Complementing IHC with real-time interaction analysis on tissue
... traces for three antibodies with 1nM affinity and different interaction dynamics. Look at 2 hours of incubation at 10 nM concentration, then 7 hours of retention. ...
... traces for three antibodies with 1nM affinity and different interaction dynamics. Look at 2 hours of incubation at 10 nM concentration, then 7 hours of retention. ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... The absolute refractory period: Prevents the neuron from generating an action potential Ensures that each action potential is separate Enforces one-way transmission of ...
... The absolute refractory period: Prevents the neuron from generating an action potential Ensures that each action potential is separate Enforces one-way transmission of ...
Neuron Function notes
... SEQUENCE OF EVENTS [AT CHOLINERGIC SYNAPSE(acetylcholine is neurotransmitter)] 1. Arriving AP depoliarizes the synaptic knob and the presynaptic membrane 2. Ca+2 ions enter the cytoplasm of the synaptic knob – membrane channels in synaptic vesicles – release Ach 3. Ach diffuses across synaptic cleft ...
... SEQUENCE OF EVENTS [AT CHOLINERGIC SYNAPSE(acetylcholine is neurotransmitter)] 1. Arriving AP depoliarizes the synaptic knob and the presynaptic membrane 2. Ca+2 ions enter the cytoplasm of the synaptic knob – membrane channels in synaptic vesicles – release Ach 3. Ach diffuses across synaptic cleft ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... 3. Voltage gated Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open, causing more negative change inside of neuron ...
... 3. Voltage gated Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open, causing more negative change inside of neuron ...
The Peripheral and Autonomic Nervous Systems
... The ANS coordinates cardiovasclar, respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive functions. Preganglionic neurons in the CNS send axon to synapse on ganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia outside the CNS The axons of the postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscles, glands, a ...
... The ANS coordinates cardiovasclar, respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive functions. Preganglionic neurons in the CNS send axon to synapse on ganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia outside the CNS The axons of the postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscles, glands, a ...
Autonomic vs. Somatic Nervous System
... Postganglionic: Cholinergic neuron; Muscarinic receptor z ...
... Postganglionic: Cholinergic neuron; Muscarinic receptor z ...
The Nervous System
... information from different types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
... information from different types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
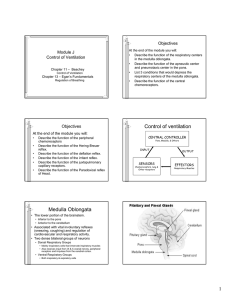
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3• The H+ ions cause the pH to in the CSF; This increases ventilation (f increases) ...
... diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3• The H+ ions cause the pH to in the CSF; This increases ventilation (f increases) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3• The H+ ions cause the pH to in the CSF; This increases ventilation (f increases) ...
... diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3• The H+ ions cause the pH to in the CSF; This increases ventilation (f increases) ...
Fluorodopa F-18
... Potential applications of proven clinical value include: 1. Neurology/Psychiatry: 18F-FDOPA is used for the study of presynaptic striatal dopaminergic function in neurologic disorders (DDx of Parkinson’s disease versus other neurodegenerative diseases with motor dysfunction). Decreased (initially of ...
... Potential applications of proven clinical value include: 1. Neurology/Psychiatry: 18F-FDOPA is used for the study of presynaptic striatal dopaminergic function in neurologic disorders (DDx of Parkinson’s disease versus other neurodegenerative diseases with motor dysfunction). Decreased (initially of ...
Exam 2
... 20. Penicillin and aspirin are both ____________________________ inhibitors because they do not dissociate from the enzyme to allow it to become active again. 21. An E6V mutation is hemoglobin leads to the disease ________________________________. 22. Draw glycerol: ...
... 20. Penicillin and aspirin are both ____________________________ inhibitors because they do not dissociate from the enzyme to allow it to become active again. 21. An E6V mutation is hemoglobin leads to the disease ________________________________. 22. Draw glycerol: ...
Neuropathic Pain (excluding headache)
... • “...unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage…” • Neuropathic pain caused by direct lesions or ...
... • “...unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage…” • Neuropathic pain caused by direct lesions or ...
the pattern of neurodegeneration in huntington`s disease
... adenosine A2a receptor binding in the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus externus and an increase in GABAA receptor binding in the globus pallidus externus. Second, intermediate neuropathological grades (grades 1, 2) showed a further marked decrease of CB1 receptor binding in the caudate n ...
