The differing effects of occipital and trunk somites on neural
... dorsal root ganglia are never fully formed. One or two ganglia do develop transiently, in the region of the caudal hypoglossal rootlets and the first cervical spinal nerve. These are known as 'Froriep's' ganglia, so named by Wilhelm His (1888) after their discoverer (Froriep, 1882). The two to four ...
... dorsal root ganglia are never fully formed. One or two ganglia do develop transiently, in the region of the caudal hypoglossal rootlets and the first cervical spinal nerve. These are known as 'Froriep's' ganglia, so named by Wilhelm His (1888) after their discoverer (Froriep, 1882). The two to four ...
Module 4 SG - HallquistCPHS.com
... __ Outline the sequence of reactions that occur when a neural impulse is generated and transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
... __ Outline the sequence of reactions that occur when a neural impulse is generated and transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
PAPER Glucosensing neurons do more than just sense glucose
... neuron that uses glucose as a signaling molecule to alter cell function and neuronal activity. This distinguishes glucosensing neurons from the majority of neurons which utilize glucose simply as a metabolic substrate to fuel increases in neuronal activity and metabolic demands. As it turns out, glu ...
... neuron that uses glucose as a signaling molecule to alter cell function and neuronal activity. This distinguishes glucosensing neurons from the majority of neurons which utilize glucose simply as a metabolic substrate to fuel increases in neuronal activity and metabolic demands. As it turns out, glu ...
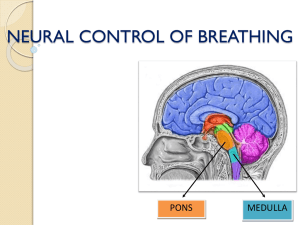
Neural Control of Breathing (By Mohit Chhabra)
... The VRG is responsible for motor control of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during exercise. They are especially important in providing the powerful expiratory signals to the abdominal muscles ...
... The VRG is responsible for motor control of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during exercise. They are especially important in providing the powerful expiratory signals to the abdominal muscles ...
Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... and axon • No microtubules in terminal • Presence of synaptic vesicles • Abundance of membrane proteins • Large number of mitochondria ...
... and axon • No microtubules in terminal • Presence of synaptic vesicles • Abundance of membrane proteins • Large number of mitochondria ...
Bridging Rate Coding and Temporal Spike Coding
... Firing rates of spikes in the brain are thought to represent information in external stimuli. However, calculation in the brain often seems to complete in a shorter time scale than the time required for temporal averaging of spike signals necessary for obtaining firing rates. Actually, precisely tim ...
... Firing rates of spikes in the brain are thought to represent information in external stimuli. However, calculation in the brain often seems to complete in a shorter time scale than the time required for temporal averaging of spike signals necessary for obtaining firing rates. Actually, precisely tim ...
Neurons in Action: Passive Axon Tutorial
... Now let’s test this prediction ie. What would be the effect on the length constant of increasing the axon diameter by four-fold? In the Passive Axon Parameters panel, increase the axon diameter four-fold. Restore the leakage conductance to the default value of 0.0003 mho/cm2. An axon with a larger d ...
... Now let’s test this prediction ie. What would be the effect on the length constant of increasing the axon diameter by four-fold? In the Passive Axon Parameters panel, increase the axon diameter four-fold. Restore the leakage conductance to the default value of 0.0003 mho/cm2. An axon with a larger d ...
A Cellular Structure for Online Routing of Digital Spiking Neuron
... Figure 4 shows the internal architecture of the glial cells. Each glial cell consists of a synapse unit, ten MUXs, and eight DFFs for routing axons and dendrites. On each side of a glial cell, there is one axonal output coming from a pipeline DFF connected to a MUX. Each axonal MUX can switch to any ...
... Figure 4 shows the internal architecture of the glial cells. Each glial cell consists of a synapse unit, ten MUXs, and eight DFFs for routing axons and dendrites. On each side of a glial cell, there is one axonal output coming from a pipeline DFF connected to a MUX. Each axonal MUX can switch to any ...
How do dendrites take their shape?
