DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
... MOMENTUM - PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A body of mass 3kg moving with a velocity of 4m/s collides head on with a body of mass 2kg moving in the opposite direction with a velocity of 5m/s. If the bodies stick together on impact, what velocity will they have after the collision? BEFORE DIAGRAM ...
... MOMENTUM - PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A body of mass 3kg moving with a velocity of 4m/s collides head on with a body of mass 2kg moving in the opposite direction with a velocity of 5m/s. If the bodies stick together on impact, what velocity will they have after the collision? BEFORE DIAGRAM ...
Chapter 3 - "Patterns of Motion"
... masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them. • F = G(m1m2)/d2 • G is a proportionality constant and is equal to 6.67 X 10-11 Nm2/kg2 – Usually the objects in our environment that we interact with on an everyday basis are so small that the force is not noticed due t ...
... masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them. • F = G(m1m2)/d2 • G is a proportionality constant and is equal to 6.67 X 10-11 Nm2/kg2 – Usually the objects in our environment that we interact with on an everyday basis are so small that the force is not noticed due t ...
Name____________________________________
... 12. The Newton is the SI unit of: a) force b) energy c) pressure d) mass 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed ...
... 12. The Newton is the SI unit of: a) force b) energy c) pressure d) mass 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed ...
Newton`s 3rd Law
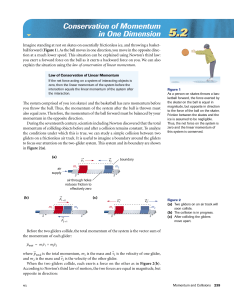
... Conservation of Momentum: • If someone bumps in to you from behind, you gain momentum & move forward. • When two objects collide, in the absence of friction, momentum is not lost. • The Law of Conservation of Momentum says that momentum does not change when objects interact, it remains the same bef ...
... Conservation of Momentum: • If someone bumps in to you from behind, you gain momentum & move forward. • When two objects collide, in the absence of friction, momentum is not lost. • The Law of Conservation of Momentum says that momentum does not change when objects interact, it remains the same bef ...
momentum class notes
... Collisions commonly occur in contact sports (such as football) and racket and bat sports (such as baseball, golf, tennis, etc.). Consider a collision in football between a fullback and a linebacker during a goal-line stand. The fullback plunges across the goal line and collides in midair with lineb ...
... Collisions commonly occur in contact sports (such as football) and racket and bat sports (such as baseball, golf, tennis, etc.). Consider a collision in football between a fullback and a linebacker during a goal-line stand. The fullback plunges across the goal line and collides in midair with lineb ...
LINEAR KINETICS (Part 1)
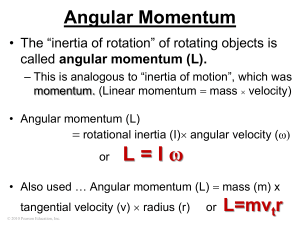
... examine their total momentum. Newton’s First Law can be restated to predict what will happen to the “system”: In the absence of _______ forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant (in both ________ and _________). Example #1: A 100 kg running back carries the ball fo ...
... examine their total momentum. Newton’s First Law can be restated to predict what will happen to the “system”: In the absence of _______ forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant (in both ________ and _________). Example #1: A 100 kg running back carries the ball fo ...