Altered States of Consciousness
... Adapted from How the Brain Might Work: A New Theory of Consciousness By SANDRA BLAKESLEE ...
... Adapted from How the Brain Might Work: A New Theory of Consciousness By SANDRA BLAKESLEE ...
Request pdf
... parts of the cell are connected by a long and extremely slender axon that does not transmit action potentials and is thought to be incapable of transmitting graded potentials. That the cell body and the terminal arborization are indeed physiologically independent is suggested by the finding of Nelso ...
... parts of the cell are connected by a long and extremely slender axon that does not transmit action potentials and is thought to be incapable of transmitting graded potentials. That the cell body and the terminal arborization are indeed physiologically independent is suggested by the finding of Nelso ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... divided into several parts: dorsal thalamus (largest part), hypothalamus, epithalamus, metathalamus (MGN, LGN), and subthalamus. The ventral and medial part of the diencephalon is the hypothalamus that contains numerous nuclei; they maintain homeostasis through regulating the function of the autonom ...
... divided into several parts: dorsal thalamus (largest part), hypothalamus, epithalamus, metathalamus (MGN, LGN), and subthalamus. The ventral and medial part of the diencephalon is the hypothalamus that contains numerous nuclei; they maintain homeostasis through regulating the function of the autonom ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... The impulse reaches axonal terminal of presynaptic neuron causing depolarization of axonal terminal/synaptic knob. Ca2+ channels open and calcium ions rush into axonal terminal causing synaptic vesicles (filled with neurotransmitter/NT) to release NT via exocytosis into the synaptic cleft. NT diffus ...
... The impulse reaches axonal terminal of presynaptic neuron causing depolarization of axonal terminal/synaptic knob. Ca2+ channels open and calcium ions rush into axonal terminal causing synaptic vesicles (filled with neurotransmitter/NT) to release NT via exocytosis into the synaptic cleft. NT diffus ...
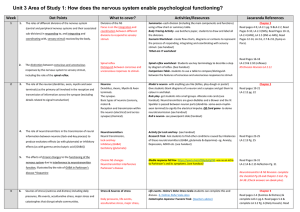
Unit 3 Area of Study 1: How does the nervous system
... Model a neuron- with anything you like (lollies, play-dough or pasta!) Give students blank diagrams of a neuron and a synapse and get them to colour in and label. Role play- get students into small groups. Allocate role cards (see handout). Neurotransmitters are given Bubbles and a blower and the li ...
... Model a neuron- with anything you like (lollies, play-dough or pasta!) Give students blank diagrams of a neuron and a synapse and get them to colour in and label. Role play- get students into small groups. Allocate role cards (see handout). Neurotransmitters are given Bubbles and a blower and the li ...
powerpoint version - University of Arizona
... - Need to be reset for new muscle length - Gamma-motor neurons innervate spindle ...
... - Need to be reset for new muscle length - Gamma-motor neurons innervate spindle ...
Galanin in Alzheimer s disease: Neuroinhibitory or neuroprotective?
... and entorhinal cortex concurrent with the appearance of dystrophic GAL-ir neurites in many of the plaques [60]. Occasional GAL-ir cell bodies were also observed in the hippocampus that were not evident in wild-type mice [60]. In addition, APP23 mice bearing two FAD-related APP mutations (V717I and K ...
... and entorhinal cortex concurrent with the appearance of dystrophic GAL-ir neurites in many of the plaques [60]. Occasional GAL-ir cell bodies were also observed in the hippocampus that were not evident in wild-type mice [60]. In addition, APP23 mice bearing two FAD-related APP mutations (V717I and K ...
Target-Derived Neurotrophic Factors Regulate the
... died after 4 and 5 d, at ages equivalent to E19 and P0 in vivo (Fig. 1i; see Fig. 3a, broken line). A total of 87% of neurons remaining viable after 5 d were GABAergic, indicating preferential loss of projection neurons. Adding medium conditioned with E19 dorsal thalamic explants (using the same pro ...
... died after 4 and 5 d, at ages equivalent to E19 and P0 in vivo (Fig. 1i; see Fig. 3a, broken line). A total of 87% of neurons remaining viable after 5 d were GABAergic, indicating preferential loss of projection neurons. Adding medium conditioned with E19 dorsal thalamic explants (using the same pro ...
Cell numbers in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei of AS and AS
... mutation generates a stop codon within the coding region of the PKC-gamma gene. The rats exhibit locomotor dysfunction, which is progressive with age. The nigrostriatal system has already been shown to be affected by this mutation that a) there is marked (80-90%) reduction in extracellular dopamine ...
... mutation generates a stop codon within the coding region of the PKC-gamma gene. The rats exhibit locomotor dysfunction, which is progressive with age. The nigrostriatal system has already been shown to be affected by this mutation that a) there is marked (80-90%) reduction in extracellular dopamine ...
23 Comp Review 1
... potential of the neuron builds up before it transmits the signal down the axon. • AXON function is to transmit signals. Some cells have many axons, some have one, some are short, and some are long. • AXON TERMINALS (also called terminal boutons or synaptic knobs) contain a neurotransmitter which, wh ...
... potential of the neuron builds up before it transmits the signal down the axon. • AXON function is to transmit signals. Some cells have many axons, some have one, some are short, and some are long. • AXON TERMINALS (also called terminal boutons or synaptic knobs) contain a neurotransmitter which, wh ...
The neuronal structure of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the
... the dendrites of relay cells in the cat GLN. It is generally considered that interneurons (Golgi type II nerve cells) play an important role in inhibitory processes [1,17,21,26]. The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary thalamic relay, through which retinal signals pass to the cortex. Retinal a ...