... adenosine A2a receptor binding in the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus externus and an increase in GABAA receptor binding in the globus pallidus externus. Second, intermediate neuropathological grades (grades 1, 2) showed a further marked decrease of CB1 receptor binding in the caudate n ...
Chronic Opioid Therapy and Opioid Tolerance: A New Hypothesis
... their effectiveness, and some aspects of this phenomenon are unique to opioids when compared to other G-protein receptor ligand systems. One hypothesis of this paper is that some aspect of opioid tolerance is caused by homeostatic upregulation of non-opioid-mediated ascending nociceptive pathways, in ...
... their effectiveness, and some aspects of this phenomenon are unique to opioids when compared to other G-protein receptor ligand systems. One hypothesis of this paper is that some aspect of opioid tolerance is caused by homeostatic upregulation of non-opioid-mediated ascending nociceptive pathways, in ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... – stabilize joints by balancing tension in extensors and flexors smoothing muscle actions ...
... – stabilize joints by balancing tension in extensors and flexors smoothing muscle actions ...
Lecture 12 - Fundamentals of the Nervous System
... Dendrites with specialized sensory receptors (in skin, muscles, viscera, etc) Cell bodies always in ganglion* outside CNS ...
... Dendrites with specialized sensory receptors (in skin, muscles, viscera, etc) Cell bodies always in ganglion* outside CNS ...
The Nervous System - History with Mr. Bayne
... CNS – Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) PNS – Peripheral Nervous System (nerve cells that send messages from CNS to all parts of the body) ...
... CNS – Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) PNS – Peripheral Nervous System (nerve cells that send messages from CNS to all parts of the body) ...
Phosphatidyl Choline - Tringali Vibrant Health
... Phosphatidyl Choline (PC) is the most predominant phospholipid building block of animal and plant cell membranes, and it’s an integral part of the structure of circulating lipoproteins. It is an integral component required for both membrane integrity and structure. Phosphatidyl Choline is a normal c ...
... Phosphatidyl Choline (PC) is the most predominant phospholipid building block of animal and plant cell membranes, and it’s an integral part of the structure of circulating lipoproteins. It is an integral component required for both membrane integrity and structure. Phosphatidyl Choline is a normal c ...
document
... billion, i.e. 1 trillion) has on average 7,000 synaptic connections to other neurons. It hast been estimated that the brain of a three-year-old child has about 1016 synapses (10,000 trillion). This number declines with age, stabilizing by adulthood. Estimates vary for an adult, ranging from 1015 to ...
... billion, i.e. 1 trillion) has on average 7,000 synaptic connections to other neurons. It hast been estimated that the brain of a three-year-old child has about 1016 synapses (10,000 trillion). This number declines with age, stabilizing by adulthood. Estimates vary for an adult, ranging from 1015 to ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
... euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
Ch. 3
... PET is one of the newest, most advanced methods for studying organs in the body such as the brain. Like an X-ray, or MRI scan PET is painless and relatively noninvasive (i.e., no surgery or opening of the body is required). Unlike X-rays and traditional MRI, PET does not produce a picture of the "st ...
... PET is one of the newest, most advanced methods for studying organs in the body such as the brain. Like an X-ray, or MRI scan PET is painless and relatively noninvasive (i.e., no surgery or opening of the body is required). Unlike X-rays and traditional MRI, PET does not produce a picture of the "st ...
2016 Poster Abstracts - Molecular Psychiatry Association
... Mood-associated Gsk3/Fxr1P pathway regulated neuronal plasticity and behavior Neuropsychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorders, depression and schizophrenia represent a major public health problem, and a heavy burden for patients and their relatives. Drugs (such as mood stabilizers) used for man ...
... Mood-associated Gsk3/Fxr1P pathway regulated neuronal plasticity and behavior Neuropsychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorders, depression and schizophrenia represent a major public health problem, and a heavy burden for patients and their relatives. Drugs (such as mood stabilizers) used for man ...
Document
... It controls important sensations involved in maintaining homeostasis, such as hunger and thirst. Temperature, water balance, and blood pressure are also controlled by the hypothalamus . In addition, it also regulates the release of many hormones. ...
... It controls important sensations involved in maintaining homeostasis, such as hunger and thirst. Temperature, water balance, and blood pressure are also controlled by the hypothalamus . In addition, it also regulates the release of many hormones. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.