Types of Variation
... All masses have a gravitational field ( g ) surrounding them and are capable of exerting gravitational forces other masses in this field. ...
... All masses have a gravitational field ( g ) surrounding them and are capable of exerting gravitational forces other masses in this field. ...
Rotational and Translational Motion
... Chapter 20 Rigid Body: Translation and Rotational Motion Kinematics ...
... Chapter 20 Rigid Body: Translation and Rotational Motion Kinematics ...
ROTATIONAL MOTION
... The driver is pushed forward by the seat ( actual force ) Observers inside the car feel pushed back into their seat for no reason ( fictitious force – the observer is accelerating ) ...
... The driver is pushed forward by the seat ( actual force ) Observers inside the car feel pushed back into their seat for no reason ( fictitious force – the observer is accelerating ) ...
Linear Kinetics - Weber State University
... • Newton’s first law (inertia) states that in the absence of external forces the momentum of an object remains constant. M = constant Principle of Conservation of Momentum • Newton’s second law (acceleration) states that the rate of change of momentum equals the net external force acting on it. ...
... • Newton’s first law (inertia) states that in the absence of external forces the momentum of an object remains constant. M = constant Principle of Conservation of Momentum • Newton’s second law (acceleration) states that the rate of change of momentum equals the net external force acting on it. ...
Newtonian mechanics problem solving
... 3. If the collision is completely inelastic and the objects stick together, use the law of conservation of momentum to solve the problem. 4. If the collision is perfectly elastic use, both conservation of momentum and conservation of mechanical energy. Each law produces an algebraic equation with tw ...
... 3. If the collision is completely inelastic and the objects stick together, use the law of conservation of momentum to solve the problem. 4. If the collision is perfectly elastic use, both conservation of momentum and conservation of mechanical energy. Each law produces an algebraic equation with tw ...
Mechanics notes
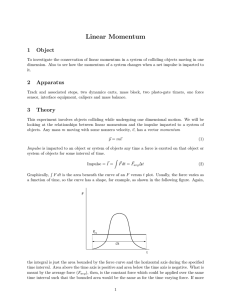
... When a resultant force acts on an object, the amount it changes the object’s momentum by depends on how long the force acts for. The force multiplied by the time it acts for is called impulse. Units: Ns Impulse equals the change in momentum. ...
... When a resultant force acts on an object, the amount it changes the object’s momentum by depends on how long the force acts for. The force multiplied by the time it acts for is called impulse. Units: Ns Impulse equals the change in momentum. ...
vector - MACscience
... When a resultant force acts on an object, the amount it changes the object’s momentum by depends on how long the force acts for. The force multiplied by the time it acts for is called impulse. Units: Ns Impulse equals the change in momentum. ...
... When a resultant force acts on an object, the amount it changes the object’s momentum by depends on how long the force acts for. The force multiplied by the time it acts for is called impulse. Units: Ns Impulse equals the change in momentum. ...