PDF
... V2a and V2b interneurons. But are these V2 neurons generated by cell divisions that produce progenitor cells and neurons or by asymmetric cell divisions of ‘pair-producing’ progenitors? On p. 3001, Kimura and co-workers report that these interneurons form by the latter process via Delta-Notch signal ...
... V2a and V2b interneurons. But are these V2 neurons generated by cell divisions that produce progenitor cells and neurons or by asymmetric cell divisions of ‘pair-producing’ progenitors? On p. 3001, Kimura and co-workers report that these interneurons form by the latter process via Delta-Notch signal ...
Plants and Pollinators
... Organization of Retina • Photoreceptors lie at the back of the retina, in front of a pigmented epithelium • For light to reach the photoreceptors, it must pass layers of neurons involved in ...
... Organization of Retina • Photoreceptors lie at the back of the retina, in front of a pigmented epithelium • For light to reach the photoreceptors, it must pass layers of neurons involved in ...
the structure of the nervous system
... • These are the large neurons that have the cell body lying to one side of the continuous dendritic process and axon • This makes it appear that the cytoplasmic process splits the axon into two portions • A peripheral process takes the action potential to the cell body ...
... • These are the large neurons that have the cell body lying to one side of the continuous dendritic process and axon • This makes it appear that the cytoplasmic process splits the axon into two portions • A peripheral process takes the action potential to the cell body ...
Acetylcholinesterase in Neuron Survival and
... Strategies to Promote Regeneration Infusion of Trophic factors Guiding growing axons (neurites) to appropriate targets Strengthen axons and synapses by stimulation Stem cell therapy Nanomaterials can contribute significantly to all of these measures ! ...
... Strategies to Promote Regeneration Infusion of Trophic factors Guiding growing axons (neurites) to appropriate targets Strengthen axons and synapses by stimulation Stem cell therapy Nanomaterials can contribute significantly to all of these measures ! ...
Nervous System
... the different types of neuroglia and list their location and function within the nervous system below each drawing DO NOT draw Schwann cells but do list its location and function ...
... the different types of neuroglia and list their location and function within the nervous system below each drawing DO NOT draw Schwann cells but do list its location and function ...
Bolt IRM Mod 03
... and Guillain-Barré syndrome. It is now clear that MS attacks the myelin sheaths of axon bundles in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. (Sclerosis means “hardening” and refers to the lesions that develop around those bundles; multiple refers to the fact that the disease attacks many sites simul ...
... and Guillain-Barré syndrome. It is now clear that MS attacks the myelin sheaths of axon bundles in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. (Sclerosis means “hardening” and refers to the lesions that develop around those bundles; multiple refers to the fact that the disease attacks many sites simul ...
Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... Nerve impulses result from the flow of ions across their plasma membranes. – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, ...
... Nerve impulses result from the flow of ions across their plasma membranes. – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Exam 1 Which of the
... 51. Neuroblasts from alar plates of the midbrain (sensory) migrate into the tectum (roof) and aggregate to form 4 large groups of neurons. Which paired colliculi are responsible for auditory reflexes? a. Superior colliculi b. Inferior colliculi c. Anterior colliculi d. Posterior colliculi 52. Neurob ...
... 51. Neuroblasts from alar plates of the midbrain (sensory) migrate into the tectum (roof) and aggregate to form 4 large groups of neurons. Which paired colliculi are responsible for auditory reflexes? a. Superior colliculi b. Inferior colliculi c. Anterior colliculi d. Posterior colliculi 52. Neurob ...
Product Information N2 Supplement (100X)
... v. Add 5 mL 100X NEAA 3. Add N2 Supplement to 1X final concentration. 4. Add FGF2 (GSR‐2001) to 20 ng/mL. For some applications you may also add EGF to 20 ng/mL. 5. The complete 1X N2 medium can be stored at 4°C for up to three weeks. To preserve FGF2 activity, avoid repeatedly warming the med ...
... v. Add 5 mL 100X NEAA 3. Add N2 Supplement to 1X final concentration. 4. Add FGF2 (GSR‐2001) to 20 ng/mL. For some applications you may also add EGF to 20 ng/mL. 5. The complete 1X N2 medium can be stored at 4°C for up to three weeks. To preserve FGF2 activity, avoid repeatedly warming the med ...
Sample Midterm Exam
... 12. How does the tongue of a supertaster differ from the tongue of a non-taster? A. supertasters have more foliate papillae on their tongues than non-tasters do B. non-tasters have no fungiform papillae on the tongue, supertasters have them C. supertasters have many more fungiform papillae on the t ...
... 12. How does the tongue of a supertaster differ from the tongue of a non-taster? A. supertasters have more foliate papillae on their tongues than non-tasters do B. non-tasters have no fungiform papillae on the tongue, supertasters have them C. supertasters have many more fungiform papillae on the t ...
