Viewpoint Synaptic Connectivity and Neuronal Morphology: Two
... A shortcoming of the axons-only network is that each axon has to make its way to every cell body. Since all the signals received by a neuron are merged in the cell body, the same functionality can be achieved by a single process reaching out in the direction of axons and meeting them halfway (Chklov ...
... A shortcoming of the axons-only network is that each axon has to make its way to every cell body. Since all the signals received by a neuron are merged in the cell body, the same functionality can be achieved by a single process reaching out in the direction of axons and meeting them halfway (Chklov ...
Sensory5
... Note: greater representation for body parts with richer sensory innervation, such as the fingers. *the representation is not static, however. Rather, it is based on use. (if a body’s sensory paths are damaged from a particular area, its cortical representation atrophies (shrinks)). 3. Modality-speci ...
... Note: greater representation for body parts with richer sensory innervation, such as the fingers. *the representation is not static, however. Rather, it is based on use. (if a body’s sensory paths are damaged from a particular area, its cortical representation atrophies (shrinks)). 3. Modality-speci ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF BREATHING Section 4, Part A
... b. rostral neurons in NA c. rostral neurons in NRA d. spatial separation occurs 3. separation of descending tracts from medullary resp. groups and tracts from cortex a. spinal lesions b. Ondine's curse II. Pontine Respiratory Centers A. Pons is not necessary for rhythmic breathing 1. removal of uppe ...
... b. rostral neurons in NA c. rostral neurons in NRA d. spatial separation occurs 3. separation of descending tracts from medullary resp. groups and tracts from cortex a. spinal lesions b. Ondine's curse II. Pontine Respiratory Centers A. Pons is not necessary for rhythmic breathing 1. removal of uppe ...
Nervous System
... from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor (Efferent) Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
... from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor (Efferent) Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
Slide ()
... B. The neural plate folds dorsally at its midline to form the neural fold. Floor plate cells (blue) differentiate at the ventral midline of the neural tube. C. The neural tube forms by fusion of the dorsal tips of the neural folds. Roof plate cells form at the dorsal midline of the neural tube. Neur ...
... B. The neural plate folds dorsally at its midline to form the neural fold. Floor plate cells (blue) differentiate at the ventral midline of the neural tube. C. The neural tube forms by fusion of the dorsal tips of the neural folds. Roof plate cells form at the dorsal midline of the neural tube. Neur ...
Biology 201-Worksheet on Autonomic Nervous System
... 8. Answer the listed questions regarding gustation. a. What is gustation? ___________________________________________________________ b. What kind of receptors are these? _______________________________________________ c. For molecules to be detected they must be: ___________________________________ ...
... 8. Answer the listed questions regarding gustation. a. What is gustation? ___________________________________________________________ b. What kind of receptors are these? _______________________________________________ c. For molecules to be detected they must be: ___________________________________ ...
neuron
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
... through the cell membrane • If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a mini ...
Chapter Outline
... a. Motor (efferent) neurons have many dendrites and a single axon; they conduct impulses from the CNS to muscles or glands. b. Sensory (afferent) neurons are unipolar; they conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. i. The process that extends from the cell body divides into two processes, ...
... a. Motor (efferent) neurons have many dendrites and a single axon; they conduct impulses from the CNS to muscles or glands. b. Sensory (afferent) neurons are unipolar; they conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. i. The process that extends from the cell body divides into two processes, ...
Slide ()
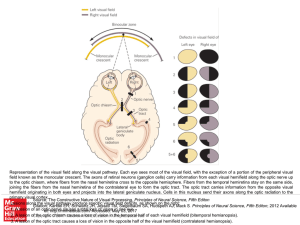
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Slide ()
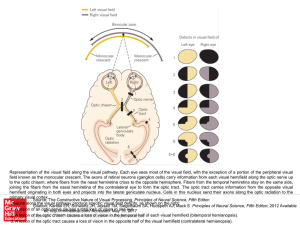
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Neurology - Porterville College
... Receive evaluate respond • Stimulation of Movement • Maintains Homeostasis – Along with the what system? • Endocrine ...
... Receive evaluate respond • Stimulation of Movement • Maintains Homeostasis – Along with the what system? • Endocrine ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7, Part 2 Notes: The Nervous
... you get hit just below your knee cap. (Note: Doctors typically check this reflex as part of a normal physical with a small mallet.) -First, the mallet hits your leg, triggering a sensory neuron. -The sensory neuron carries the signal to the dorsal root of the spinal cord (dorsal meaning facing the b ...
... you get hit just below your knee cap. (Note: Doctors typically check this reflex as part of a normal physical with a small mallet.) -First, the mallet hits your leg, triggering a sensory neuron. -The sensory neuron carries the signal to the dorsal root of the spinal cord (dorsal meaning facing the b ...
