COMPARISON BETWEEN ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS AND
... measurement noise. The work described in this article is still under development and is part of an interdepartmental project at the University of Aveiro, which will lead to the control of the atmosphere inside the kiln using two loops for temperature and for air/oxygen ratio control. To test the mod ...
... measurement noise. The work described in this article is still under development and is part of an interdepartmental project at the University of Aveiro, which will lead to the control of the atmosphere inside the kiln using two loops for temperature and for air/oxygen ratio control. To test the mod ...
“Epileptic Neurons” in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
... factor in the neuronal hyperexcitability seen in both acute and chronic epilepsy models. The demonstration of the de novo appearance of Ca2+-dependent intrinsic bursting in the pilocarpine model of TLE is intriguing. It would be of utmost importance to identify the molecular basis of this alteration ...
... factor in the neuronal hyperexcitability seen in both acute and chronic epilepsy models. The demonstration of the de novo appearance of Ca2+-dependent intrinsic bursting in the pilocarpine model of TLE is intriguing. It would be of utmost importance to identify the molecular basis of this alteration ...
the biological perspective
... Glial cells affect both the functioning and structure of neurons and specific types also have properties similar to stem cells, which allow them to develop into new neurons, both during prenatal development and in adult mammals (Bullock et al., 2005; Kriegstein & Alvarez-Buylla, 2009). Glial cells a ...
... Glial cells affect both the functioning and structure of neurons and specific types also have properties similar to stem cells, which allow them to develop into new neurons, both during prenatal development and in adult mammals (Bullock et al., 2005; Kriegstein & Alvarez-Buylla, 2009). Glial cells a ...
Alterations of the Giant Pyramidal Neurons (Betz Cells) in
... protein concentrations are within hippocampal CA1 and CA3 neurons (Reagan & McEwen, 2002). This down regulation of NOS mRNA may provide a partial explanation for the impaired long-term potentiation that is seen in the diabetic hippocampus, because induction and maintenance of potentiation are depend ...
... protein concentrations are within hippocampal CA1 and CA3 neurons (Reagan & McEwen, 2002). This down regulation of NOS mRNA may provide a partial explanation for the impaired long-term potentiation that is seen in the diabetic hippocampus, because induction and maintenance of potentiation are depend ...
Connectivity in Real and Simulated Associative Memories
... networks can arise due to a preferential growth process in which nodes that are already well connected are favoured by new connections. ...
... networks can arise due to a preferential growth process in which nodes that are already well connected are favoured by new connections. ...
Homework
... and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons all have a role in sensation, thought and response. Essential Questions: 1. How does the structure of the nervous system allow it to function? 2. H ...
... and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons all have a role in sensation, thought and response. Essential Questions: 1. How does the structure of the nervous system allow it to function? 2. H ...
The manifold nature of interpersonal relations: the quest for a
... special ways. If we share the same culture, we will, for example, all tattoo our body in a special striped fashion, pierce different parts of our body, or wear the same striped scarf when attending the games of our favourite soccer team. If we share with other individuals a given perspective on how ...
... special ways. If we share the same culture, we will, for example, all tattoo our body in a special striped fashion, pierce different parts of our body, or wear the same striped scarf when attending the games of our favourite soccer team. If we share with other individuals a given perspective on how ...
Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity
... (such as a Ca2+-activated cation current ICan) could require neuromodulatory signals such as acetylcholine15. Even if single cells are not bistable, the behavior of a cortical network is always the result of the interplay between intrinsic cellular properties and synaptic mechanisms16. Experiments a ...
... (such as a Ca2+-activated cation current ICan) could require neuromodulatory signals such as acetylcholine15. Even if single cells are not bistable, the behavior of a cortical network is always the result of the interplay between intrinsic cellular properties and synaptic mechanisms16. Experiments a ...
Review on Methods of Selecting Number of Hidden Nodes in
... expected output is not presented to the network. The system learns of its own by discovering and adapting to the structural features in the input pattern. In Reinforced learning method a supervisor is present but expected output is not present to the network. Its only indicates that either output is ...
... expected output is not presented to the network. The system learns of its own by discovering and adapting to the structural features in the input pattern. In Reinforced learning method a supervisor is present but expected output is not present to the network. Its only indicates that either output is ...
chapter30_Sensory Perception(1
... • 16 whales beached themselves when the US Navy tested a new sonar system – autopsies revealed blood in their ears and in acoustic fat ...
... • 16 whales beached themselves when the US Navy tested a new sonar system – autopsies revealed blood in their ears and in acoustic fat ...
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan
... Sensory (ascending) & Motor (descending) Pathways Before discussing the ascending and descending pathways, we need to give an orientation to the various areas of the cortex. (Figure 1) is a map of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s ar ...
... Sensory (ascending) & Motor (descending) Pathways Before discussing the ascending and descending pathways, we need to give an orientation to the various areas of the cortex. (Figure 1) is a map of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s ar ...
Bio Chap 13 - mlfarrispsych
... volumes and reduced white matter connections. Researchers argue that these brain changes result in decreased connectivity in the default mode network and a disruption of the attention-inhibition network. • In support, control children activated a discrete network ...
... volumes and reduced white matter connections. Researchers argue that these brain changes result in decreased connectivity in the default mode network and a disruption of the attention-inhibition network. • In support, control children activated a discrete network ...
