Maintenance and Regeneration of the Nerve Net in Hydra1 The
... stitial cells was initially assumed to be the answer (e.g., Bode and David, 1978), recent evidence indicates the second explanation is more probable. Both large and small interstitial cells are capable of migration as single cells, and possibly in pairs (Tardent and Morgenthaler, 1966; Campbell, 196 ...
... stitial cells was initially assumed to be the answer (e.g., Bode and David, 1978), recent evidence indicates the second explanation is more probable. Both large and small interstitial cells are capable of migration as single cells, and possibly in pairs (Tardent and Morgenthaler, 1966; Campbell, 196 ...
A Primer on Neurobiology and the Brain for Information Systems
... (see Fig. 2.4). Typically, a cell body has multiple dendrites, but only one axon (note ...
... (see Fig. 2.4). Typically, a cell body has multiple dendrites, but only one axon (note ...
Distinct or Gradually Changing Spatial and Nonspatial
... Figure 1. Properties of place-field size, theta oscillation, and nonspatial responses along the dorsoventral axis of the hippocampus. A, Summary of data from different studies (Jung et al., 1994; Maurer et al., 2005; Kjelstrup et al., 2008; Royer et al., 2010) showing the ratio of place-field size i ...
... Figure 1. Properties of place-field size, theta oscillation, and nonspatial responses along the dorsoventral axis of the hippocampus. A, Summary of data from different studies (Jung et al., 1994; Maurer et al., 2005; Kjelstrup et al., 2008; Royer et al., 2010) showing the ratio of place-field size i ...
Lectin and Peptide Expression in Nodose
... stained with GSA I-B4 in purely-fixed tissue than those stained with GSA I-B4 in well-fixed tissue (13). The presence of GSA I-B4 in neurons of NG indicates that these neurons contribute to the innervation of the nucleus of the solitary track (NTS) and area postrema of the brain stem, the central pr ...
... stained with GSA I-B4 in purely-fixed tissue than those stained with GSA I-B4 in well-fixed tissue (13). The presence of GSA I-B4 in neurons of NG indicates that these neurons contribute to the innervation of the nucleus of the solitary track (NTS) and area postrema of the brain stem, the central pr ...
Chapter 8
... • A neuron whose axon forms synapses with extrafusal muscle fibers of a skeletal muscle: activation contracts the muscle fibers. • Intrafusal Muscle Fiber • a muscle fiber that functions as a stretch receptor; arranged parallel to the extrafusal muscle fibers, thus detecting changes in muscle length ...
... • A neuron whose axon forms synapses with extrafusal muscle fibers of a skeletal muscle: activation contracts the muscle fibers. • Intrafusal Muscle Fiber • a muscle fiber that functions as a stretch receptor; arranged parallel to the extrafusal muscle fibers, thus detecting changes in muscle length ...
Nervous_system_Tissue_Overview0
... In order to prevent continuous stimulation, NT is removed from the synapse through: ...
... In order to prevent continuous stimulation, NT is removed from the synapse through: ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous (5days)
... The cell body of a neuron contains the nucleus, which regulates the production of proteins within the cell. ...
... The cell body of a neuron contains the nucleus, which regulates the production of proteins within the cell. ...
Mental Processes -- How the Mind Arises from the Brain Roger Ellman
... structure and its biological / electrochemical functioning. But, it is the "software", how the neural components logically interact, that produces the results that we experience in our own minds. The objective is intelligence -- how we see, think, remember, know ourselves, learn, plan create. To des ...
... structure and its biological / electrochemical functioning. But, it is the "software", how the neural components logically interact, that produces the results that we experience in our own minds. The objective is intelligence -- how we see, think, remember, know ourselves, learn, plan create. To des ...
Nervous Systems
... glycogen to glucose, and the adrenal medulla increases secretion of epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Activation of the parasympathetic division generally causes opposite responses that promote calming and a return to selfmaintenance functions (“rest and digest”). Thus, heart rate decreas ...
... glycogen to glucose, and the adrenal medulla increases secretion of epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Activation of the parasympathetic division generally causes opposite responses that promote calming and a return to selfmaintenance functions (“rest and digest”). Thus, heart rate decreas ...
Neural Substrate Expansion for the Restoration of Brain
... this deficiency could be the result of a lack of experimental emphasis or suitable models, it may be that these biological strategies for neural substrate expansion lack the fundamental organization to support complex brain function. The highly precise architecture of the brain, at the scale of micr ...
... this deficiency could be the result of a lack of experimental emphasis or suitable models, it may be that these biological strategies for neural substrate expansion lack the fundamental organization to support complex brain function. The highly precise architecture of the brain, at the scale of micr ...