... tantly, that endogenous neurotrophins are necessary for dendritic growth. The signal transduction mechanisms are likely to be complex, as different splice variants of a given trk receptor (for example, trk B) are expressed differentially during development26, and can cell-autonomously mediate distin ...
... tantly, that endogenous neurotrophins are necessary for dendritic growth. The signal transduction mechanisms are likely to be complex, as different splice variants of a given trk receptor (for example, trk B) are expressed differentially during development26, and can cell-autonomously mediate distin ...
The habenular nuclei - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... complex. The habenulae form part of the dorsal diencephalic conduction (DDC) system, a highly conserved pathway found in all vertebrates. In this review, we shall describe the neuroanatomy of the DDC, consider its physiology and behavioural involvement, and discuss examples of neural asymmetries wit ...
... complex. The habenulae form part of the dorsal diencephalic conduction (DDC) system, a highly conserved pathway found in all vertebrates. In this review, we shall describe the neuroanatomy of the DDC, consider its physiology and behavioural involvement, and discuss examples of neural asymmetries wit ...
NeuralNets
... Several Branched Rough Surface (dendritic spines) Have ribosomes No myelin insulation ...
... Several Branched Rough Surface (dendritic spines) Have ribosomes No myelin insulation ...
the spatial control of ganglionic neurite growth by the substrate
... material bound to the substrate diffuses off and exerts its effects at a distance. The neurite-guiding activity is found in partially purified fractions of conditioned medium which also contain a substrate-bound inducer of neurite outgrowth. It is possible that both activities may be due to the same ...
... material bound to the substrate diffuses off and exerts its effects at a distance. The neurite-guiding activity is found in partially purified fractions of conditioned medium which also contain a substrate-bound inducer of neurite outgrowth. It is possible that both activities may be due to the same ...
A forward genetic screen with a thalamocortical emx2
... Background: The dorsal thalamus acts as a gateway and modulator for information going to and from the cerebral cortex. This activity requires the formation of reciprocal topographic axon connections between thalamus and cortex. The axons grow along a complex multistep pathway, making sharp turns, cr ...
... Background: The dorsal thalamus acts as a gateway and modulator for information going to and from the cerebral cortex. This activity requires the formation of reciprocal topographic axon connections between thalamus and cortex. The axons grow along a complex multistep pathway, making sharp turns, cr ...
Nissl substance and cellular structures involved in the intraneuronal
... distribution within nerve cells is maintained. These questions are the parts of the general problem – intracellular organization and integration of synthetic and transport processes. Another significant problem is the study of the mechanisms of neuroglial interactions: which ultrastructural elements ...
... distribution within nerve cells is maintained. These questions are the parts of the general problem – intracellular organization and integration of synthetic and transport processes. Another significant problem is the study of the mechanisms of neuroglial interactions: which ultrastructural elements ...
Long Term Potentiation
... formed, they have no effect on the phenomenon. On the other hand, research indicates that another type of glutamate receptor, AMPA, does play an important role in sustained long term potentiation. When a neuron in the dentate gyrus is examined, after long term potentiation, there is a significant ch ...
... formed, they have no effect on the phenomenon. On the other hand, research indicates that another type of glutamate receptor, AMPA, does play an important role in sustained long term potentiation. When a neuron in the dentate gyrus is examined, after long term potentiation, there is a significant ch ...
Somatosensory system
... The first neuron always has its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal nerve (if sensation is in head or neck, it will be the trigeminal nerve ganglia or the ganglia of other sensory cranial nerves). The second neuron has its cell body either in the spinal cord or in the brainstem. This ...
... The first neuron always has its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal nerve (if sensation is in head or neck, it will be the trigeminal nerve ganglia or the ganglia of other sensory cranial nerves). The second neuron has its cell body either in the spinal cord or in the brainstem. This ...
17_QuizShowQuestions
... a. Some of their cell bodies form autonomic nuclei in spinal segments S2-S4. b. In the brain, the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata contain preganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies that form autonomic nuclei associated with N III, VIII, IX, and X. c. The preganglionic fibers, from the brain ...
