nervous system
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes ...
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes ...
Neurons
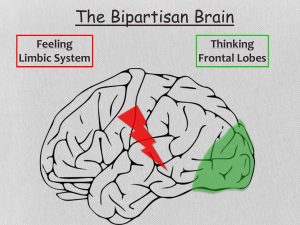
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
03/14 PPT
... Is there a map of different smells in the brain? Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) ...
... Is there a map of different smells in the brain? Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) ...
Nervous System
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
Drugs
... than the one intended • Tolerance is a condition in which a persons body becomes used to the effect of a medicine and needs greater amounts • What happens when you mix medications – Medicine may have a stronger effect than it would by itself – Combining may produce unexpected effects – One medicine ...
... than the one intended • Tolerance is a condition in which a persons body becomes used to the effect of a medicine and needs greater amounts • What happens when you mix medications – Medicine may have a stronger effect than it would by itself – Combining may produce unexpected effects – One medicine ...
Benzodiazepines - Sarah M. Brothwell
... GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter. Meaning that it tells the neurons that it comes in contact with to slow down ...
... GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter. Meaning that it tells the neurons that it comes in contact with to slow down ...
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction- L4
... attached to plasma carrier proteins. Hormones dissociate from carrier proteins to pass through lipid component of the target plasma membrane. Receptors for the lipophilic hormones are known as nuclear hormone receptors. ...
... attached to plasma carrier proteins. Hormones dissociate from carrier proteins to pass through lipid component of the target plasma membrane. Receptors for the lipophilic hormones are known as nuclear hormone receptors. ...
Pull out the stops for plasticity
... allow the relatively slow metabotropic process to take effect and enable LTP. This might seem unusual — after all, we don’t need to be presented with information 300 times before learning a new association. Why was such a strong protocol required? In an intact brain, specific neuromodulator chemical ...
... allow the relatively slow metabotropic process to take effect and enable LTP. This might seem unusual — after all, we don’t need to be presented with information 300 times before learning a new association. Why was such a strong protocol required? In an intact brain, specific neuromodulator chemical ...
Chapter 9b final
... Pineal Gland – gland attached to the dorsal tectum; produces melatonin and plays a role in circadian and seasonal rhythms. ...
... Pineal Gland – gland attached to the dorsal tectum; produces melatonin and plays a role in circadian and seasonal rhythms. ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
Unit 2 The Brain
... which of the following is TRUE? – A. the action potential will move much slower down the axon – B. The action potential will move much faster down the axon – C. The neuron must be a sensory neuron – D. The threshold of excitation will increase – E. the threshold of excitation will decrease ...
... which of the following is TRUE? – A. the action potential will move much slower down the axon – B. The action potential will move much faster down the axon – C. The neuron must be a sensory neuron – D. The threshold of excitation will increase – E. the threshold of excitation will decrease ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... at the University of Parma, Italy discovered mirror neurons in 1995. It was an accidental discovery that occurred while conducting research on motor neurons in monkeys. ...
... at the University of Parma, Italy discovered mirror neurons in 1995. It was an accidental discovery that occurred while conducting research on motor neurons in monkeys. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... vesicles with the presynaptic membrane 4. Acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane 5. When binding occurs, they open up their channels and depolarize the postsynaptic membrane 6. The spreading depolarization fires an action potentia ...
... vesicles with the presynaptic membrane 4. Acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane 5. When binding occurs, they open up their channels and depolarize the postsynaptic membrane 6. The spreading depolarization fires an action potentia ...
ee 497 – recent trends in biomedical engineering
... order to appreciate biomedical informatics 2. recognize biomolecule as tiny machine performing functions like motors and sensors 3. identify frontiers in biomedical engineering sciences and exploratory technology to find solutions to biomedical problems including issues like drug delivery, drug desi ...
... order to appreciate biomedical informatics 2. recognize biomolecule as tiny machine performing functions like motors and sensors 3. identify frontiers in biomedical engineering sciences and exploratory technology to find solutions to biomedical problems including issues like drug delivery, drug desi ...
study notes quiz 1
... 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance”: communicates with caudate and basil ganglia; involved in control of voluntary movement. (c) CONTROLS EYE MOVEMENTS Diencephalon: “two-brains” 1) surrounds the ...
... 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance”: communicates with caudate and basil ganglia; involved in control of voluntary movement. (c) CONTROLS EYE MOVEMENTS Diencephalon: “two-brains” 1) surrounds the ...
Practice Test #2
... 2. After 3 hours of playing a physically exhausting professional tennis match, Chitra began to experience a sense of physical exhilaration and pleasure. It is likely that her feelings were most directly linked to the release of: a. dopamine. b. acetylcholine. c. endorphins. d. serotonin. 3. The reti ...
... 2. After 3 hours of playing a physically exhausting professional tennis match, Chitra began to experience a sense of physical exhilaration and pleasure. It is likely that her feelings were most directly linked to the release of: a. dopamine. b. acetylcholine. c. endorphins. d. serotonin. 3. The reti ...
The Nervous System
... neurons Nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain Your brain interprets the impulses Impulses travel along thousands of motor neurons Motor neurons send the impulses to muscles, which carry out the response ...
... neurons Nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain Your brain interprets the impulses Impulses travel along thousands of motor neurons Motor neurons send the impulses to muscles, which carry out the response ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse ...
... nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse ...
Review #2 - Course Notes
... experience a sense of physical exhilaration and pleasure. It is likely that her feelings were most directly linked to the release of: a. dopamine. b. acetylcholine. c. endorphins. d. serotonin. 3. The reticular formation is located in the: a. brainstem. b. limbic system. c. somatosensory cortex. d. ...
... experience a sense of physical exhilaration and pleasure. It is likely that her feelings were most directly linked to the release of: a. dopamine. b. acetylcholine. c. endorphins. d. serotonin. 3. The reticular formation is located in the: a. brainstem. b. limbic system. c. somatosensory cortex. d. ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
Eagleman Ch 3. Neurons and Synapses
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals released by the presynaptic cell to affect the postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft is the 20- to 30-nm space between the cells. The small size of the synaptic cleft allows the concentration of the neurotransmitter to change rapidly. ...
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals released by the presynaptic cell to affect the postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft is the 20- to 30-nm space between the cells. The small size of the synaptic cleft allows the concentration of the neurotransmitter to change rapidly. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.