... the dendrites of relay cells in the cat GLN. It is generally considered that interneurons (Golgi type II nerve cells) play an important role in inhibitory processes [1,17,21,26]. The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary thalamic relay, through which retinal signals pass to the cortex. Retinal a ...
Spinal Cord
... • Receptors organ, afferent neuron, efferent neuron and effector organ are located on same side of spinal segment, i.e., stretch reflex. ...
... • Receptors organ, afferent neuron, efferent neuron and effector organ are located on same side of spinal segment, i.e., stretch reflex. ...
Neurodevelopmental mechanisms of schizophrenia: understanding
... young adulthood, especially by examining possible convergence of promising SZ genetic susceptibility factors at the functional levels in vivo. The extraordinary advances in the field over the past 1–2 years enable us to provide an overview of these issues. In particular, we focus on the significance ...
... young adulthood, especially by examining possible convergence of promising SZ genetic susceptibility factors at the functional levels in vivo. The extraordinary advances in the field over the past 1–2 years enable us to provide an overview of these issues. In particular, we focus on the significance ...
THE AMAZING HUMAN MIND
... In vertebrates, the spinal cord contains neural circuitry capable of generating reflex responses as well as simple movement such as swimming or walking. Sophisticated complex sensory input requires the information-integrating capabilities and control of behavior on the basis of a centralized brain. ...
... In vertebrates, the spinal cord contains neural circuitry capable of generating reflex responses as well as simple movement such as swimming or walking. Sophisticated complex sensory input requires the information-integrating capabilities and control of behavior on the basis of a centralized brain. ...
Hypothalamic pathways linking energy balance and reproduction
... levels of both NPY and its mRNA that are normalized by systemic insulin therapy (1, 80). High numbers of IRs are also found on POMC/CART neurons (9). Interestingly, no obvious metabolic or reproductive phenotype was seen in mice lacking IRs only in POMC neurons (59). Although LepRs are expressed in ...
... levels of both NPY and its mRNA that are normalized by systemic insulin therapy (1, 80). High numbers of IRs are also found on POMC/CART neurons (9). Interestingly, no obvious metabolic or reproductive phenotype was seen in mice lacking IRs only in POMC neurons (59). Although LepRs are expressed in ...
neuron
... – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane • living cells are polarized • resting membrane potential (RMP) – charge difference across the plasma membrane – -70 mV in a resting, unstimulated neuron – negative value means there are mor ...
... – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane • living cells are polarized • resting membrane potential (RMP) – charge difference across the plasma membrane – -70 mV in a resting, unstimulated neuron – negative value means there are mor ...
Inhibition
... more easily and faster oriented in a direction of a location in which it already has been rather than shifting to another location ...
... more easily and faster oriented in a direction of a location in which it already has been rather than shifting to another location ...
Proceedings from the 2015 UK-Korea Neuroscience Symposium
... Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) medications for the depressed patients generally show severe therapeutic delay, in spite of their immediate effect on serotonergic neurotransmission, suggesting the involvement of complicated downstream mechanisms for the onset of their therapeutic effec ...
... Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) medications for the depressed patients generally show severe therapeutic delay, in spite of their immediate effect on serotonergic neurotransmission, suggesting the involvement of complicated downstream mechanisms for the onset of their therapeutic effec ...
Supplemental Data Millisecond-Timescale Optical Control of Neural
... together and classified as one multiunit, then if any of the neurons are light-modulated, the entire multiunit will likely be classified as light-modulated). However, the fact that almost all cells recorded were modulated by light is consistent with the idea that the observed modulations were largel ...
... together and classified as one multiunit, then if any of the neurons are light-modulated, the entire multiunit will likely be classified as light-modulated). However, the fact that almost all cells recorded were modulated by light is consistent with the idea that the observed modulations were largel ...
Restoring axonal localization and transport of transmembrane
... re-establish axon transport, but rather how can it be done in a controlled site-specific, age-specific manner. Within this review we have discussed how reinstating age-associated changes in signalling pathways can lead to enhanced repair after injury, but when it comes to CNS injury this is only hal ...
... re-establish axon transport, but rather how can it be done in a controlled site-specific, age-specific manner. Within this review we have discussed how reinstating age-associated changes in signalling pathways can lead to enhanced repair after injury, but when it comes to CNS injury this is only hal ...
The nervous tissue is made up of
... The anterior spinal artery is derived by the union of the anterior spinal artery from each vertebral artery. It runs in a midline groove (Ventral median fissure) on the ventral aspect of the spinal cord. Each posterior spinal artery is a branch the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebell ...
... The anterior spinal artery is derived by the union of the anterior spinal artery from each vertebral artery. It runs in a midline groove (Ventral median fissure) on the ventral aspect of the spinal cord. Each posterior spinal artery is a branch the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebell ...
Making Memories Stick
... For a protein to be produced, a stretch of DNA inside the cell nucleus must be transcribed into a portable form called messenger RNA (mRNA), which then travels out to the cell's cytoplasm, where cellular machinery translates its encoded instructions into a protein. These researchers had found that b ...
... For a protein to be produced, a stretch of DNA inside the cell nucleus must be transcribed into a portable form called messenger RNA (mRNA), which then travels out to the cell's cytoplasm, where cellular machinery translates its encoded instructions into a protein. These researchers had found that b ...
Nervous
... “Gateway to cerebral cortex” Most sensory stimuli project to the thalamus, which in turn projects to the cerebrum. Thalamus also influences moods and activities associated with strong emotion. (Two concepts: Sensory integration and Mood) ...
... “Gateway to cerebral cortex” Most sensory stimuli project to the thalamus, which in turn projects to the cerebrum. Thalamus also influences moods and activities associated with strong emotion. (Two concepts: Sensory integration and Mood) ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.