... a. Some of their cell bodies form autonomic nuclei in spinal segments S2-S4. b. In the brain, the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata contain preganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies that form autonomic nuclei associated with N III, VIII, IX, and X. c. The preganglionic fibers, from the brain ...
binding, internalization, and retrograde transport of `251
... the actions of NGF in target cells. It may be that plasma using modified 35-mm culture dishes (Hawrot and Patmembrane-localized binding of NGF mediates a set of terson, 1979; Hawrot, 1980). The growth of non-neuronal rapid responses, such as the efflux of Na+ ions (Skaper cells was prevented by trea ...
... the actions of NGF in target cells. It may be that plasma using modified 35-mm culture dishes (Hawrot and Patmembrane-localized binding of NGF mediates a set of terson, 1979; Hawrot, 1980). The growth of non-neuronal rapid responses, such as the efflux of Na+ ions (Skaper cells was prevented by trea ...
7. Nervous Tissue, Overview of the Nervous System.
... The functionality of nervous tissue rests largely on its ability of its cells (neurons) to generate, transmit and process information. “Information” gathered from body or its surroundings is described as sensations. Information which directs body tissues into activity is described as being ‘motor’ i ...
... The functionality of nervous tissue rests largely on its ability of its cells (neurons) to generate, transmit and process information. “Information” gathered from body or its surroundings is described as sensations. Information which directs body tissues into activity is described as being ‘motor’ i ...
Cerebellum Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the
... 2. Spinocerebellum has two components; I.The vermis which projects to the fastigial nucleus, II. the intermediate zone which projects to the interpositus. It controls posture, locomotion, gaze. Compares the commands emanating from motor cortex with the actual velocity and position of the movin ...
... 2. Spinocerebellum has two components; I.The vermis which projects to the fastigial nucleus, II. the intermediate zone which projects to the interpositus. It controls posture, locomotion, gaze. Compares the commands emanating from motor cortex with the actual velocity and position of the movin ...
Axonal morphometry of hippocampal pyramidal neurons semi
... 1 inch margins. The fields of view within these boxes represent unitary regions of interest (Fig. 1b) whose relative spatial position is labeled on the sheet with a univocal alphanumeric designation. For example, the adjacent boxes on the top, right, bottom, and left of the box in sheet M3 are found ...
... 1 inch margins. The fields of view within these boxes represent unitary regions of interest (Fig. 1b) whose relative spatial position is labeled on the sheet with a univocal alphanumeric designation. For example, the adjacent boxes on the top, right, bottom, and left of the box in sheet M3 are found ...
Huber et al. (2008), Sparse optical microstimulation in barrel cortex
... and the probability of spiking of ChR2–GFP-expressing neurons. During cell-attached recordings we stimulated with 1 ms light pulses while varying the photostimulus. With decreasing light intensity, neurons switched abruptly from firing action potentials with high probability to firing no action pote ...
... and the probability of spiking of ChR2–GFP-expressing neurons. During cell-attached recordings we stimulated with 1 ms light pulses while varying the photostimulus. With decreasing light intensity, neurons switched abruptly from firing action potentials with high probability to firing no action pote ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
7. MODELING THE SOMATOTOPIC MAP 7.1 The Somatotopic Map
... the somatosensory cortex. This projection connects neurons of the cortex with touch receptors in the skin surface such that neighborhood relations are preserved. Adjacent touch receptors in the skin surface are thus connected to adjacent neurons (Kaas et al. 1979). However, the projection is strongl ...
... the somatosensory cortex. This projection connects neurons of the cortex with touch receptors in the skin surface such that neighborhood relations are preserved. Adjacent touch receptors in the skin surface are thus connected to adjacent neurons (Kaas et al. 1979). However, the projection is strongl ...
Predicting Spiking Activities in DLS Neurons with Linear
... Figure 3: The Top Principal Components of the Linear Coefficients The current study identified subpopulations of neurons that primarily correlate with different feature modalities. The proportion of neurons that are identified to be correlated with head position history is higher (32 out of 47) when ...
... Figure 3: The Top Principal Components of the Linear Coefficients The current study identified subpopulations of neurons that primarily correlate with different feature modalities. The proportion of neurons that are identified to be correlated with head position history is higher (32 out of 47) when ...