OUTLINE FORMAT-Unit 3A Biological Basis of Behavior Directions
... Directions: Include all underlined headings and subheadings that appear in this guide. Number and answer questions one 1 through 12. Define numbers 1 through 44, being sure to highlight and number the terms. ...
... Directions: Include all underlined headings and subheadings that appear in this guide. Number and answer questions one 1 through 12. Define numbers 1 through 44, being sure to highlight and number the terms. ...
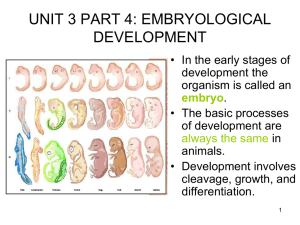
Unit 3 part 4 PPT
... will become the lining of the digestive system. • The blastopore is the future anus of the embryo. ...
... will become the lining of the digestive system. • The blastopore is the future anus of the embryo. ...
Mechanisms of development: cell movement
... http://www.endotext.org/pediatrics/pediatrics7/pediatrics7.html ...
... http://www.endotext.org/pediatrics/pediatrics7/pediatrics7.html ...
2806nn1
... Network Design? 1) Restricting the network architecture through the use of local connections known as receptive fields. 2) Constraining the choice of synaptic weights through the use of weight-sharing. ...
... Network Design? 1) Restricting the network architecture through the use of local connections known as receptive fields. 2) Constraining the choice of synaptic weights through the use of weight-sharing. ...
Effects of experience on brain development
... Of course, the establishment of a synaptic connection also requires efforts on the part of the postsynaptic cell; this cell must contribute its parts of the synapse, including the postsynaptic receptors. The chemical signals that the cells exchange to tell one another to establish these connections ...
... Of course, the establishment of a synaptic connection also requires efforts on the part of the postsynaptic cell; this cell must contribute its parts of the synapse, including the postsynaptic receptors. The chemical signals that the cells exchange to tell one another to establish these connections ...
Chapter 14 Part 2
... neurons have temperature gated channels – Sense cold or warm: burning is sensed by different neurons called nociceptors which signal damaging temperature extremes ...
... neurons have temperature gated channels – Sense cold or warm: burning is sensed by different neurons called nociceptors which signal damaging temperature extremes ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... travel along the spinal cord. Contains grey matter – made up of nerve cell bodies. Axons of these cells form the white matter of the spinal cord. ...
... travel along the spinal cord. Contains grey matter – made up of nerve cell bodies. Axons of these cells form the white matter of the spinal cord. ...
CNS Embryology 2pptx (2)
... • Paraxial mesenchyme in the trunk and caudal regions of the head. • Neural crest in regions rostral to the mesencephalon. • The meninges may be divided in development into the pachymeninx (dura mater) and leptomeninges (arachnoid mater, subarachnoid space with arachnoid cells and fibres, and pia ma ...
... • Paraxial mesenchyme in the trunk and caudal regions of the head. • Neural crest in regions rostral to the mesencephalon. • The meninges may be divided in development into the pachymeninx (dura mater) and leptomeninges (arachnoid mater, subarachnoid space with arachnoid cells and fibres, and pia ma ...
Nervous System - science
... peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
... peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue
... between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synaptic cleft. Provides slow one-way information flow ...
... between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synaptic cleft. Provides slow one-way information flow ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... Schwann cells - in peripheral ns only; form myelin sheath and neurolemma around axons of neurons outside of brain and spinal cord. (more on myelin sheaths later) *List five types of glial cells and tell what the function is of each. *Which glial cells are only in the central nervous system (brain a ...
... Schwann cells - in peripheral ns only; form myelin sheath and neurolemma around axons of neurons outside of brain and spinal cord. (more on myelin sheaths later) *List five types of glial cells and tell what the function is of each. *Which glial cells are only in the central nervous system (brain a ...
Human Brain Development - Life Sciences Outreach Program
... Neurons migrate towards the marginal side in waves Each wave of neurons travel past the earlier layers Neural Tube (early CNS) Central Canal (early spinal cord or brain ventricles) ...
... Neurons migrate towards the marginal side in waves Each wave of neurons travel past the earlier layers Neural Tube (early CNS) Central Canal (early spinal cord or brain ventricles) ...
PSYC465 - neuroanatomy
... blood vessels. Cells in the walls of cerebral blood vessels are tightly packed. This provides a barrier for the passage of some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is ...
... blood vessels. Cells in the walls of cerebral blood vessels are tightly packed. This provides a barrier for the passage of some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is ...
answers (complete)
... C. The nine-banded armadillo normally gives birth to monozygotic (genetically identical) quadruplets, the only mammal to do this. The fertilized egg develops to a single blastocyst with an unusually large epiblast composed of four cup-shaped quadrants, all underlain by a continuous hypoblast layer ( ...
... C. The nine-banded armadillo normally gives birth to monozygotic (genetically identical) quadruplets, the only mammal to do this. The fertilized egg develops to a single blastocyst with an unusually large epiblast composed of four cup-shaped quadrants, all underlain by a continuous hypoblast layer ( ...