essen-ch13-presentat..
... The LR market supply curve is horizontal if 1) all firms have identical costs, and 2) costs do not change as other firms enter or exit the market. ...
... The LR market supply curve is horizontal if 1) all firms have identical costs, and 2) costs do not change as other firms enter or exit the market. ...
Monopoly2 - Rio Hondo Community College Faculty Websites
... One firm may be more efficient than other firms because it is better at producing a good than those other firms making it. ...
... One firm may be more efficient than other firms because it is better at producing a good than those other firms making it. ...
Chapter Eight - pm
... The Shutdown Point (cont’d) • The leftmost graph on Figure 8.10 depicts a firm that is receiving a price above the minimum of the AVC, but below the minimum of the ATC. In this case, the firm is losing profits, but must not shut down. • The middle graph on Figure 8.10 depicts a firm that is receivi ...
... The Shutdown Point (cont’d) • The leftmost graph on Figure 8.10 depicts a firm that is receiving a price above the minimum of the AVC, but below the minimum of the ATC. In this case, the firm is losing profits, but must not shut down. • The middle graph on Figure 8.10 depicts a firm that is receivi ...
w06ex1 - Rose
... If a linear, positively-sloped supply curve cuts the horizontal axis, then: a ten percent increase in price would cause a greater than ten percent increase in quantity supplied. a ten percent increase in price would cause a ten percent increase in quantity supplied. a ten percent increase in price w ...
... If a linear, positively-sloped supply curve cuts the horizontal axis, then: a ten percent increase in price would cause a greater than ten percent increase in quantity supplied. a ten percent increase in price would cause a ten percent increase in quantity supplied. a ten percent increase in price w ...
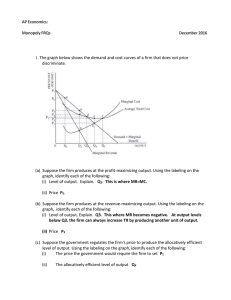
Monopoly FRQs answers
... (d) Now assume that GCR's patent on Aspy expires. What will happen to GCR's economic profits in the long run? Explain. 6. Assume that Clark Electronics has a monopoly in the production and sale of a new device for detecting and destroying a computer virus. Clark Electronics currently incurs short-ru ...
... (d) Now assume that GCR's patent on Aspy expires. What will happen to GCR's economic profits in the long run? Explain. 6. Assume that Clark Electronics has a monopoly in the production and sale of a new device for detecting and destroying a computer virus. Clark Electronics currently incurs short-ru ...
Year 12 Economic Notes
... Repeatedly doing the same job can result in boredom for the workers If a worker cannot complete his or her job on time this may result in a bottleneck for the whole production process. ...
... Repeatedly doing the same job can result in boredom for the workers If a worker cannot complete his or her job on time this may result in a bottleneck for the whole production process. ...
ECS101 – DEC 2009
... The 3 major flows in an economy as a whole is total production, total income and total spending Final goods and services is an aspect of the goods market Annual gold production is a flow variable The prices and quantities traded in the goods market are determined by the interaction of demand and sup ...
... The 3 major flows in an economy as a whole is total production, total income and total spending Final goods and services is an aspect of the goods market Annual gold production is a flow variable The prices and quantities traded in the goods market are determined by the interaction of demand and sup ...
The McGraw-Hill Series Managerial Economics
... utility levels of all goods & services • All bundles of goods can be ranked based on their ability to provide utility – for any pair of bundles A & B: • Prefer bundle A to bundle B • Prefer bundle B to bundle A • Indifferent between the two bundles ...
... utility levels of all goods & services • All bundles of goods can be ranked based on their ability to provide utility – for any pair of bundles A & B: • Prefer bundle A to bundle B • Prefer bundle B to bundle A • Indifferent between the two bundles ...
Chapter - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... utility levels of all goods & services • All bundles of goods can be ranked based on their ability to provide utility – for any pair of bundles A & B: • Prefer bundle A to bundle B • Prefer bundle B to bundle A • Indifferent between the two bundles ...
... utility levels of all goods & services • All bundles of goods can be ranked based on their ability to provide utility – for any pair of bundles A & B: • Prefer bundle A to bundle B • Prefer bundle B to bundle A • Indifferent between the two bundles ...
answer 10-1
... variable cost curve passes through the origin, which means that the variable cost of producing zero units of output is equal to zero. The TC curve, which is the sum of the FC and VC curves, is parallel to the VC curve and lies FC = $30/hour above it. ...
... variable cost curve passes through the origin, which means that the variable cost of producing zero units of output is equal to zero. The TC curve, which is the sum of the FC and VC curves, is parallel to the VC curve and lies FC = $30/hour above it. ...
The Basics of Supply & Demand
... • Thus, in demand scenarios, the relationship between P and Q is INVERSE ...
... • Thus, in demand scenarios, the relationship between P and Q is INVERSE ...
Solution to Income and Substitution Effects Exercise
... should issue allowance to all smokers to offset the tax increase. Suppose Arnold has telepathic powers so that he knows the utility function of smokers. How much allowance on income has to be made—in other words, by how much income has to be raised—so that Leonardo gets just as much utility as befor ...
... should issue allowance to all smokers to offset the tax increase. Suppose Arnold has telepathic powers so that he knows the utility function of smokers. How much allowance on income has to be made—in other words, by how much income has to be raised—so that Leonardo gets just as much utility as befor ...
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... Answer: The obstacles basically fall into two camps: Obstacles that occur because the government does not intervene in the market and obstacles that occur because the government does intervene in the market. In the first group are the issues of externalities, public goods and common resources, and m ...
... Answer: The obstacles basically fall into two camps: Obstacles that occur because the government does not intervene in the market and obstacles that occur because the government does intervene in the market. In the first group are the issues of externalities, public goods and common resources, and m ...
CHAPTER 11
... Internet allows firms to enter and leave markets at will making them closer to a purely competitive market. Applying the Tools: The Broader Importance of the MR = MC Equilibrium Condition The MR = MC equilibrium condition is simple, but it is enormously powerful. Understanding this condition is to ...
... Internet allows firms to enter and leave markets at will making them closer to a purely competitive market. Applying the Tools: The Broader Importance of the MR = MC Equilibrium Condition The MR = MC equilibrium condition is simple, but it is enormously powerful. Understanding this condition is to ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.