Newton`s Laws of Motion
... A roller skating session demonstrates how friction, applied by the toe stop of a skate, makes the skater stop. When two students on skates push against each other, each skater is moved backward, showing that when one body exerts a force on another, the second exerts an equal, but opposite force. Whe ...
... A roller skating session demonstrates how friction, applied by the toe stop of a skate, makes the skater stop. When two students on skates push against each other, each skater is moved backward, showing that when one body exerts a force on another, the second exerts an equal, but opposite force. Whe ...
FREE Sample Here
... as wheels with spokes (like traditional bike wheels) or you may make them as having solid rims all the way through. Which design would you pick given that the racing aspect of the machine is the most important? Please explain. ANS: If the wheels had to have a given mass, then the question would be a ...
... as wheels with spokes (like traditional bike wheels) or you may make them as having solid rims all the way through. Which design would you pick given that the racing aspect of the machine is the most important? Please explain. ANS: If the wheels had to have a given mass, then the question would be a ...
MATH10222, Chapter 2: Newtonian Dynamics 1 Newton`s Laws 2
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics
... (a) [5 pts] Calculate the total angular momentum vector of the uniformly precessing gyroscope in the orientation show above; i.e., the total of the spin and precession angular momentum vectors. (b) [5 pts] The pivot mount is accelerated upward with magnitude A. Calculate the precession angular veloc ...
... (a) [5 pts] Calculate the total angular momentum vector of the uniformly precessing gyroscope in the orientation show above; i.e., the total of the spin and precession angular momentum vectors. (b) [5 pts] The pivot mount is accelerated upward with magnitude A. Calculate the precession angular veloc ...
relative - Purdue Physics
... farther in the lab than you’d predict from their restframe proper decay lifetime. • From the point of view of the pions, the kilometerslong lab has Lorentz-contracted to a few meters length! So the pion has no problem living long enough to go that short distance. ...
... farther in the lab than you’d predict from their restframe proper decay lifetime. • From the point of view of the pions, the kilometerslong lab has Lorentz-contracted to a few meters length! So the pion has no problem living long enough to go that short distance. ...
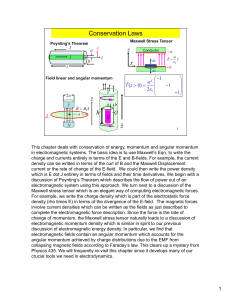
Radiation pressure and momentum transfer in dielectrics: The
... currents Lagrangian supplies all that is required for the kind of problem of interest here. To counter the claim sometimes made that only the Abraham tensor is correct, we devote the remainder of this section to an outline of the historical reasons for the claim and to the justification for safely i ...
... currents Lagrangian supplies all that is required for the kind of problem of interest here. To counter the claim sometimes made that only the Abraham tensor is correct, we devote the remainder of this section to an outline of the historical reasons for the claim and to the justification for safely i ...
teacher background information force
... zero), the magnitude of the net force acting on the object is equal to zero. This law states that if the forces are balanced, meaning the magnitude of the net force is equal to zero, then an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant velocity (same direction, same speed). Ne ...
... zero), the magnitude of the net force acting on the object is equal to zero. This law states that if the forces are balanced, meaning the magnitude of the net force is equal to zero, then an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant velocity (same direction, same speed). Ne ...
Physics - cloudfront.net
... farthest from the Sun during July. During which month is the gravitational potential energy of the Earth with respect to the Sun the greatest? ...
... farthest from the Sun during July. During which month is the gravitational potential energy of the Earth with respect to the Sun the greatest? ...
chapter8_PC - Wikispaces : gandell
... We wish to locate the point of application of the single force whose magnitude is equal to the weight of the object, and whose effect on the rotation is the same as all the individual particles. This point is called the center of gravity of the object ...
... We wish to locate the point of application of the single force whose magnitude is equal to the weight of the object, and whose effect on the rotation is the same as all the individual particles. This point is called the center of gravity of the object ...
Physics Notes Ch 7 and 8 - Circular Motion, Equilibrium, and
... The first child has a mass m1 of 25 kg and sits at the left end of the see-saw, while the second child has a mass m2 of 50 kg and sits somewhere on the see-saw to the right of the axis. At what distance r2 from the axis should the second child sit to keep the see-saw horizontal? 3m ...
... The first child has a mass m1 of 25 kg and sits at the left end of the see-saw, while the second child has a mass m2 of 50 kg and sits somewhere on the see-saw to the right of the axis. At what distance r2 from the axis should the second child sit to keep the see-saw horizontal? 3m ...
Chapter 11 Force and Newton`s Laws
... What is the momentum of a car with a mass of 900 kg traveling north at 27 m/s? p=m*v p = 900 kg * 27 m/s North p = 24,300 kg · m/s North ...
... What is the momentum of a car with a mass of 900 kg traveling north at 27 m/s? p=m*v p = 900 kg * 27 m/s North p = 24,300 kg · m/s North ...