Neural Science, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 136-791, Republic of Korea. The master circadian clock in mammals is located in the supr ...
... ¹ Department of Physiology and Neuroscience Research Institute, Korea University, College of Medicine Seoul 136-705, Republic of Korea ²Center for Neural Science, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 136-791, Republic of Korea. The master circadian clock in mammals is located in the supr ...
Richard G. Schuster, DO
... Lower Cross Syndromes… …are common patterns of abnormal motor control. They can be easily identified, relatively quickly assessed, and treated. This will be the focus of our following laboratory section. ...
... Lower Cross Syndromes… …are common patterns of abnormal motor control. They can be easily identified, relatively quickly assessed, and treated. This will be the focus of our following laboratory section. ...
The Synergists: An Exploration of Choreography, Media, and Science
... you can take to push yourself. In developing this honors research project, I wanted to challenge myself to create a work that incorporated a multimedia element in addition to the choreography. I have always been interested in technology and how it can be incorporated in creating a dance work. I ques ...
... you can take to push yourself. In developing this honors research project, I wanted to challenge myself to create a work that incorporated a multimedia element in addition to the choreography. I have always been interested in technology and how it can be incorporated in creating a dance work. I ques ...
Slide 1
... 1. Name the major regions of the adult brain. 2. Name and locate the ventricles of the brain. 3. List the major lobes, fissures, and functional areas of the cerebral cortex. 4. Describe the location of the diencephalon, and name its subdivisions and functions. 5. Identify the three major regions of ...
... 1. Name the major regions of the adult brain. 2. Name and locate the ventricles of the brain. 3. List the major lobes, fissures, and functional areas of the cerebral cortex. 4. Describe the location of the diencephalon, and name its subdivisions and functions. 5. Identify the three major regions of ...
Lecture 9 - Websupport1
... muscle position) to cerebellum. • Cardiovascular and respiratory rhythmicity centers • Other nuclei in the medulla control reflexes such as vomiting, coughing, sneezing, blood pressure. • Reticular formation begins in the medulla oblongata and extends into more superior portions of the brainstem ...
... muscle position) to cerebellum. • Cardiovascular and respiratory rhythmicity centers • Other nuclei in the medulla control reflexes such as vomiting, coughing, sneezing, blood pressure. • Reticular formation begins in the medulla oblongata and extends into more superior portions of the brainstem ...
Ne_plas_cause
... Signs and symptoms of disorders • Not everything can be seen on MRI or other imaging techniques • Not everything has positive laboratory tests ...
... Signs and symptoms of disorders • Not everything can be seen on MRI or other imaging techniques • Not everything has positive laboratory tests ...
the central nervous system
... limitless amounts of information for very long periods • Limitless capacity ...
... limitless amounts of information for very long periods • Limitless capacity ...
Understanding Cancer-related Cognitive Impairment
... – The combined treatment of tamoxifen and chemotherapy leads to greater difficulties than chemotherapy alone ...
... – The combined treatment of tamoxifen and chemotherapy leads to greater difficulties than chemotherapy alone ...
Stereological estimation of dendritic coverage in the capybara SCG
... The functional importance of the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) including its complex arborisation in mammals is defined by the fact that this autonomic ganglion supplies sympathetic nerve fibres to the large cerebral vessels and iris and hence SCG is implicated in the neural control of cerebral b ...
... The functional importance of the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) including its complex arborisation in mammals is defined by the fact that this autonomic ganglion supplies sympathetic nerve fibres to the large cerebral vessels and iris and hence SCG is implicated in the neural control of cerebral b ...
REFLEX ARC A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a
... A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of ...
... A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of ...
reflex
... A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of ...
... A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of ...
physiological role of neuropeptide y in sympathetic neurotransmission
... release of NE and this was attenuated by theY2 antagonist BIIE0246. The Y2 agonists all had their greatest inhibitory effect at low frequencies of nerve stimulation and the inhibitory effect was lost at high frequencies of nerve stimulation. In contrast the Y2 antagonist BIIE0246 enhanced the nerve ...
... release of NE and this was attenuated by theY2 antagonist BIIE0246. The Y2 agonists all had their greatest inhibitory effect at low frequencies of nerve stimulation and the inhibitory effect was lost at high frequencies of nerve stimulation. In contrast the Y2 antagonist BIIE0246 enhanced the nerve ...
Chapter 2 ciccarelli
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
The Science of Psychology
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
Ch. 2 ppt
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
Pursuing commitments
... movement reaches its target, does the tracking that ensues immediately thereafter adopt the intermediate velocity, or has the pursuit system been forced to commit to one velocity? They observed the latter: stimulating the FEF caused not only an eye movement but also a commitment to tracking the targ ...
... movement reaches its target, does the tracking that ensues immediately thereafter adopt the intermediate velocity, or has the pursuit system been forced to commit to one velocity? They observed the latter: stimulating the FEF caused not only an eye movement but also a commitment to tracking the targ ...
Evidence for a modulatory effect of sulbutiamine on
... induced by sulbutiamine. Thus, the changes in density of kainate receptor in the cortex lead to suggest that sulbutiamine and/or its metabolites may modulate the cortical glutamatergic transmission. In fact, the rapid decrease observed immediately following a single injection suggests a direct effec ...
... induced by sulbutiamine. Thus, the changes in density of kainate receptor in the cortex lead to suggest that sulbutiamine and/or its metabolites may modulate the cortical glutamatergic transmission. In fact, the rapid decrease observed immediately following a single injection suggests a direct effec ...