Chapter 1 Quick Review
... 2. A thin-walled hollow tube rolls without sliding along the floor. The ratio of its translational kinetic energy to its rotational kinetic energy (about an axis through its center of mass) is: (Kinetic Energy of Rolling Motion.) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.1/2 e. 1/3 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the ...
... 2. A thin-walled hollow tube rolls without sliding along the floor. The ratio of its translational kinetic energy to its rotational kinetic energy (about an axis through its center of mass) is: (Kinetic Energy of Rolling Motion.) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.1/2 e. 1/3 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the ...
Conservation Of Momentum
... system – two or more objects that interact with each other during an event. They experience equal and opposite forces during the event, so they have the same impulse. event – the physical interaction between two or more objects during which an impulse occurs. collisions and explosions. Events are de ...
... system – two or more objects that interact with each other during an event. They experience equal and opposite forces during the event, so they have the same impulse. event – the physical interaction between two or more objects during which an impulse occurs. collisions and explosions. Events are de ...
Name: Date: Period: Study Guide for Quiz Directions: Answer each
... 8. When you want to jump from one building to another and clearing the jump nicely without getting hurt, which Newton’s law does this apply to? What are you building in order to clear the jump nicely (Hint: Starts with an M)? ...
... 8. When you want to jump from one building to another and clearing the jump nicely without getting hurt, which Newton’s law does this apply to? What are you building in order to clear the jump nicely (Hint: Starts with an M)? ...
Momentum and Impulse
... • Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum • Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity. • Momentum = mass * velocity • ρ=m*v • where m = mass and v=velocity ...
... • Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum • Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity. • Momentum = mass * velocity • ρ=m*v • where m = mass and v=velocity ...
conservation of momentum in two dimensions
... In Newton’s time it was known that momentum of objects was conserved in collisions. Momentum is defined as: ...
... In Newton’s time it was known that momentum of objects was conserved in collisions. Momentum is defined as: ...
Objectives: 1. Describe examples of force and identify appropriate SI
... 2. Explain how the motion of an object is affected when balanced and unbalanced forces act on it. 3. Compare and contrast four kinds of friction 4. Describe how earth’s gravity and air resistance affect falling objects 5. Describe the path of a projectile and identify the forces that produce project ...
... 2. Explain how the motion of an object is affected when balanced and unbalanced forces act on it. 3. Compare and contrast four kinds of friction 4. Describe how earth’s gravity and air resistance affect falling objects 5. Describe the path of a projectile and identify the forces that produce project ...
Are you ready for the Motion #2 Unit Test
... ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4. A 1.25 tonne car is accelerating at 1.2 ms-2 north along a straight road whilst towing a 350 kg trailer. Friction forces on the car and trailer are 750 N and 250 N respectively. Find:(a) the driving force acting on ...
... ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4. A 1.25 tonne car is accelerating at 1.2 ms-2 north along a straight road whilst towing a 350 kg trailer. Friction forces on the car and trailer are 750 N and 250 N respectively. Find:(a) the driving force acting on ...
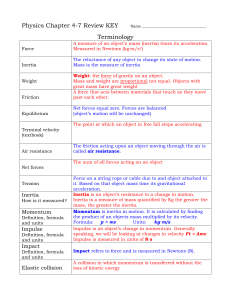
Physics Chapter 1-3 Review
... Weight: the force of gravity on an object. Mass and weight are proportional not equal. Objects with great mass have great weight A force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. ...
... Weight: the force of gravity on an object. Mass and weight are proportional not equal. Objects with great mass have great weight A force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. ...