Anti-inflammatory properties of amniotic membrane patch following
... replacement were completed. Gross intraoperative findings of the pericardial space included thick, gelatinous material on the anterior surface of the heart, and the pericardium and Gore-Tex membrane were fused to the thickened pericardium on the anterior surface of the heart. (Fig. 2a) Prior to clos ...
... replacement were completed. Gross intraoperative findings of the pericardial space included thick, gelatinous material on the anterior surface of the heart, and the pericardium and Gore-Tex membrane were fused to the thickened pericardium on the anterior surface of the heart. (Fig. 2a) Prior to clos ...
Slow Heartbeat - Heart Rhythm Society
... caused by activity, diet, medicines, and age are normal and common. Abnormally slow heart rates are usually those below 60 beats a minute and can be either harmless or life threatening. At certain times, though, such as during sleep, heart rate will be slow and still be normal. What counts as an abn ...
... caused by activity, diet, medicines, and age are normal and common. Abnormally slow heart rates are usually those below 60 beats a minute and can be either harmless or life threatening. At certain times, though, such as during sleep, heart rate will be slow and still be normal. What counts as an abn ...
High Arteriovenous (AV) Access Flow and Cardiac Complications
... arterial blood is shunted from the left-sided circulation to the right-sided circulation via the fistula. Patients may present with the usual signs of high-output heart failure including tachycardia, elevated pulse pressure, hyperkinetic precordium, and jugular venous distension. The nephrologist is ...
... arterial blood is shunted from the left-sided circulation to the right-sided circulation via the fistula. Patients may present with the usual signs of high-output heart failure including tachycardia, elevated pulse pressure, hyperkinetic precordium, and jugular venous distension. The nephrologist is ...
Behçet`s Disease and the Heart
... difficult to know how much of the problem is caused by the Behçet’s disease and how much is incidental. Problems with the heart may be caused by thrombosis (blockage due to clotting) of large blood vessels or by vasculitis (inflammation) of smaller blood vessels, such as the arteries providing the b ...
... difficult to know how much of the problem is caused by the Behçet’s disease and how much is incidental. Problems with the heart may be caused by thrombosis (blockage due to clotting) of large blood vessels or by vasculitis (inflammation) of smaller blood vessels, such as the arteries providing the b ...
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Facilitated by Extracorporeal
... The treatment of patients with cardiogenic shock is based mostly on extrapolated data from other patients with acute coronary syndromes and on expert consensus opinion, given the lack of randomized trials answering specific questions in these patients. The European Society of Cardiology guidelines f ...
... The treatment of patients with cardiogenic shock is based mostly on extrapolated data from other patients with acute coronary syndromes and on expert consensus opinion, given the lack of randomized trials answering specific questions in these patients. The European Society of Cardiology guidelines f ...
7-Days Holter
... non-permanent AF in China. After providing informed consent, patients will be randomly assigned to one of four groups(the valsartan group, the fluvastatin plus dihydropyridine CCBs group, the valsartan plus fluvastatin group, and the dihydropyridine CCBs group)by the School of Public Health of Tianj ...
... non-permanent AF in China. After providing informed consent, patients will be randomly assigned to one of four groups(the valsartan group, the fluvastatin plus dihydropyridine CCBs group, the valsartan plus fluvastatin group, and the dihydropyridine CCBs group)by the School of Public Health of Tianj ...
Isolated ventricular septal defect caused by
... appeared 4 months later. When the murmur is delayed, it may be that the ventricular septum is initially only contused; the contused myocardium then becomes necrotic, sloughs, and finally ruptures. The presence of shock also may account for the absence of a precordial murmur immediately. Abrasions or ...
... appeared 4 months later. When the murmur is delayed, it may be that the ventricular septum is initially only contused; the contused myocardium then becomes necrotic, sloughs, and finally ruptures. The presence of shock also may account for the absence of a precordial murmur immediately. Abrasions or ...
Slide 1
... PRI: Because of the unusual configuration of the P wave ( flutter wave ) and the proximity of the wave to the QRS complex, it is often impossible to determine a PRI in this arrhythmia . Therefore , the PRI is not measured in atrial flutter . ...
... PRI: Because of the unusual configuration of the P wave ( flutter wave ) and the proximity of the wave to the QRS complex, it is often impossible to determine a PRI in this arrhythmia . Therefore , the PRI is not measured in atrial flutter . ...
Bradycardia - MBBS Students Club
... sequence of atrial depolarizations at rates between 200 and 380 beats per minute. The ventricles rarely keep pace with the racing atria. Because the conducting tissue’s refractory period is longer than that of the atrial muscle, the AV node is unable to respond to every impulse that converges on it ...
