CH_5_Economics_Notes_Website
... used to produce a good, will affect supply. As input costs increase, the firm’s marginal costs also increase, decreasing profitability and supply. Input costs can also decrease. New technology can greatly decrease costs and increase supply. ...
... used to produce a good, will affect supply. As input costs increase, the firm’s marginal costs also increase, decreasing profitability and supply. Input costs can also decrease. New technology can greatly decrease costs and increase supply. ...
How? When? What? The economics of competitive advantage Why?
... 5.3 Economic and accounting costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary ...
... 5.3 Economic and accounting costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary ...
Supply
... used to produce a good, will affect supply. As input costs increase, the firm’s marginal costs also increase, decreasing profitability and supply. Input costs can also decrease. New technology can greatly decrease costs and increase supply. ...
... used to produce a good, will affect supply. As input costs increase, the firm’s marginal costs also increase, decreasing profitability and supply. Input costs can also decrease. New technology can greatly decrease costs and increase supply. ...
EC 203
... firm’s short-run production function is q = 524x – 4x2, where x is the amount of variable factor used. The price of the output is $3 per unit and the price of the variable factor is $12 per unit. In the short run, how many units of x should the firm use? a. 130 b. 32 c. 25 d. 65 e. None of the above ...
... firm’s short-run production function is q = 524x – 4x2, where x is the amount of variable factor used. The price of the output is $3 per unit and the price of the variable factor is $12 per unit. In the short run, how many units of x should the firm use? a. 130 b. 32 c. 25 d. 65 e. None of the above ...
Final from F2003
... 34. Rebecca is a single-price, profit-maximizing monopolist in the sale of singing lessons. If her demand and marginal cost curves are as shown, how much will she charge for each lesson and how many lessons will she sell each week? A. $6 per lesson, 6 lessons per week. B. $8 per lesson, 8 lessons pe ...
... 34. Rebecca is a single-price, profit-maximizing monopolist in the sale of singing lessons. If her demand and marginal cost curves are as shown, how much will she charge for each lesson and how many lessons will she sell each week? A. $6 per lesson, 6 lessons per week. B. $8 per lesson, 8 lessons pe ...
File
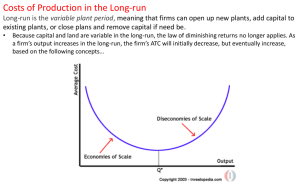
... The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor increases at first due to increased specialization, then diminishes as more labor is added to fixed land and capital. Mar ...
... The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor increases at first due to increased specialization, then diminishes as more labor is added to fixed land and capital. Mar ...
Tutorial
... B. The purpose of price ceilings is to set a maximum price by law. If it is set lower than the equilibrium price, it will have no effect on the equilibrium price as illustrated on the ...
... B. The purpose of price ceilings is to set a maximum price by law. If it is set lower than the equilibrium price, it will have no effect on the equilibrium price as illustrated on the ...
Demand and Marginal Benefit
... Demand and Marginal Benefit Demand, Willingness to Pay, and Value Value is what we get, price is what we pay. We measure value as the maximum price that a person is willing to pay. But willingness to pay determines demand. A demand curve is a marginal benefit curve. ...
... Demand and Marginal Benefit Demand, Willingness to Pay, and Value Value is what we get, price is what we pay. We measure value as the maximum price that a person is willing to pay. But willingness to pay determines demand. A demand curve is a marginal benefit curve. ...
COMPETITION AND THE SEARCH FOR AN HONEST BUCK
... return on your investment Characteristics of perfect competition • Perfectly homogeneous goods [corollary: Perfect divisibility of output] • Perfect information [corollaries: No transaction costs, No externalities] • Price taking ...
... return on your investment Characteristics of perfect competition • Perfectly homogeneous goods [corollary: Perfect divisibility of output] • Perfect information [corollaries: No transaction costs, No externalities] • Price taking ...
Midterm Exam #3
... 28) The key feature of an oligopoly is that there A) exists product differentiation. B) is one seller. C) are only a few sellers. D) are many buyers and sellers. 29) With respect to redistribution, one reason "The Big Tradeoff" exists is because A) government policymakers must choose between funding ...
... 28) The key feature of an oligopoly is that there A) exists product differentiation. B) is one seller. C) are only a few sellers. D) are many buyers and sellers. 29) With respect to redistribution, one reason "The Big Tradeoff" exists is because A) government policymakers must choose between funding ...
Section 1.1
... Step 1 We can round the size and cost of the carpet to 20 square yards and $25 per square yard. We can also round the length and cost of the wall to 15 feet and $30 per foot. Step 2 The estimated carpet cost is 20 x $25 = $500. (area of carpet times cost) The estimated wallpaper cost is 15 x $30 = $ ...
... Step 1 We can round the size and cost of the carpet to 20 square yards and $25 per square yard. We can also round the length and cost of the wall to 15 feet and $30 per foot. Step 2 The estimated carpet cost is 20 x $25 = $500. (area of carpet times cost) The estimated wallpaper cost is 15 x $30 = $ ...
Unit IIB Review Questions
... ____ 17. (Figure 59-4: A Perfectly Competitive Firm in the Short Run) The firm's total revenue from the sale of its most profitable level of output is: a. 0GLD. b. 0GHB. c. BH. d. DL. e. NFKU. ____ 18. In the short run, if P < AVC, a perfectly competitive firm: a. produces output and earns an econom ...
... ____ 17. (Figure 59-4: A Perfectly Competitive Firm in the Short Run) The firm's total revenue from the sale of its most profitable level of output is: a. 0GLD. b. 0GHB. c. BH. d. DL. e. NFKU. ____ 18. In the short run, if P < AVC, a perfectly competitive firm: a. produces output and earns an econom ...
2015 Chapter 5 homework
... Formulate a linear programming model for John's firm. Write the dual to the problem formulated in part a. Give an economic interpretation of 1) The dual variables 2) The dual objective function 3) The dual constraints ...
... Formulate a linear programming model for John's firm. Write the dual to the problem formulated in part a. Give an economic interpretation of 1) The dual variables 2) The dual objective function 3) The dual constraints ...
Market equilibrium with trade and policy
... So what do we see, and why do we see it? The incidence of each policy is price change X qty. affected, or economic surplus – a useful measure of welfare change For example, the U.S. market for avocados P($/lb) Policy is an import quota (M) ...
... So what do we see, and why do we see it? The incidence of each policy is price change X qty. affected, or economic surplus – a useful measure of welfare change For example, the U.S. market for avocados P($/lb) Policy is an import quota (M) ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.