Chapter 47
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
Ectopic Pax-3 Activates MyoD and Myf
... lane 7). Thus, whereas Wnt or Shh signals alone are insufficient to induce high level expression of either Pax-3 and Pax-7 or myogenic markers (i.e., MyoD, Myf-5, myogenin, and MHC), the combination of these two signals is sufficient to induce both dermomyotomal (Pax-3 and Pax-7) and myogenic marker ...
... lane 7). Thus, whereas Wnt or Shh signals alone are insufficient to induce high level expression of either Pax-3 and Pax-7 or myogenic markers (i.e., MyoD, Myf-5, myogenin, and MHC), the combination of these two signals is sufficient to induce both dermomyotomal (Pax-3 and Pax-7) and myogenic marker ...
Neurobilogy of Sleep
... Neurons in the LDT and PPT areas that are located in the dorsal midbrain and pons make up the majority of the dorsal RAS pathway through the pons and are cholinergic. • Some of the neurons are active during wake and REM sleep (wake/ REM-on), whereas others are active mainly during REM sleep (REM-on) ...
... Neurons in the LDT and PPT areas that are located in the dorsal midbrain and pons make up the majority of the dorsal RAS pathway through the pons and are cholinergic. • Some of the neurons are active during wake and REM sleep (wake/ REM-on), whereas others are active mainly during REM sleep (REM-on) ...
Deciphering a neural code for vision
... detecting the patterns of coherent activity. Neural coding by this relatively simple eye helps explain how horseshoe crabs find mates and may lead to a better understanding of how more complex sensory organs process information. Living in a world rich with information, animals are highly efficient a ...
... detecting the patterns of coherent activity. Neural coding by this relatively simple eye helps explain how horseshoe crabs find mates and may lead to a better understanding of how more complex sensory organs process information. Living in a world rich with information, animals are highly efficient a ...
49-Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
Beyond George Engel`s Model of Psychopathology
... conscious "mind" remains problematic. Nevertheless, biopsychosocial ideas about mental illness derive their principle recent theoretical support by extrapolating from the non-quantum assumption that normal individual consciousness and group psychology emerge, phase-like, out of classical neural netw ...
... conscious "mind" remains problematic. Nevertheless, biopsychosocial ideas about mental illness derive their principle recent theoretical support by extrapolating from the non-quantum assumption that normal individual consciousness and group psychology emerge, phase-like, out of classical neural netw ...
Principle of Superposition-free Memory - Deep Blue
... of firing. The problem of memory is thus to reconstruct this pattern, but in response to a secondary pattern of firing concomitant to an event other than the original input (for example, part of the original input or some other input with which it has been associated). Presumably this means that at ...
... of firing. The problem of memory is thus to reconstruct this pattern, but in response to a secondary pattern of firing concomitant to an event other than the original input (for example, part of the original input or some other input with which it has been associated). Presumably this means that at ...
NIH Public Access
... NIH-PA Author Manuscript NIH-PA Author Manuscript NIH-PA Author Manuscript ...
... NIH-PA Author Manuscript NIH-PA Author Manuscript NIH-PA Author Manuscript ...
Chapter 1 - Hyman Hartman
... development of the nervous system (Brain and Spinal Chord), the circulatory system (Heart, Arteries and Veins) the skeletal system (Skull, Vertebrate Column and Limbs) the muscular system (Skeletal Muscle, Cardiac Muscle and Smooth Muscle), the immunological system (Bone Marrow, Macrophages, B and T ...
... development of the nervous system (Brain and Spinal Chord), the circulatory system (Heart, Arteries and Veins) the skeletal system (Skull, Vertebrate Column and Limbs) the muscular system (Skeletal Muscle, Cardiac Muscle and Smooth Muscle), the immunological system (Bone Marrow, Macrophages, B and T ...
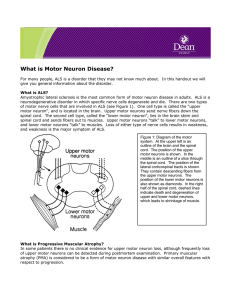
What is Motor Neuron
... food (from a grocery store of from a farm), source of drinking water (city or from a well), occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is ...
... food (from a grocery store of from a farm), source of drinking water (city or from a well), occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is ...
POWERPOINT VERSION ()
... • two hemispheres • vermis connects hemispheres • cerebellar cortex – gray matter • arbor vitae – white matter • cerebellar peduncles – nerve fiber tracts • dentate nucleus – largest nucleus in cerebellum • integrates sensory information concerning position of body parts • coordinates skeletal muscl ...
... • two hemispheres • vermis connects hemispheres • cerebellar cortex – gray matter • arbor vitae – white matter • cerebellar peduncles – nerve fiber tracts • dentate nucleus – largest nucleus in cerebellum • integrates sensory information concerning position of body parts • coordinates skeletal muscl ...