Classification, nomenclature, taxonomy,identification
... C. septicum - nontraumatic myonecrosis, patients immunocompromised - Ca of colon - breakdown of the integrity of colon, spread of clostridia in tissues, hyperacute course C. difficile - pseudomembranouse colitis connected with broad spectrum ATB therapy, produces 2 toxins, part of FF, exposition to ...
... C. septicum - nontraumatic myonecrosis, patients immunocompromised - Ca of colon - breakdown of the integrity of colon, spread of clostridia in tissues, hyperacute course C. difficile - pseudomembranouse colitis connected with broad spectrum ATB therapy, produces 2 toxins, part of FF, exposition to ...
Staphylococcus
... “stapyle” (bunch of grapes) – Include major human pathogen and skin commensals ...
... “stapyle” (bunch of grapes) – Include major human pathogen and skin commensals ...
Digestive (GI) System Flashcards
... of food takes place. 65. Folds in the small intestine. 66. What is a Brush Border? 67. Regions of the small intestine. 68. Where is the site of action of liver and ...
... of food takes place. 65. Folds in the small intestine. 66. What is a Brush Border? 67. Regions of the small intestine. 68. Where is the site of action of liver and ...
nodulation.2 - Malcolm Stilson Archives and Special Collections
... Nodulation is a symbiosis between N-fixing prokaryotes and plant roots. The relationship is facultative: both can exist freeliving. Rhizobial bacteria are symbionts to 600 Genera and 1800 spp. of Leguminaseae. Many studies on Trifolium spp. ...
... Nodulation is a symbiosis between N-fixing prokaryotes and plant roots. The relationship is facultative: both can exist freeliving. Rhizobial bacteria are symbionts to 600 Genera and 1800 spp. of Leguminaseae. Many studies on Trifolium spp. ...
Digestive System
... molecules that can be absorbed by the body in one long tube from mouth to anus ...
... molecules that can be absorbed by the body in one long tube from mouth to anus ...
Factors Affecting the Toxicity of Oxygen Towards
... and the signals were greatly enhanced when the freeze-dried bacteria were exposed to oxygen, presumably because paramagnetic molecules such as oxygen react readily with free radicals to form peroxyradicals. Such events probably occur when bacteria are sprayed into air at low RH values. The peroxyrad ...
... and the signals were greatly enhanced when the freeze-dried bacteria were exposed to oxygen, presumably because paramagnetic molecules such as oxygen react readily with free radicals to form peroxyradicals. Such events probably occur when bacteria are sprayed into air at low RH values. The peroxyrad ...
Streptococcus pyogenes Fact Sheet
... the presence of a hyaluronic acid capsule and a betahaemolytic ability. Beta-hemolytic streptococci are able to destroy red blood cells and other cells using toxins known as streptolycins. Streptococcus is present in many humans and can cause opportunistic infections. ...
... the presence of a hyaluronic acid capsule and a betahaemolytic ability. Beta-hemolytic streptococci are able to destroy red blood cells and other cells using toxins known as streptolycins. Streptococcus is present in many humans and can cause opportunistic infections. ...
JEFFERSON COLLEGE CONCEPTS IN BIOLOGY
... Know the structures and functions of the major structure of the human brain. Be able to describe the functions of the major senses in the human and where the sense organs are located. ...
... Know the structures and functions of the major structure of the human brain. Be able to describe the functions of the major senses in the human and where the sense organs are located. ...
Cell wall deformation and Staphylococcus aureus surface sensing
... mechanical and chemical stresses, such as the host immune response, fluid shear and antibiotic treatment. All these phenomenal changes in S. aureus physiology occurs due to adhesion and biofilm formation, therefore a sense of touch or mechanical sensitivity towards surface adhesion is an important c ...
... mechanical and chemical stresses, such as the host immune response, fluid shear and antibiotic treatment. All these phenomenal changes in S. aureus physiology occurs due to adhesion and biofilm formation, therefore a sense of touch or mechanical sensitivity towards surface adhesion is an important c ...
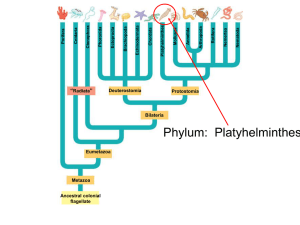
Platyhelminthes - The Bronx High School of Science
... •sensory cells (statocysts sense gravity, light sensory cells at eyespots, chemosensory cells) •2 nerve cords run length of body •simple excretory system- protonephridia •consists of flame cells (specialized ciliated cells) •move fluid through branched ducts to outside via ...
