Is neuroimaging measuring information in the brain? | SpringerLink
... need to be decoded by a receiver. Thus, in Shannon’s formulation, the quantification of information over a channel was contingent on the existence of a ‘receiver’. The importance of a receiver in Shannon’s formulation seems to be neglected in modern neuroscience, perhaps because, for the communicati ...
... need to be decoded by a receiver. Thus, in Shannon’s formulation, the quantification of information over a channel was contingent on the existence of a ‘receiver’. The importance of a receiver in Shannon’s formulation seems to be neglected in modern neuroscience, perhaps because, for the communicati ...
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter?
... ACC is itself subdivided: - Dorsal ‘Cognitive’ division (red) - Ventral ‘Affective’ division (blue); “Activated in conflict between incompatible streams of information. Following conflict detection, the lateral prefrontal cortices… are engaged to resolve the conflict.” (Van Veen and Carter, 2002 ...
... ACC is itself subdivided: - Dorsal ‘Cognitive’ division (red) - Ventral ‘Affective’ division (blue); “Activated in conflict between incompatible streams of information. Following conflict detection, the lateral prefrontal cortices… are engaged to resolve the conflict.” (Van Veen and Carter, 2002 ...
PPT - Sheffield Department of Computer Science
... This is a good example of need to find a good way of representing the input can’t just present words to a net; have to find a way of encoding those words so they can be presented as a set of inputs. Assessing output: compare the pattern of output Wickelphone activations to the pattern that the corr ...
... This is a good example of need to find a good way of representing the input can’t just present words to a net; have to find a way of encoding those words so they can be presented as a set of inputs. Assessing output: compare the pattern of output Wickelphone activations to the pattern that the corr ...
Infancy: Physical Development
... Brain Development in Infancy • Myelination contributes to what infants are able to do. • Reflexive functions such as breathing due to myelination • Myelination of motor pathways allows neonates to show stereotyped reflexes. • Myelination will allow the disorganized movements of the neonate to come ...
... Brain Development in Infancy • Myelination contributes to what infants are able to do. • Reflexive functions such as breathing due to myelination • Myelination of motor pathways allows neonates to show stereotyped reflexes. • Myelination will allow the disorganized movements of the neonate to come ...
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake
... Peptide tyrosine-tyrosine (PYY) peptides produced by enteroendocrine cells in the lining of the gut ...
... Peptide tyrosine-tyrosine (PYY) peptides produced by enteroendocrine cells in the lining of the gut ...
Information Processing in Motor Learning
... Efferent neurons Motor Carry signals from the brain Sport Books Publisher ...
... Efferent neurons Motor Carry signals from the brain Sport Books Publisher ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Cerebellum receives impulses from cerebral cortex of intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction ...
... • Cerebellum receives impulses from cerebral cortex of intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction ...
e.4.1 state that some presynaptic neurons excite post synaptic
... GABA is a NT that opens _______________________ on the postsynaptic membrane. Cl- rushes in, _____________________ the post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reducing activity). It prevents neurons ...
... GABA is a NT that opens _______________________ on the postsynaptic membrane. Cl- rushes in, _____________________ the post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reducing activity). It prevents neurons ...
Lab Activity Sheets
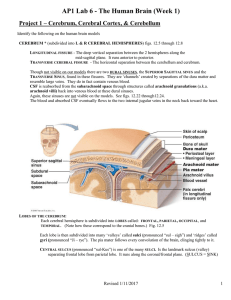
... LATERAL VENTRICLES (There are two… one in each cerebral hemisphere.) The deep cavity visible between the corpus callosum and the fornix. The depth of these will be best appreciated when you dissect the cow brain later. THIRD VENTRICLE– from the medial view, note the shallow groove beneath the fornix ...
... LATERAL VENTRICLES (There are two… one in each cerebral hemisphere.) The deep cavity visible between the corpus callosum and the fornix. The depth of these will be best appreciated when you dissect the cow brain later. THIRD VENTRICLE– from the medial view, note the shallow groove beneath the fornix ...
Reinig_Commentary
... of the neuron, temporarily changing the charge of the neuron during a phase called action potential. This action potential is transmitted down the axon to the synapse. If the synapse is a chemical synapse, the nerve impulse is transmitted via neurotransmitters. With an electrical synapse, where neur ...
... of the neuron, temporarily changing the charge of the neuron during a phase called action potential. This action potential is transmitted down the axon to the synapse. If the synapse is a chemical synapse, the nerve impulse is transmitted via neurotransmitters. With an electrical synapse, where neur ...
Brain Day Volunteer Instructor Manual
... Taste receptors are clustered into taste buds on our tongue, all over our mouth on the roof of our mouth, epiglottis and upper esophagus. At the top of each taste bud is an opening called a taste pore. This is where the taste bud comes into contact with food molecules to recognize four basic tastes: ...
... Taste receptors are clustered into taste buds on our tongue, all over our mouth on the roof of our mouth, epiglottis and upper esophagus. At the top of each taste bud is an opening called a taste pore. This is where the taste bud comes into contact with food molecules to recognize four basic tastes: ...