Neuroscience 5a – Touch and Proprioception
... its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion. It then goes from the dorsal root ganglion, up the dorsal column (gracile and cuneate faciculus) of the spinal cord and synapses in the brainstem (specifically the gracile and cuneate nuclei in the medulla). The inputs from the face come from the trigeminal ...
... its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion. It then goes from the dorsal root ganglion, up the dorsal column (gracile and cuneate faciculus) of the spinal cord and synapses in the brainstem (specifically the gracile and cuneate nuclei in the medulla). The inputs from the face come from the trigeminal ...
Taste and Smell
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
Motor Areas - Motlow State Community College
... integrates sensory interpretations from all sensory association areas allowing formation of thoughts based on variety of sensory inputs ...
... integrates sensory interpretations from all sensory association areas allowing formation of thoughts based on variety of sensory inputs ...
Teacher Guide
... Note to teacher: Italicized commentary are notes for teachers. Red statements show sample correct student responses. Purpose: Determine the volume of helium gas in an irregularly-shaped Mylar balloon. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neur ...
... Note to teacher: Italicized commentary are notes for teachers. Red statements show sample correct student responses. Purpose: Determine the volume of helium gas in an irregularly-shaped Mylar balloon. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neur ...
Living scaffolds for neuroregeneration
... axons along the length of the glia [11]. Peripheral glial cells also direct pathfinding of axons in the transition zone between the PNS and CNS. Sepp et al. showed that during Drosophila development, peripheral glia formed funnel-shaped arrays that guided pioneering motor axons into the periphery. Th ...
... axons along the length of the glia [11]. Peripheral glial cells also direct pathfinding of axons in the transition zone between the PNS and CNS. Sepp et al. showed that during Drosophila development, peripheral glia formed funnel-shaped arrays that guided pioneering motor axons into the periphery. Th ...
Brain development
... • Undeveloped neuron needs to establish basic “polarity:” which end is which? • Involves specific proteins • Axons: Affords a sensitivity to chemical signals emitted by targets ...
... • Undeveloped neuron needs to establish basic “polarity:” which end is which? • Involves specific proteins • Axons: Affords a sensitivity to chemical signals emitted by targets ...
word - My eCoach
... rapidly beating heart are all possible responses to a stressful situation. These body responses are most likely a direct result of the interaction between the a. nervous and endocrine systems. b. nervous and circulatory systems. c. digestive and endocrine systems. d. digestive and circulatory system ...
... rapidly beating heart are all possible responses to a stressful situation. These body responses are most likely a direct result of the interaction between the a. nervous and endocrine systems. b. nervous and circulatory systems. c. digestive and endocrine systems. d. digestive and circulatory system ...
chapt10_holes_lecture_animation
... Identify the two major groups of nervous system organs. 10.2: General Functions of the Nervous System List the functions of sensory receptors. Describe how the nervous system responds to stimuli. 10.3: Description of Cells of the Nervous System Describe the three major parts of a neuron. D ...
... Identify the two major groups of nervous system organs. 10.2: General Functions of the Nervous System List the functions of sensory receptors. Describe how the nervous system responds to stimuli. 10.3: Description of Cells of the Nervous System Describe the three major parts of a neuron. D ...
Notes to Resp. 4
... pacemaker nuclei in the medulla (PN) of the brain stem (analogous to the pacemakers in the heart). This area is called the respiratory center and it communicates with the dorsal respiratory group (DRG) which in turns communicates with the phrenic nerves (see below). The autonomic character of this c ...
... pacemaker nuclei in the medulla (PN) of the brain stem (analogous to the pacemakers in the heart). This area is called the respiratory center and it communicates with the dorsal respiratory group (DRG) which in turns communicates with the phrenic nerves (see below). The autonomic character of this c ...
Inquiry into Life, Eleventh Edition
... – Composed of nerves (bundles of axons) and ganglia (swellings associated with nerves that contain cell bodies) – Cranial nerves- 12 pairs • Attached to the brain • Some are purely sensory, some motor, and some are mixed • Largely concerned with head, neck, and face with the exception of the vagus n ...
... – Composed of nerves (bundles of axons) and ganglia (swellings associated with nerves that contain cell bodies) – Cranial nerves- 12 pairs • Attached to the brain • Some are purely sensory, some motor, and some are mixed • Largely concerned with head, neck, and face with the exception of the vagus n ...
Parts of the Nervous System
... Stellate cells of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum Spiny stellate cells represent the other major excitatory input to cortical pyramidal cells Small multipolar cells with local dendritic and axonal arborizations use glutamate or aspartate as transmitter. (NB. multipolar, meaning they have more tha ...
... Stellate cells of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum Spiny stellate cells represent the other major excitatory input to cortical pyramidal cells Small multipolar cells with local dendritic and axonal arborizations use glutamate or aspartate as transmitter. (NB. multipolar, meaning they have more tha ...