... •sensory cells (statocysts sense gravity, light sensory cells at eyespots, chemosensory cells) •2 nerve cords run length of body •simple excretory system- protonephridia •consists of flame cells (specialized ciliated cells) •move fluid through branched ducts to outside via ...
Supplementary Information (doc 48K)
... circle indicates a 2-fold change. Genes with grey background are excluded due to failure in the qPCR quality control test with an undetectable expression. ...
... circle indicates a 2-fold change. Genes with grey background are excluded due to failure in the qPCR quality control test with an undetectable expression. ...
Farrowing Room Management
... H. Parasuis • This bacteria is known to cause disease and the clinical signs we are seeing. • It can be cultured from the lungs without causing disease. • In this case it was only cultured from the lungs. • Less likely to be the pathogen responsible for disease. ...
... H. Parasuis • This bacteria is known to cause disease and the clinical signs we are seeing. • It can be cultured from the lungs without causing disease. • In this case it was only cultured from the lungs. • Less likely to be the pathogen responsible for disease. ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Sterile Processing
... package indicators or Bowie-Dick-type indicators), or biological indicators. These process monitors help detect failures in the sterilization process and keep patients safe.6 These monitors can be considered the SPD’s alarm systems. ...
... package indicators or Bowie-Dick-type indicators), or biological indicators. These process monitors help detect failures in the sterilization process and keep patients safe.6 These monitors can be considered the SPD’s alarm systems. ...
Appendix XV: Microbial Food Cultures Including Probiotics
... quarter and one third of the food consumed in Central Europe belongs to the category of fermented food.1 The microbes used to bring about these transformations are diverse taxonomically and functionally, and include (but are not limited to) species of the bacteria phyla Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, a ...
... quarter and one third of the food consumed in Central Europe belongs to the category of fermented food.1 The microbes used to bring about these transformations are diverse taxonomically and functionally, and include (but are not limited to) species of the bacteria phyla Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, a ...
Vie Milieu
... they have independently co-evolved similar mechanisms. Deciphering similar infection mechanisms is also relevant to understanding how organisms can adapt to a specific host environment rapidly, and whether mechanisms such as horizontal gene transfer has some influence on the chimeric nature of such ...
... they have independently co-evolved similar mechanisms. Deciphering similar infection mechanisms is also relevant to understanding how organisms can adapt to a specific host environment rapidly, and whether mechanisms such as horizontal gene transfer has some influence on the chimeric nature of such ...
C H A P T E R 1 9
... The organs of digestion are divided into two main groups: those composing the GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) TRACT and those composing the ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS. The GI TRACT is a continuous tube running from the mouth to the anus. The organs involved are the MOUTH, PHARYNX, ESOPHAGUS, STOMACH, SMALL IN ...
... The organs of digestion are divided into two main groups: those composing the GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) TRACT and those composing the ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS. The GI TRACT is a continuous tube running from the mouth to the anus. The organs involved are the MOUTH, PHARYNX, ESOPHAGUS, STOMACH, SMALL IN ...
PROBIOTICS Past, Present & Future
... benefits of Probiotics. Human breast milk contains a protein that stimulates the growth of good bacteria to help with digestion. Therefore a way to create and maintain a perfect balance of gut bacteria in babies has been in existence for as long as babies have been born • Probiotics in Infant Formul ...
... benefits of Probiotics. Human breast milk contains a protein that stimulates the growth of good bacteria to help with digestion. Therefore a way to create and maintain a perfect balance of gut bacteria in babies has been in existence for as long as babies have been born • Probiotics in Infant Formul ...
Eds., N. Hamamura, S. Suzuki, S. Mendo, C. M. Barroso,... © by TERRAPUB, 2010.
... present in eukaryotes or they have different characteristics from those of eukaryotic cells. However, as shown in Table 2, bacteria inherently have potential drug resistance mechanisms or they can acquire exogenous genes conferring drug resistance. Drug resistance therefore occurs by such mechanisms ...
... present in eukaryotes or they have different characteristics from those of eukaryotic cells. However, as shown in Table 2, bacteria inherently have potential drug resistance mechanisms or they can acquire exogenous genes conferring drug resistance. Drug resistance therefore occurs by such mechanisms ...