... sequence of atrial depolarizations at rates between 200 and 380 beats per minute. The ventricles rarely keep pace with the racing atria. Because the conducting tissue’s refractory period is longer than that of the atrial muscle, the AV node is unable to respond to every impulse that converges on it ...
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
... achieved, the nature of induced chest pain, the maximum amount of ST-segment depression, changes in heart rate and blood pressure, and other parameters should be recorded as structured data. However, from an electronic health record perspective (the subject of this document), the data elements we ha ...
... achieved, the nature of induced chest pain, the maximum amount of ST-segment depression, changes in heart rate and blood pressure, and other parameters should be recorded as structured data. However, from an electronic health record perspective (the subject of this document), the data elements we ha ...
PDF - Circulation
... ment is 2- to 4-fold faster, the duration of force transients is shorter, and the ATPase activity is 2- to 3-fold higher for the ␣-MyHC (fast) than for the -MyHC (slow) isoform.6,7 Hence, to perform the same workload, ␣-MyHC uses more ATP than the -MyHC.8 Accordingly, the relative distribution of ...
... ment is 2- to 4-fold faster, the duration of force transients is shorter, and the ATPase activity is 2- to 3-fold higher for the ␣-MyHC (fast) than for the -MyHC (slow) isoform.6,7 Hence, to perform the same workload, ␣-MyHC uses more ATP than the -MyHC.8 Accordingly, the relative distribution of ...
Episodic Central Nervous System Ischemia of
... histological evaluation, 18 ' lfl these patients usually continue to have puzzling neurological and systemic symptoms. 10 - 14 ' 20-21 The patients described in the present report were admitted to the hospital on numerous occasions and, despite repeated examinations by many physicians, the basic nat ...
... histological evaluation, 18 ' lfl these patients usually continue to have puzzling neurological and systemic symptoms. 10 - 14 ' 20-21 The patients described in the present report were admitted to the hospital on numerous occasions and, despite repeated examinations by many physicians, the basic nat ...
HEART FAILURE - MEDICINE DEPARTMENT of MMC
... undergoing chronic optimal medical therapy, and have reasonable expectation of survival with a good functional status for more than 1 year. (Level of Evidence: A) 10. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy is recommended for primary prevention to reduce total mortality by a reduction in sudd ...
... undergoing chronic optimal medical therapy, and have reasonable expectation of survival with a good functional status for more than 1 year. (Level of Evidence: A) 10. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy is recommended for primary prevention to reduce total mortality by a reduction in sudd ...
Slide 1
... 1. superior & inferior vena cava empty deoxygenated blood into right atrium 2. through tricuspid (AV) valve into right ventricle 3. through pulmonary semilunar valve into pulmonary artery 4. to lungs 5. oxygenated blood returns to heart thru pulmonary veins 6. left atrium 7. through bicu ...
... 1. superior & inferior vena cava empty deoxygenated blood into right atrium 2. through tricuspid (AV) valve into right ventricle 3. through pulmonary semilunar valve into pulmonary artery 4. to lungs 5. oxygenated blood returns to heart thru pulmonary veins 6. left atrium 7. through bicu ...
Myocardial Performance Index or Tei Index
... affected by changes in loading in both the right and left ventricles. One significant problem affecting the reliability of the Tei index is the bidirectional course of the isovolumic relaxation time during the development of heart failure, because of the complex interaction between systolic and dias ...
... affected by changes in loading in both the right and left ventricles. One significant problem affecting the reliability of the Tei index is the bidirectional course of the isovolumic relaxation time during the development of heart failure, because of the complex interaction between systolic and dias ...
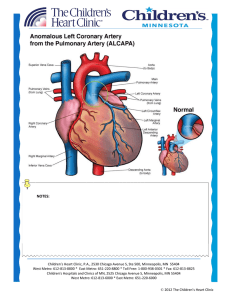
notes - Children`s Heart Clinic
... Echocardiogram: Aids in diagnoses and evaluation for additional cardiac anomalies. Medical Management/Treatment: 80-100% mortality with medical management alone. Surgery to create a two-coronary artery system: - Left coronary artery transfer: A “button” or flap around the opening of the left c ...
... Echocardiogram: Aids in diagnoses and evaluation for additional cardiac anomalies. Medical Management/Treatment: 80-100% mortality with medical management alone. Surgery to create a two-coronary artery system: - Left coronary artery transfer: A “button” or flap around the opening of the left c ...
