swiss ephemeris - Welcome, but
... The problem of defining the zodiac .............................................................................................................. 22 The Babylonian tradition and the Fagan/Bradley ayanamsha ....................................................................... 22 The Hipparchan trad ...
... The problem of defining the zodiac .............................................................................................................. 22 The Babylonian tradition and the Fagan/Bradley ayanamsha ....................................................................... 22 The Hipparchan trad ...
Solar Radiation - Energy
... 1.3.1 Thermal radiation All physical objects emit electromagnetic radiation. Light is electromagnetic radiation in a certain range of frequencies and wavelengths. Nevertheless, not all bodies emit light. Actually, most visible objects we do not perceive because of the radiation they emit but because ...
... 1.3.1 Thermal radiation All physical objects emit electromagnetic radiation. Light is electromagnetic radiation in a certain range of frequencies and wavelengths. Nevertheless, not all bodies emit light. Actually, most visible objects we do not perceive because of the radiation they emit but because ...
The Mathematics of the Longitude
... twenty-fourth of that, or fifteen degrees. Each hour's time difference between the ship and the starting point therefore marks a progress of fifteen degrees of longitude to the east or west. Unfortunately, although navigators could figure out their local time at sea by watching the sun every day to ...
... twenty-fourth of that, or fifteen degrees. Each hour's time difference between the ship and the starting point therefore marks a progress of fifteen degrees of longitude to the east or west. Unfortunately, although navigators could figure out their local time at sea by watching the sun every day to ...
The Project Gutenberg eBook #31344: Mathematical Geography
... thread to it and connect the other end of the thread to a point on the sill where the shadow falls. A still better method is shown on p. 172. Since the shadow is north, the sun is as high in the sky as it will get during the day, and the angle thus measured gives the highest altitude of the sun for ...
... thread to it and connect the other end of the thread to a point on the sill where the shadow falls. A still better method is shown on p. 172. Since the shadow is north, the sun is as high in the sky as it will get during the day, and the angle thus measured gives the highest altitude of the sun for ...
qbo-period-8-0822
... record of 1953-2005, and found that the correlation coefficient between the period of the QBO and a solar cycle was zero. They showed the anti-correlation during the three cycles with SC-min at 1965, 1976 and 1986, confirming Salby and Callaghan [2000]. However, an in-phase relationship was found st ...
... record of 1953-2005, and found that the correlation coefficient between the period of the QBO and a solar cycle was zero. They showed the anti-correlation during the three cycles with SC-min at 1965, 1976 and 1986, confirming Salby and Callaghan [2000]. However, an in-phase relationship was found st ...
Long-term monitoring of the short period SU UMa
... recorded normal outburst in V844 Her. We also examined superhump period changes during 2002 May and 2006 April-May superoutbursts, both of which showed increasing superhump period over the course of the plateau stage. In order to examine the long-term behavior of V844 Her, we analyzed archival data ...
... recorded normal outburst in V844 Her. We also examined superhump period changes during 2002 May and 2006 April-May superoutbursts, both of which showed increasing superhump period over the course of the plateau stage. In order to examine the long-term behavior of V844 Her, we analyzed archival data ...
The Celestial Sphere CHAPTER 1
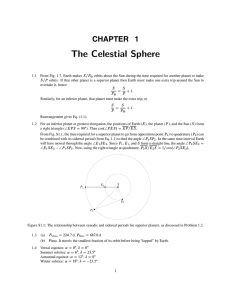
... Figure S2.2: Results for Problem 2.16. 2.17 (Note: Orbit can be downloaded from the companion web site at http://www.aw-bc.com/astrophysics.) (a) See Fig. S2.3. (b) See Fig. S2.3. (c) Figure S2.3 shows that the orbit of Mars is very close to a perfect circle, with the center of the circle slightly o ...
... Figure S2.2: Results for Problem 2.16. 2.17 (Note: Orbit can be downloaded from the companion web site at http://www.aw-bc.com/astrophysics.) (a) See Fig. S2.3. (b) See Fig. S2.3. (c) Figure S2.3 shows that the orbit of Mars is very close to a perfect circle, with the center of the circle slightly o ...