BIOL260 Chapter 1 Lecture
... Bacteria were once classified as plants, giving rise to use of the term flora for microbes This term has been replaced by microbiota Microbes normally present in and on the human body are called normal microbiota Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Bacteria were once classified as plants, giving rise to use of the term flora for microbes This term has been replaced by microbiota Microbes normally present in and on the human body are called normal microbiota Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
CHAPTER 8
... provides about 20 % of the nutrients absorbed by the host animal, the composition of microorganisms is important. • The bacteria dry matter contains about 100 g/kg, but only 80 % of this is in the form of amino acids, the remaining 20% being present as nuclic acid N. • Some of the amino acids are co ...
... provides about 20 % of the nutrients absorbed by the host animal, the composition of microorganisms is important. • The bacteria dry matter contains about 100 g/kg, but only 80 % of this is in the form of amino acids, the remaining 20% being present as nuclic acid N. • Some of the amino acids are co ...
Microbiology Laboratories Report on Training Visit
... The assumption is that each viable bacterial cell is separate from all others and will develop into a single discrete colony. However, organism normally forms multiple cell arrangements, such as chains, the colony-forming unit may consist of a chain of bacteria rather than a single bacterium. Theref ...
... The assumption is that each viable bacterial cell is separate from all others and will develop into a single discrete colony. However, organism normally forms multiple cell arrangements, such as chains, the colony-forming unit may consist of a chain of bacteria rather than a single bacterium. Theref ...
Chapter 5 Concepts 1. Microorganisms require about 10 elements
... Nitrogen is needed for the synthesis of amino acids, purines, pyrimidines, some carbohydrates and lipids, enzyme cofactors, and other substances. Many microorganisms can use the nitrogen in amino acids, and ammonia often is directly incorporated through the action of such enzymes as glutamate dehydr ...
... Nitrogen is needed for the synthesis of amino acids, purines, pyrimidines, some carbohydrates and lipids, enzyme cofactors, and other substances. Many microorganisms can use the nitrogen in amino acids, and ammonia often is directly incorporated through the action of such enzymes as glutamate dehydr ...
metronidazole - Fakultas Farmasi Unand
... • STORAGE: Metronidazole should be stored at room temperature and protected from light. ...
... • STORAGE: Metronidazole should be stored at room temperature and protected from light. ...
Antibiotics Currently in Clinical Development
... A ‘yes’ in this column indicates that a drug has in vitro data showing both activity against one or more Gram-negative species that are considered ESKAPE pathogens (Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumanii, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species) and the potential for clinically si ...
... A ‘yes’ in this column indicates that a drug has in vitro data showing both activity against one or more Gram-negative species that are considered ESKAPE pathogens (Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumanii, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species) and the potential for clinically si ...
Human microbiota

The human microbiota is the aggregate of microorganisms, a microbiome that resides on the surface and in deep layers of skin (including in mammary glands), in the saliva and oral mucosa, in the conjunctiva, and in the gastrointestinal tracts. They include bacteria, fungi, and archaea. Micro-animals which live on the human body are excluded. The human microbiome refer to their genomes.One study indicated they outnumber human cells 10 to 1. Some of these organisms perform tasks that are useful for the human host. However, the majority have been too poorly researched for us to understand the role they play, however communities of microflora have been shown to change their behavior in diseased individuals. Those that are expected to be present, and that under normal circumstances do not cause disease, but instead participate in maintaining health, are deemed members of the normal flora. Though widely known as microflora, this is a misnomer in technical terms, since the word root flora pertains to plants, and biota refers to the total collection of organisms in a particular ecosystem. Recently, the more appropriate term microbiota is applied, though its use has not eclipsed the entrenched use and recognition of flora with regard to bacteria and other microorganisms. Both terms are being used in different literature.Studies in 2009 questioned whether the decline in biota (including microfauna) as a result of human intervention might impede human health.Most of the microbes associated with humans appear to be not harmful at all, but rather assist in maintaining processes necessary for a healthy body. A surprising finding was that at specific sites on the body, a different set of microbes may perform the same function for different people. For example, on the tongues of two people, two entirely different sets of organisms will break down sugars in the same way. This suggests that medical science may be forced to abandon the ""one only"" microbe model of infectious disease, and rather pay attention to functions of groups of microbes that have somehow gone awry.