Essentials of Economics, Krugman Wells Olney
... see Wayne Gretzky and Michael Jordan play their last games. How much would you pay to see a music star, such as Jennifer Lopez, one last time? What about your favorite athlete? ...
... see Wayne Gretzky and Michael Jordan play their last games. How much would you pay to see a music star, such as Jennifer Lopez, one last time? What about your favorite athlete? ...
chap007 - QC Economics
... supply curve for a competitive firm. – Supply curve – A curve describing the quantities of a good a producer is willing and able to sell (produce) at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. ...
... supply curve for a competitive firm. – Supply curve – A curve describing the quantities of a good a producer is willing and able to sell (produce) at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. ...
The Impact of Trade on Organization and Productivity"
... which to analyze individual …rm experiences in an international trade context. However, in this literature a …rm is just a technology to produce goods at a given marginal cost. The basic equilibrium framework of our model is similar to the one used in this literature but incorporates a much richer o ...
... which to analyze individual …rm experiences in an international trade context. However, in this literature a …rm is just a technology to produce goods at a given marginal cost. The basic equilibrium framework of our model is similar to the one used in this literature but incorporates a much richer o ...
1 - Alexander Mosesov`s
... Naturally, both authors and students are products of their own cultures. Their educational interaction is yet another reflection of the cultural backgrounds in many ways: in semantics, in paradigms, in mentality, etc. It is hard to expect from a Middle-Eastern or an EasternEuropean student to clearl ...
... Naturally, both authors and students are products of their own cultures. Their educational interaction is yet another reflection of the cultural backgrounds in many ways: in semantics, in paradigms, in mentality, etc. It is hard to expect from a Middle-Eastern or an EasternEuropean student to clearl ...
EPP Chapter 05.ppt [Read
... then supply is likely to be elastic. • If the nature of production is such that adjustments take longer, then supply is likely to be inelastic. ...
... then supply is likely to be elastic. • If the nature of production is such that adjustments take longer, then supply is likely to be inelastic. ...
demand in product/output markets
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement along a Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets Pr ...
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement along a Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets Pr ...
utility - Pearson
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
Document
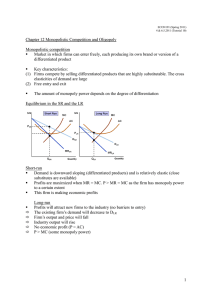
... (1) Market power relatively small and deadweight loss is small (2) Inefficiency is balanced by the benefit of increased product diversity which may easily outweigh deadweight loss ...
... (1) Market power relatively small and deadweight loss is small (2) Inefficiency is balanced by the benefit of increased product diversity which may easily outweigh deadweight loss ...
Chapter 12
... Consumer efficiency is achieved when it is not possible for consumers to become better off — to increase utility — by reallocating their budgets. • On the household’s demand curve • External benefits Producer efficiency occurs when a firm is producing at any point on its marginal cost curve, or equi ...
... Consumer efficiency is achieved when it is not possible for consumers to become better off — to increase utility — by reallocating their budgets. • On the household’s demand curve • External benefits Producer efficiency occurs when a firm is producing at any point on its marginal cost curve, or equi ...
of Demand - Ector County ISD.
... purchasing power increases for consumers –This is also demonstrated when the ...
... purchasing power increases for consumers –This is also demonstrated when the ...
Supply and Demand
... – Resource costs: cost to purchase factors of production will influence business decisions – Subsidies and taxes: government subsides encourage production, while taxes discourage production • NOTERS: factors that shift the supply curve ...
... – Resource costs: cost to purchase factors of production will influence business decisions – Subsidies and taxes: government subsides encourage production, while taxes discourage production • NOTERS: factors that shift the supply curve ...
single-price monopoly
... Among units of a good. Quantity discounts are an example. (But quantity discounts that reflect lower costs at higher volumes are not price discrimination.) ...
... Among units of a good. Quantity discounts are an example. (But quantity discounts that reflect lower costs at higher volumes are not price discrimination.) ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.