The evolution of the Sun`s birth cluster and the search for the solar
... The Galactic bar The central bar is modelled with a Ferrers potential (Ferrers 1877) which describes the potential associated to an elliptical distribution of mass. In an inertial frame located at the Galactic centre, the bar rotates with a constant pattern speed of 40–70 km s−1 kpc−1 (Martı́nez-Bar ...
... The Galactic bar The central bar is modelled with a Ferrers potential (Ferrers 1877) which describes the potential associated to an elliptical distribution of mass. In an inertial frame located at the Galactic centre, the bar rotates with a constant pattern speed of 40–70 km s−1 kpc−1 (Martı́nez-Bar ...
The celestial sphere
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion across celestial sphere. ...
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion across celestial sphere. ...
EXPOSITION OF TIME
... The birth of the solar system A contraction of a gas cloud enabled the formation of the solar system 4.5 billion years ago. Time: 15 billion years Present time The Universe is mostly empty today, dark and cold. The medium temperature of the background radiation, which floods the Universe”, is about ...
... The birth of the solar system A contraction of a gas cloud enabled the formation of the solar system 4.5 billion years ago. Time: 15 billion years Present time The Universe is mostly empty today, dark and cold. The medium temperature of the background radiation, which floods the Universe”, is about ...
Rigorous treatment of barycentric stellar motion
... and tangential components of stellar coordinates. While stellar distances are seldom known to a relative precision better than 10−2 , their angular coordinates may be determined at least six orders of magnitude more accurately. This has two important consequences. First, that astrometric observation ...
... and tangential components of stellar coordinates. While stellar distances are seldom known to a relative precision better than 10−2 , their angular coordinates may be determined at least six orders of magnitude more accurately. This has two important consequences. First, that astrometric observation ...
Chapter 2 CELESTIAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS
... There are several different ways of representing the appearance of the sky or describing the locations of objects that we see in the sky. One way is to imagine that every object in the sky is located on a very large and distant sphere called the celestial sphere. This imaginary sphere has its center ...
... There are several different ways of representing the appearance of the sky or describing the locations of objects that we see in the sky. One way is to imagine that every object in the sky is located on a very large and distant sphere called the celestial sphere. This imaginary sphere has its center ...
Answers to Chapter Review Questions and Problems for The
... 1. Why do the constellations not change their shape (stick figure) over a year’s time? Answer: Any change in the shape of a constellation is due to the proper motion of the stars. This motion is so slow, that it requires hundreds of years for any noticeable change (by naked-eye) in the constellation ...
... 1. Why do the constellations not change their shape (stick figure) over a year’s time? Answer: Any change in the shape of a constellation is due to the proper motion of the stars. This motion is so slow, that it requires hundreds of years for any noticeable change (by naked-eye) in the constellation ...
- x sin a + ycos a = ad cos b
... types, which in general contain both old and young stars, will be a mixture of stars that have quite different kinematic properties. Indeed, within almost any group of stars chosen according to spectral type only, there will he a certain degree of kinematic heterogeneity, either because the group co ...
... types, which in general contain both old and young stars, will be a mixture of stars that have quite different kinematic properties. Indeed, within almost any group of stars chosen according to spectral type only, there will he a certain degree of kinematic heterogeneity, either because the group co ...
A Detailed Derivation of the Radial Velocity Equation
... Of the over 300 extrasolar planets discovered to date, the vast majority have been found using the RADIAL VELOCITY METHOD (also known as DOPPLER SPECTROSCOPY or the DOPPLER METHOD). The purpose of this paper is to derive the theoretical equation that is asso ...
... Of the over 300 extrasolar planets discovered to date, the vast majority have been found using the RADIAL VELOCITY METHOD (also known as DOPPLER SPECTROSCOPY or the DOPPLER METHOD). The purpose of this paper is to derive the theoretical equation that is asso ...
The Galactic Environment of the Sun
... ieces of interstellar matter are constantly passing through our solar system. These galactic visitors—atomic particles and bits of dust—flow through interplanetary space and may collide with the major bodies in the solar system—the earth and the other planets. Although each particle is microscopic, ...
... ieces of interstellar matter are constantly passing through our solar system. These galactic visitors—atomic particles and bits of dust—flow through interplanetary space and may collide with the major bodies in the solar system—the earth and the other planets. Although each particle is microscopic, ...
PHY216_lect3_2014_sub
... Universal Time is the name by which Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) became known for scientific purposes in 1928. UT is based on the daily rotation of the Earth. However, the Earth’s rotation is somewhat irregular and can therefore no longer be used as a precise system of time. Versions of UT: UT1: • The ...
