mORE MONOPOLY
... • Find the profit maximising quantity by finding the intersection of MR and MC. • Find the profit maximising price by finding the highest quantity at which the firm can sell that quantity. • You can read the price by going up vertically from the best quantity and finding the best price on the demand ...
... • Find the profit maximising quantity by finding the intersection of MR and MC. • Find the profit maximising price by finding the highest quantity at which the firm can sell that quantity. • You can read the price by going up vertically from the best quantity and finding the best price on the demand ...
Brief Outline - Fullerton College Staff Web Pages
... and market demand, change in demand, (reaction to determinants of demand) (46-50) change in quantity demanded (reaction to price change) (51) the law of supply, change in supply (reaction to determinants of supply (51-54) change in quantity supplied (reaction to price change) (54) market equilibrium ...
... and market demand, change in demand, (reaction to determinants of demand) (46-50) change in quantity demanded (reaction to price change) (51) the law of supply, change in supply (reaction to determinants of supply (51-54) change in quantity supplied (reaction to price change) (54) market equilibrium ...
Homework #5
... d. What is the equation(s) for the market demand for lighthouses? To find the market demand for lighthouses you need to vertically sum the individual demand curves. We vertically sum the demand curves because the good is nonrival: my consumption of the good does not diminish your ability to consume ...
... d. What is the equation(s) for the market demand for lighthouses? To find the market demand for lighthouses you need to vertically sum the individual demand curves. We vertically sum the demand curves because the good is nonrival: my consumption of the good does not diminish your ability to consume ...
The monopolist`s firm demand curve is:
... maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue. c. maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to average total cost. d. are price takers. Which of the following is true for a monopolist? a. The firm has a perfectly elastic demand curve. b. The firm has a perfectly inelastic d ...
... maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue. c. maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to average total cost. d. are price takers. Which of the following is true for a monopolist? a. The firm has a perfectly elastic demand curve. b. The firm has a perfectly inelastic d ...
The monopolist`s firm demand curve is:
... maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue. c. maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to average total cost. d. are price takers. 6. Which of the following is true for a monopolist? a. The firm has a perfectly elastic demand curve. b. The firm has a perfectly inelasti ...
... maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue. c. maximize profit by setting marginal cost equal to average total cost. d. are price takers. 6. Which of the following is true for a monopolist? a. The firm has a perfectly elastic demand curve. b. The firm has a perfectly inelasti ...
Supply Student Notes Answers
... a. Input Costs- Any change in the cost of an input used to produce a good – such as raw materials, machinery, or labor – will affect supply. How does input cost affect supply? A rise in the cost of an input will cause a fall in supply at all price levels because the good has become more expensive ...
... a. Input Costs- Any change in the cost of an input used to produce a good – such as raw materials, machinery, or labor – will affect supply. How does input cost affect supply? A rise in the cost of an input will cause a fall in supply at all price levels because the good has become more expensive ...
Costs
... – It has assured all its workers and unions that there would be no lay-offs – SW doesn’t use the word “employee”, and gives them enough room to grow and learn – SW has enjoyed big savings by never having the type of defined-benefit pension plans which has proved so costly for other airlines Other ...
... – It has assured all its workers and unions that there would be no lay-offs – SW doesn’t use the word “employee”, and gives them enough room to grow and learn – SW has enjoyed big savings by never having the type of defined-benefit pension plans which has proved so costly for other airlines Other ...
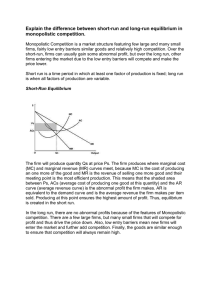
Explain the difference between short-run and long-run
... firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low entry barriers will compete and make the price lower. Short run is a time period in w ...
... firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low entry barriers will compete and make the price lower. Short run is a time period in w ...
Chapter 17
... Some argue that clean air and water are above monetary evaluation and should be treated in special ways. They often don’t see how private firms could ever be induced to do what is desirable for society. As a result, they tend to prefer the use of direct controls. Economists can emphasize that market ...
... Some argue that clean air and water are above monetary evaluation and should be treated in special ways. They often don’t see how private firms could ever be induced to do what is desirable for society. As a result, they tend to prefer the use of direct controls. Economists can emphasize that market ...
www.tceq.state.tx.us
... Presentation for the Science Advisory Committee to the Study Commission on Water for Environmental Flows June 18, 2004 ...
... Presentation for the Science Advisory Committee to the Study Commission on Water for Environmental Flows June 18, 2004 ...
David L. Perez - Doral Academy Preparatory
... over time. An example is a farmer that sells tomatoes that cant increase his output. So he begins to plant more and more trees overtime until he increases his supply. As this process becomes more effective, he will be able to sell more tomatoes at a higher market price. ...
... over time. An example is a farmer that sells tomatoes that cant increase his output. So he begins to plant more and more trees overtime until he increases his supply. As this process becomes more effective, he will be able to sell more tomatoes at a higher market price. ...
Power Point
... the cheaper it is per item to produce them Later on, increasing production will actually hurt the company’s profits ...
... the cheaper it is per item to produce them Later on, increasing production will actually hurt the company’s profits ...
Document
... A) compares the cost of the typical basket of goods consumed in period 1 to the cost of a basket of goods typically consumed in period 2. B) compares the cost in the current period to the cost in a reference base period of a basket of goods typically consumed in the base period. C) measures the incr ...
... A) compares the cost of the typical basket of goods consumed in period 1 to the cost of a basket of goods typically consumed in period 2. B) compares the cost in the current period to the cost in a reference base period of a basket of goods typically consumed in the base period. C) measures the incr ...
t7. scarcity, opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and
... income, and goods and services have positive prices. Time is the ultimate scarce resource – even Bill Gates has only twenty-four hours in a day. We say that goods and services are scarce if the quantity demanded is larger than the quantity supplied at a zero price – if supply exceeds demand at a zer ...
... income, and goods and services have positive prices. Time is the ultimate scarce resource – even Bill Gates has only twenty-four hours in a day. We say that goods and services are scarce if the quantity demanded is larger than the quantity supplied at a zero price – if supply exceeds demand at a zer ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.