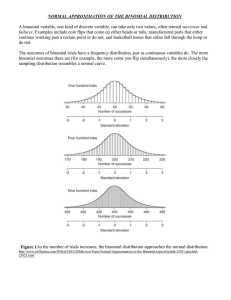
View/Open
... In our case, h(P ) = logit P , so that h−1 (X) = exp(X)/{1+exp(X)} and h′ {h−1 (X)} = {1 + exp(X)}2 / exp(X). In Stata terms, beta densities transformed to the logit scale are the product of betaden(p) or betaden(invlogit(x)) and exp(x)/(1+exp(x))^2. The latter term may be recognized as a logistic d ...
... In our case, h(P ) = logit P , so that h−1 (X) = exp(X)/{1+exp(X)} and h′ {h−1 (X)} = {1 + exp(X)}2 / exp(X). In Stata terms, beta densities transformed to the logit scale are the product of betaden(p) or betaden(invlogit(x)) and exp(x)/(1+exp(x))^2. The latter term may be recognized as a logistic d ...
MATH 1410/4.1 and 4.2 pp
... If x is the net gain to a player in a game of chance, then E(X) is usually negative. This value gives the average amount per game the player can expect to lose. A charity organization is selling $5 raffle tickets. First prize is a trip to Mexico valued at $3450, second prize is a spa package valued ...
... If x is the net gain to a player in a game of chance, then E(X) is usually negative. This value gives the average amount per game the player can expect to lose. A charity organization is selling $5 raffle tickets. First prize is a trip to Mexico valued at $3450, second prize is a spa package valued ...
VT PowerPoint Template
... • Discrete Predictor - Contingency Table of Mean of Y (μy) versus categories of X ...
... • Discrete Predictor - Contingency Table of Mean of Y (μy) versus categories of X ...