... Universal Time is the name by which Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) became known for scientific purposes in 1928. UT is based on the daily rotation of the Earth. However, the Earth’s rotation is somewhat irregular and can therefore no longer be used as a precise system of time. Versions of UT: UT1: • The ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 2. During a night, how do the stars move? What angle does their nightly path make with respect to the horizon? How does it depend on latitude? During the course of a night the stars appear to move westward, rising somewhere along the eastern horizon (except for the circumpolar stars that never rise ...
... 2. During a night, how do the stars move? What angle does their nightly path make with respect to the horizon? How does it depend on latitude? During the course of a night the stars appear to move westward, rising somewhere along the eastern horizon (except for the circumpolar stars that never rise ...
The Solar System - Royal Astronomical Society of Canada
... merely a projection of the ea rth ’s equator far out among the stars, while the Ecliptic is merely a projection of the earth's orbit far out among the stars. The planes of these two great circles are fixed, the former with reference to the earth and the latter with reference to the sky, at an angle ...
... merely a projection of the ea rth ’s equator far out among the stars, while the Ecliptic is merely a projection of the earth's orbit far out among the stars. The planes of these two great circles are fixed, the former with reference to the earth and the latter with reference to the sky, at an angle ...
Collisions and Encounters of Stellar Systems
... masses, and the violently changing gravitational field leads to a merger remnant that looks quite different from either of its progenitors. In contrast, minor mergers, in which one of the merging galaxies is much smaller than the other, leave the larger galaxy relatively unchanged. Not every close e ...
... masses, and the violently changing gravitational field leads to a merger remnant that looks quite different from either of its progenitors. In contrast, minor mergers, in which one of the merging galaxies is much smaller than the other, leave the larger galaxy relatively unchanged. Not every close e ...
chapter 15 navigational astronomy
... into the Sun’s glare. At this time they are between the Earth and Sun (known as inferior conjunction) or on the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth (superior conjunction). On rare occasions at inferior conjunction, the planet will cross the face of the Sun as seen from the Earth. This is known a ...
... into the Sun’s glare. At this time they are between the Earth and Sun (known as inferior conjunction) or on the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth (superior conjunction). On rare occasions at inferior conjunction, the planet will cross the face of the Sun as seen from the Earth. This is known a ...
Determination of accurate stellar radial
... minor planets to define a velocity zero point is inconsistent with this aim, except at a superficial accuracy level (∼0.5 km s−1 for normal stars). In this paper we describe and apply a procedure to derive accurate radial-velocity measures from digital échelle spectra. While there may be many other ...
... minor planets to define a velocity zero point is inconsistent with this aim, except at a superficial accuracy level (∼0.5 km s−1 for normal stars). In this paper we describe and apply a procedure to derive accurate radial-velocity measures from digital échelle spectra. While there may be many other ...
THE EVOLUTION OF SOLAR FLUX FROM 0.1 nm TO 160μm
... in the Sun by a rotational dynamo (Parker 1970), couples to the solar wind out to the solar Alfvén radius, approximately 20 Solar radii. This coupling of internal rotational energy to the outer reaches of the stellar atmosphere enables the stellar wind to shed angular momentum over the solar lifeti ...
... in the Sun by a rotational dynamo (Parker 1970), couples to the solar wind out to the solar Alfvén radius, approximately 20 Solar radii. This coupling of internal rotational energy to the outer reaches of the stellar atmosphere enables the stellar wind to shed angular momentum over the solar lifeti ...
Equation of time
The equation of time describes the discrepancy between two kinds of solar time. These are apparent solar time, which directly tracks the motion of the sun, and mean solar time, which tracks a fictitious ""mean"" sun with noons 24 hours apart. Apparent (or true) solar time can be obtained by measurement of the current position (hour angle) of the Sun, or indicated (with limited accuracy) by a sundial. Mean solar time, for the same place, would be the time indicated by a steady clock set so that over the year its differences from apparent solar time average to zero.The equation of time is the east or west component of the analemma, a curve representing the angular offset of the Sun from its mean position on the celestial sphere as viewed from Earth. The equation of time values for each day of the year, compiled by astronomical observatories, were widely listed in almanacs and ephemerides.