Community Ecology
... Predator Prey Interactions - Prey species increases, predator also increases. Prey species declines, ...
... Predator Prey Interactions - Prey species increases, predator also increases. Prey species declines, ...
Characteristics of exponential and logistic growth
... What are some interspecific interactions in a community? What are some defenses against predation or herbivory? What are some things that can influence species richness? What IS species richness? How does a keystone species differ from a dominant species? What do pyramids of energy (production) and ...
... What are some interspecific interactions in a community? What are some defenses against predation or herbivory? What are some things that can influence species richness? What IS species richness? How does a keystone species differ from a dominant species? What do pyramids of energy (production) and ...
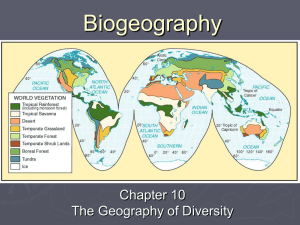
Chapter 10: The Geography of Diversity
... the organism on the left occurs in a hot desert habitat and the one on the right occurs in a cold tundra environment ...
... the organism on the left occurs in a hot desert habitat and the one on the right occurs in a cold tundra environment ...
Adaptation strategy - Wisconsin Initiative on Climate Change Impacts
... example, amphibians that have permeable skin and require water for reproduction will suffer from drought while species that need snow cover to rest under in the winter may not have adequate protection. Adaptation strategy: Land Protection should be grounded in climate-sound strategies such as repres ...
... example, amphibians that have permeable skin and require water for reproduction will suffer from drought while species that need snow cover to rest under in the winter may not have adequate protection. Adaptation strategy: Land Protection should be grounded in climate-sound strategies such as repres ...
Tortoise Tales
... 2. Predation: One organism (the predator) kills and consumes another (the prey) for food (energy). 3. Parasitism: One organism (the parasite) takes food (energy) from another (the host) without killing it. 4. Mutualism: A relationship involving two organisms in which both organisms benefit. 5. Comme ...
... 2. Predation: One organism (the predator) kills and consumes another (the prey) for food (energy). 3. Parasitism: One organism (the parasite) takes food (energy) from another (the host) without killing it. 4. Mutualism: A relationship involving two organisms in which both organisms benefit. 5. Comme ...
Chapter 8, Section 2 Notes
... Bellringer “As more individuals are produced that can possibly survive, there must…be a struggle for existence, either one individual with another of the same species, or with the individuals of distinct species, or with the physical conditions of life.” - Charles Darwin How does this quote relate t ...
... Bellringer “As more individuals are produced that can possibly survive, there must…be a struggle for existence, either one individual with another of the same species, or with the individuals of distinct species, or with the physical conditions of life.” - Charles Darwin How does this quote relate t ...
ecosystem answers
... Habitat (/environment) + community (/described)/ abiotic and biotic factors in a defined area/named area; ...
... Habitat (/environment) + community (/described)/ abiotic and biotic factors in a defined area/named area; ...
Vocab Chapter 22-24
... allo- other; -metron measure (allometric growth: the variation in the relative rates of growth of various parts of the body, which helps shape the organism) ana- up; -genesis origin, birth (anagenesis: a pattern of evolutionary change involving the transformation of an entire population, sometimes t ...
... allo- other; -metron measure (allometric growth: the variation in the relative rates of growth of various parts of the body, which helps shape the organism) ana- up; -genesis origin, birth (anagenesis: a pattern of evolutionary change involving the transformation of an entire population, sometimes t ...
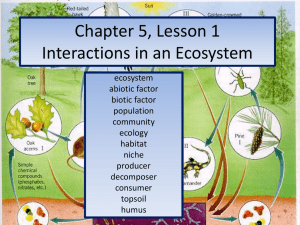
Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Interactions in an Ecosystem
... niche – the role of an organism in its community What does the species eat? What eats the species? ...
... niche – the role of an organism in its community What does the species eat? What eats the species? ...
The Macaques: Studies in Ecology, Behavior and Evolution, D.G.
... have neglected to point out which species combinations occur together in the wild and which do not. For instance, 19 of the 32 hybrids that are listed on page 128 are impossible in the wild, and it is intriguing that there are more live hybrids with the 'impossible' combinations than with the 'possi ...
... have neglected to point out which species combinations occur together in the wild and which do not. For instance, 19 of the 32 hybrids that are listed on page 128 are impossible in the wild, and it is intriguing that there are more live hybrids with the 'impossible' combinations than with the 'possi ...
Predator or Prey? - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... Neither can survive for long periods without the other ...
... Neither can survive for long periods without the other ...
Community Ecology
... • I can evaluate the claims, evidence and reasoning that the complex interactions in ecosystems maintain relatively consistent numbers and types of organisms in stable conditions, but changing conditions may result in a new ecosystem. ...
... • I can evaluate the claims, evidence and reasoning that the complex interactions in ecosystems maintain relatively consistent numbers and types of organisms in stable conditions, but changing conditions may result in a new ecosystem. ...