Motor Pathways
... – Reticulospinal tract: automatic postural adjustments and movements (hip; shoulder) – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
... – Reticulospinal tract: automatic postural adjustments and movements (hip; shoulder) – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
1. Main hypotheses, concepts and theories in the study of
... plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles, has been revealed as an important pathological factor in the neural system[43]. An investigation which studied the amyloid deposition in the brain and other organs in 105 consecutive autopsy cases, aged 59 to 101 years, had verified a close relationship between ...
... plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles, has been revealed as an important pathological factor in the neural system[43]. An investigation which studied the amyloid deposition in the brain and other organs in 105 consecutive autopsy cases, aged 59 to 101 years, had verified a close relationship between ...
PDF-document - homepage.ruhr-uni
... during specific phases of visually guided reaches (Figure 1). A surprisingly high proportion of the SC units that modulated during the reach tasks were significantly distinct from previously described reach neurons (Werner, 1993; Werner et al., 1997a, 1997b; Stuphorn et al., 1999; Lünenburger et al ...
... during specific phases of visually guided reaches (Figure 1). A surprisingly high proportion of the SC units that modulated during the reach tasks were significantly distinct from previously described reach neurons (Werner, 1993; Werner et al., 1997a, 1997b; Stuphorn et al., 1999; Lünenburger et al ...
evolution of the first nervous systems ii
... comb jellies, have both complex nervous and mesoderm-derived muscular systems. These holoplanktonic predators also have sophisticated ciliated locomotion, behaviour and distinct development. Here, I will summarize the analysis of ctenophore’s neuro-muscular organization performed by our laboratory a ...
... comb jellies, have both complex nervous and mesoderm-derived muscular systems. These holoplanktonic predators also have sophisticated ciliated locomotion, behaviour and distinct development. Here, I will summarize the analysis of ctenophore’s neuro-muscular organization performed by our laboratory a ...
Unimodal or Bimodal Distribution of Synaptic Weights?
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
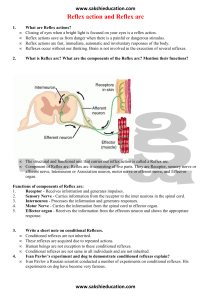
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... Reflex actions save us from danger when there is a painful or dangerous stimulus. Reflex actions are fast, immediate, automatic and involuntary responses of the body. Reflexes occur without our thinking. Brain is not involved in the execution of several reflexes. What is Reflex arc? What are the com ...
... Reflex actions save us from danger when there is a painful or dangerous stimulus. Reflex actions are fast, immediate, automatic and involuntary responses of the body. Reflexes occur without our thinking. Brain is not involved in the execution of several reflexes. What is Reflex arc? What are the com ...
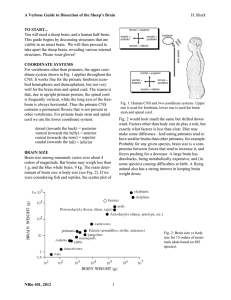
A Verbose Guide to Dissection of the Sheep`s Brain H
... current viewing distance). The abducens nerve is easy to identify if it is still attached. The little trochlear nerve violates the general rule and emerges from the dorsal surface of the brain stem. (It is visible on many of these sheep brains, though rarely on the human brains.) Although these same ...
... current viewing distance). The abducens nerve is easy to identify if it is still attached. The little trochlear nerve violates the general rule and emerges from the dorsal surface of the brain stem. (It is visible on many of these sheep brains, though rarely on the human brains.) Although these same ...
chapter 4 anatomy of the nervous system
... All somatic motor neurons are located within that lie outside the nervous system. the central nervous system. The autonomic motor neurons are The efferent pathway to skeletal muscle is activated by preganglionic neurons within monosynaptic. The motor neurons project the brain stem and the spinal cor ...
... All somatic motor neurons are located within that lie outside the nervous system. the central nervous system. The autonomic motor neurons are The efferent pathway to skeletal muscle is activated by preganglionic neurons within monosynaptic. The motor neurons project the brain stem and the spinal cor ...
Text S1.
... coordinates as each other (image registration to create fraction templates). Second, the transformed images of the horizontal (H) sectioning series at a 50 m resolution were referred to as an Anatomical Image Atlas that showed the macroscopic anatomical information in the same coordinates as the fr ...
... coordinates as each other (image registration to create fraction templates). Second, the transformed images of the horizontal (H) sectioning series at a 50 m resolution were referred to as an Anatomical Image Atlas that showed the macroscopic anatomical information in the same coordinates as the fr ...
Evolution of Nervous Systems and Brains
... some polychaetes there are giant fibers with very fast conduction velocity (three in oligochaetes) separated from the thinner fibers. Annelids possess a large variety of tactile and chemosensory organs, feelers or antennae, palps, and one ciliated “nuchal organ” possibly involved in light detection. ...
... some polychaetes there are giant fibers with very fast conduction velocity (three in oligochaetes) separated from the thinner fibers. Annelids possess a large variety of tactile and chemosensory organs, feelers or antennae, palps, and one ciliated “nuchal organ” possibly involved in light detection. ...
Before the Americans
... of the membranes as being a principle of function for the meninges. Sutherland introduced the idea that a fulcrum is a point of rest, balance, and an opportunity for change within the system. He also discovered, as did Swedenborg and Still, the divinity of life force within the waters of the brain. ...
... of the membranes as being a principle of function for the meninges. Sutherland introduced the idea that a fulcrum is a point of rest, balance, and an opportunity for change within the system. He also discovered, as did Swedenborg and Still, the divinity of life force within the waters of the brain. ...