PDF
... water molecules which effectively results in the transport of these osmolyte-bound water molecules to ECF against a water gradient (Baslow, 1999a). However, these bound water molecules cannot be easily removed from ECF unless they are first released as free water. Thus, in addition to catabolizing N ...
... water molecules which effectively results in the transport of these osmolyte-bound water molecules to ECF against a water gradient (Baslow, 1999a). However, these bound water molecules cannot be easily removed from ECF unless they are first released as free water. Thus, in addition to catabolizing N ...
Neural tube formation: Previously- apical constriction, convergence
... 7. Does SHH work directly as a morphogen, or might it set up a relay of signals? Use of chimeras between wild-type, and smo-/- SHH non-responsive cells (which should provide a SHH non-responsive “barrier” to a relay) proves that SHH can move over a distance as a morphogen, and is not activating a re ...
... 7. Does SHH work directly as a morphogen, or might it set up a relay of signals? Use of chimeras between wild-type, and smo-/- SHH non-responsive cells (which should provide a SHH non-responsive “barrier” to a relay) proves that SHH can move over a distance as a morphogen, and is not activating a re ...
Chapter 15a
... Kindling Model of Epilepsy A series of alternating bilateral brain stimulations eventually elicits convulsions – the kindling phenomenon Typically amygdala or hippocampus Neural changes are permanent Produced by stimulation distributed over time ...
... Kindling Model of Epilepsy A series of alternating bilateral brain stimulations eventually elicits convulsions – the kindling phenomenon Typically amygdala or hippocampus Neural changes are permanent Produced by stimulation distributed over time ...
Unit06
... each hemisphere in the cerebrum Third ventricle - a vertical slit between the lateral ventricles and inferior to the right and left halves of the thalamus Fourth ventricle - space between the brainstem and the cerebellum ...
... each hemisphere in the cerebrum Third ventricle - a vertical slit between the lateral ventricles and inferior to the right and left halves of the thalamus Fourth ventricle - space between the brainstem and the cerebellum ...
Diverse Origins of Network Rhythms in Local Cortical Circuits
... has been argued that observation of brain rhythms is epiphenomenal—that methods for measuring electrical activity in populations of neurons requires local synchronization in order to generate a signal large enough to detect, e.g., using surface electroencephalography (EEG) electrodes. Because local ...
... has been argued that observation of brain rhythms is epiphenomenal—that methods for measuring electrical activity in populations of neurons requires local synchronization in order to generate a signal large enough to detect, e.g., using surface electroencephalography (EEG) electrodes. Because local ...
CDKL5 UK study
... “speckles” (Ricciardi et al. 2009) where CDKL5 may be important in the phosphorylation of the RS domain of serine-‐rich (SR) splicing factors. Phosphorylation of these splicing factors is neces ...
... “speckles” (Ricciardi et al. 2009) where CDKL5 may be important in the phosphorylation of the RS domain of serine-‐rich (SR) splicing factors. Phosphorylation of these splicing factors is neces ...
Resources: - Real Science
... We probably spend more time thinking about what we are going to do than in what we have done, says Karl Szpunar. “But not much is known about how we form these mental images of the future." Szpunar is lead author of the study. He is a psychology doctoral student in Arts & Sciences at Washington Uni ...
... We probably spend more time thinking about what we are going to do than in what we have done, says Karl Szpunar. “But not much is known about how we form these mental images of the future." Szpunar is lead author of the study. He is a psychology doctoral student in Arts & Sciences at Washington Uni ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... psychology to explore the causal link between inheritance and behavior. a. Chromosome b. Behavior ...
... psychology to explore the causal link between inheritance and behavior. a. Chromosome b. Behavior ...
Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human
... cells in the human cerebral cortex as 3, 7, 14, 19 –23, or 21–26 billion neurons and, very recently, 28 –39 billion glial cells (Pelvig et al., 2008), and the number of cells in the human cerebellum has been estimated as 70 or 101 billion neurons (Lange, 1975; Andersen et al., 1992) and fewer than 4 ...
... cells in the human cerebral cortex as 3, 7, 14, 19 –23, or 21–26 billion neurons and, very recently, 28 –39 billion glial cells (Pelvig et al., 2008), and the number of cells in the human cerebellum has been estimated as 70 or 101 billion neurons (Lange, 1975; Andersen et al., 1992) and fewer than 4 ...
Quiz
... 14. The ________ and _________ are important because they are involved in the myelination of nerve axons. a. Oligodendrocytes and microglia b. Astrocytes and Schwann cells c. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells d. Mi ...
... 14. The ________ and _________ are important because they are involved in the myelination of nerve axons. a. Oligodendrocytes and microglia b. Astrocytes and Schwann cells c. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells d. Mi ...
The Human Nervous System
... – Millions of sensory receptors detect changes, called stimuli, which occur inside and outside the body. ...
... – Millions of sensory receptors detect changes, called stimuli, which occur inside and outside the body. ...
Slide 1
... Sequence of events following addition of a surround stimulus to a center stimulus in an inhibition-stabilized network model of primary visual cortex. The circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that re ...
... Sequence of events following addition of a surround stimulus to a center stimulus in an inhibition-stabilized network model of primary visual cortex. The circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that re ...