Lecture and General Ecology Textbooks
... pioneer, and describe it’s characteristics. Identify a Non-pioneer plant and describe it’s characteristics. What would be the end point of succession? ...
... pioneer, and describe it’s characteristics. Identify a Non-pioneer plant and describe it’s characteristics. What would be the end point of succession? ...
Biology Notes: Community Interactions
... – ______________________, nutrients, light, ______________________, space – Occurs due to a______________________ number of ______________________ ...
... – ______________________, nutrients, light, ______________________, space – Occurs due to a______________________ number of ______________________ ...
Notes - 3.3 - Invasive Species and Succession Powerpoint
... NICHE • The role an organism plays in a community/ecosystem • Examples: Worm as a composter, Wolves in Alaska control Caribou population ...
... NICHE • The role an organism plays in a community/ecosystem • Examples: Worm as a composter, Wolves in Alaska control Caribou population ...
F2009L02526 F2009L02526
... It is typically found in valley bottoms and gentle slopes below 600 m above seal level (asl) (but can occur up to 700 m asl); It is typically treeless with, at most, a sparse tree cover; The vegetation is predominantly native; Dominant1 grasses often form a dense sward; The ecological community occu ...
... It is typically found in valley bottoms and gentle slopes below 600 m above seal level (asl) (but can occur up to 700 m asl); It is typically treeless with, at most, a sparse tree cover; The vegetation is predominantly native; Dominant1 grasses often form a dense sward; The ecological community occu ...
Community Ecology
... A scientist grew 2 species of Galium (Bedstraw) The presence/absence of a species determined by competition with other species; (2) that conditions of the environment (in this case, soil type) affected the outcome of competition; (3) that competition might be felt very broadly at first (i.e., from ...
... A scientist grew 2 species of Galium (Bedstraw) The presence/absence of a species determined by competition with other species; (2) that conditions of the environment (in this case, soil type) affected the outcome of competition; (3) that competition might be felt very broadly at first (i.e., from ...
Unit 2- Ecology
... Planet Earth from Pole to Pole, symbiosis lab, bottleneck gene lab, natural selection (Kettlewell) lab, designs for defense video, wildlife specimen lab, Bill Nye Food Web, Owl Pellet lab, Forest food chain game, I am Legend Clip, Succession flow charts ...
... Planet Earth from Pole to Pole, symbiosis lab, bottleneck gene lab, natural selection (Kettlewell) lab, designs for defense video, wildlife specimen lab, Bill Nye Food Web, Owl Pellet lab, Forest food chain game, I am Legend Clip, Succession flow charts ...
File
... feeds on another organism The organism doing the killing is the predator The organism being killed is the prey ...
... feeds on another organism The organism doing the killing is the predator The organism being killed is the prey ...
7th grade Science
... population reproduce at a constant rate, so that the larger a population gets, the faster it grows ...
... population reproduce at a constant rate, so that the larger a population gets, the faster it grows ...
glossary
... Biotic Potential: the capacity of a population of organisms to increase in numbers under optimum environmental conditions. Interspecific Competition: Predation: a relation between animals in which one organism captures and feeds on others. In this relationship, only the predator benefits. Extinction ...
... Biotic Potential: the capacity of a population of organisms to increase in numbers under optimum environmental conditions. Interspecific Competition: Predation: a relation between animals in which one organism captures and feeds on others. In this relationship, only the predator benefits. Extinction ...
GEOG 346: Day 13
... relatively robust ecological cores and corridors linking these that allow migration from one to another, and the repopulation of areas low in species diversity or in need of mates of reproduction. The corridors can also serve as alternative transportation greenways. The idea is not new but goes back ...
... relatively robust ecological cores and corridors linking these that allow migration from one to another, and the repopulation of areas low in species diversity or in need of mates of reproduction. The corridors can also serve as alternative transportation greenways. The idea is not new but goes back ...
Ecological fitting

Ecological fitting is ""the process whereby organisms colonize and persist in novel environments, use novel resources or form novel associations with other species as a result of the suites of traits that they carry at the time they encounter the novel condition.” It can be understood as a situation in which a species' interactions with its biotic and abiotic environment seem to indicate a history of coevolution, when in actuality the relevant traits evolved in response to a different set of biotic and abiotic conditions. The simplest form of ecological fitting is resource tracking, in which an organism continues to exploit the same resources, but in a new host or environment. In this framework, the organism occupies a multidimensional operative environment defined by the conditions in which it can persist, similar to the idea of the Hutchinsonian niche. In this case, a species can colonize new environments (e.g. an area with the same temperature and water regime) and/or form new species interactions (e.g. a parasite infecting a new host) which can lead to the misinterpretation of the relationship as coevolution, although the organism has not evolved and is continuing to exploit the same resources it always has. The more strict definition of ecological fitting requires that a species encounter an environment or host outside of its original operative environment and obtain realized fitness based on traits developed in previous environments that are now co-opted for a new purpose. This strict form of ecological fitting can also be expressed either as colonization of new habitat or the formation of new species interactions.