Supply - Images
... technology changes and there is a more efficient way to produce cars. This can increase productivity and lower the cost, which may allow GM to sell 650 cars at $20,000 instead of 600. A change in the cost of inputs may cause a loss for the firm. If the cost of labor goes up, or raw materials, or hi ...
... technology changes and there is a more efficient way to produce cars. This can increase productivity and lower the cost, which may allow GM to sell 650 cars at $20,000 instead of 600. A change in the cost of inputs may cause a loss for the firm. If the cost of labor goes up, or raw materials, or hi ...
PS5
... 21) The most important of the factors that make a firm successful and that can be controlled by the firm's owners and managers are A) the selection of the prices of its products and the selection of the most productive and loyal employees. B) the differentiation of its products and the production of ...
... 21) The most important of the factors that make a firm successful and that can be controlled by the firm's owners and managers are A) the selection of the prices of its products and the selection of the most productive and loyal employees. B) the differentiation of its products and the production of ...
Chapters20through21
... 8. Within the first range, demand is elastic. As price falls, therefore, total revenue rises and the total revenue curve is increasing. Within the second range, demand is at first elastic and then inelastic. When price falls, therefore, total revenue and the total revenue curve are initially rising. ...
... 8. Within the first range, demand is elastic. As price falls, therefore, total revenue rises and the total revenue curve is increasing. Within the second range, demand is at first elastic and then inelastic. When price falls, therefore, total revenue and the total revenue curve are initially rising. ...
Chapter 5 Notes - Cloudfront.net
... sometimes result in side effects for people not directly connected to the production or consumption ...
... sometimes result in side effects for people not directly connected to the production or consumption ...
SL 151 - Rose
... When appropriate, use math, graphs, or equations to help explain your answer. Completely label all graphs. If you require more space, right on the back of each page, indicating that you have done so. ...
... When appropriate, use math, graphs, or equations to help explain your answer. Completely label all graphs. If you require more space, right on the back of each page, indicating that you have done so. ...
11a - Harper College
... 4. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Shortrun equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: 1. diagram a only. 2. diagram b only. 3. diagram c only. 4. both diagrams a and c. 5. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competi ...
... 4. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Shortrun equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: 1. diagram a only. 2. diagram b only. 3. diagram c only. 4. both diagrams a and c. 5. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competi ...
Economics 11 Caltech Spring 2010
... 1.C. 2pt Please explain: What is an inferior good? It is a good such that the share of the budget devoted to that good falls as income goes up Partial credit for a good such that consumption falls as income goes up _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1.C. 2pt Please explain: What is an inferior good? It is a good such that the share of the budget devoted to that good falls as income goes up Partial credit for a good such that consumption falls as income goes up _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Econ 201 Chpt 14: Perfect Competition 1
... Starbucks locations in 25 states. • Starbucks, at the end of last year, had 7,087 companyowned stores in the U.S., but it was not disclosed how many stores would be operating in April as the company is slowing down its growth. Starbucks had an additional 4,081 licensed stores and has more than 15,00 ...
... Starbucks locations in 25 states. • Starbucks, at the end of last year, had 7,087 companyowned stores in the U.S., but it was not disclosed how many stores would be operating in April as the company is slowing down its growth. Starbucks had an additional 4,081 licensed stores and has more than 15,00 ...
Chapters 1, 2, 3 Review Name ______ Below are three statements
... c. “Rains from El Nino again hit the California region causing severe flooding in farms. The prices for citrus and produce are expected to rise sharply.” ...
... c. “Rains from El Nino again hit the California region causing severe flooding in farms. The prices for citrus and produce are expected to rise sharply.” ...
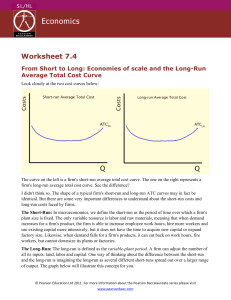
Units of Output
... • U-shape of LRATC curve – Economies of scale at relatively low levels of output – Constant returns to scale at some intermediate levels of output – Diseconomies of scale at relatively high levels of output ...
... • U-shape of LRATC curve – Economies of scale at relatively low levels of output – Constant returns to scale at some intermediate levels of output – Diseconomies of scale at relatively high levels of output ...
Spreading Ecological Economics Through Contagion: Neoclassical
... functions and other services, essential for survival of all species ...
... functions and other services, essential for survival of all species ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.