ECG Findings in Active Patients
... (40-42). The mechanism is considered to be atrial fibrillation with rapid conduction down the accessory pathway resulting in ventricular fibrillation. Symptomatic WPW patients should have an electrophysiologic study to establish the potential for the bypass tract to conduct rapidly to the ventricle. ...
... (40-42). The mechanism is considered to be atrial fibrillation with rapid conduction down the accessory pathway resulting in ventricular fibrillation. Symptomatic WPW patients should have an electrophysiologic study to establish the potential for the bypass tract to conduct rapidly to the ventricle. ...
HFHP AIM Codes_2017_All Programs
... MRI Cardiac for morphology and function without contrast material(s), followed by contrast 75561 material(s) and further sequences; MRI Cardiac for morphology and function without contrast material(s), followed by contrast 75563 material(s) and further sequences; with stress imaging Cardiac magnetic ...
... MRI Cardiac for morphology and function without contrast material(s), followed by contrast 75561 material(s) and further sequences; MRI Cardiac for morphology and function without contrast material(s), followed by contrast 75563 material(s) and further sequences; with stress imaging Cardiac magnetic ...
A CARE STUDY OF A PATIENT WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
... • The two largest veins of the body, the superior and inferior vena cava, empty their contents in to the right atrium .This blood passes via the right atrio ventricular valve into the right ventricle, and from there it is pumped in to the pulmonary artery or trunk (the only artery in the body which ...
... • The two largest veins of the body, the superior and inferior vena cava, empty their contents in to the right atrium .This blood passes via the right atrio ventricular valve into the right ventricle, and from there it is pumped in to the pulmonary artery or trunk (the only artery in the body which ...
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY AND MANIFISTATIONS
... The semilunar valves: Allow for the blood to pass from the ventricles into the arteries during ventricular systole. During ventricular diastole, these valves prevent back flow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles (as these valves become closed during ventricular diastole). ...
... The semilunar valves: Allow for the blood to pass from the ventricles into the arteries during ventricular systole. During ventricular diastole, these valves prevent back flow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles (as these valves become closed during ventricular diastole). ...
Interventional Cardiology
... dysfunction, with an adverse impact on clinical outcome. Hence, it is important to recognize and effectively treat systemic HTN in patients with AS. Antihypertensive treatment should be carefully titrated to avoid hypotension, especially in patients with severe AS and in the presence of LV dysfuncti ...
... dysfunction, with an adverse impact on clinical outcome. Hence, it is important to recognize and effectively treat systemic HTN in patients with AS. Antihypertensive treatment should be carefully titrated to avoid hypotension, especially in patients with severe AS and in the presence of LV dysfuncti ...
Outcome of patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
... of cardiovascular diseases differ between men and women possibly due to the protective effect of oestrogen. In addition, the skewed distribution of risk factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption among males in Sri Lanka may have resulted in higher male preponderance among STEMI patients. More ...
... of cardiovascular diseases differ between men and women possibly due to the protective effect of oestrogen. In addition, the skewed distribution of risk factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption among males in Sri Lanka may have resulted in higher male preponderance among STEMI patients. More ...
Cardiac contractility modulation
.jpg?width=300)
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) is a treatment for patients with moderate to severe left ventricular systolic heart failure (NYHA class II–IV). The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances both the strength of ventricular contraction and the heart’s pumping capacity. The CCM mechanism is based on stimulation of the cardiac muscle by non-excitatory electrical signals (NES). CCM treatment is delivered by a pacemaker-like device that applies the NES, adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.In CCM therapy, electrical stimulation is applied to the cardiac muscle during the absolute refractory period. In this phase of the cardiac cycle, electrical signals cannot trigger new cardiac muscle contractions, hence this type of stimulation is known as a non-excitatory stimulation. However, the electrical CCM signals increase the influx of calcium ions into the cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). In contrast to other electrical stimulation treatments for heart failure, such as pacemaker therapy or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), CCM does not affect the cardiac rhythm directly. Rather, the aim is to enhance the heart’s natural contraction (the native cardiac contractility) sustainably over long periods of time. Furthermore, unlike most interventions that increase cardiac contractility, CCM is not associated with an unfavorable increase in oxygen demand by the heart (measured in terms of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption or MVO2). This may be explained by the beneficial effect CCM has in improving cardiac efficiency. A meta-analysis in 2014 and an overview of device-based treatment options in heart failure in 2013 concluded that CCM treatment is safe, that it is generally beneficial to patients and that CCM treatment increases the exercise tolerance (ET) and quality of life (QoL) of patients. Furthermore, preliminary long-term survival data shows that CCM is associated with lower long-term mortality in heart failure patients when compared with expected rates among similar patients not treated with CCM.