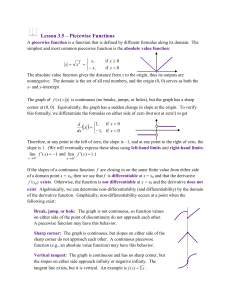
Approximating the Probability of an Itemset being Frequent
... bP (l) > 10 In this case, the discrete Poisson Distribution itself is approximated by the continuous Normal Distribution and we have to take care of the continuity correction. For Sl , the following expression can be found: ...
... bP (l) > 10 In this case, the discrete Poisson Distribution itself is approximated by the continuous Normal Distribution and we have to take care of the continuity correction. For Sl , the following expression can be found: ...
Please make your selection
... MAT 155 Chapter 5 The following is a brief review of Chapter 4. This does NOT cover all the material in that chapter. Click on Slide Show and View Slide Show. Read and note your answer to the question. Advance the slide to see the answer. Thanks to Ms. Valerie Melvin for her portion of this review. ...
... MAT 155 Chapter 5 The following is a brief review of Chapter 4. This does NOT cover all the material in that chapter. Click on Slide Show and View Slide Show. Read and note your answer to the question. Advance the slide to see the answer. Thanks to Ms. Valerie Melvin for her portion of this review. ...
Chapter 14: Binomial Distributions Binomial Probability Distributions
... Binomial Probability Distributions is one of Finite Probability Distribution. Requirements of Binomial Probability Distributions 1) The procedure has a fixed number of observations (n). 2) The observations must be independent. 3) Each observation must have all outcomes classified into two categories ...
... Binomial Probability Distributions is one of Finite Probability Distribution. Requirements of Binomial Probability Distributions 1) The procedure has a fixed number of observations (n). 2) The observations must be independent. 3) Each observation must have all outcomes classified into two categories ...
4.1AB: Random Variables and Probability Distributions Objectives: 1
... 2. The number of songs played by a band 3. The length of time it takes to complete a test 4. The height of a tree at a nursery 5. The number of suitcases lost by an airline 6. The number of skittles in a bag 7. The weight of newborn babies ...
... 2. The number of songs played by a band 3. The length of time it takes to complete a test 4. The height of a tree at a nursery 5. The number of suitcases lost by an airline 6. The number of skittles in a bag 7. The weight of newborn babies ...
quantitative techniques
... QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES 1. DECISION MAKING AND QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Problem solving and decision making Quantitative analysis and decision making Steps in quantitative analysis Methods of cost, revenue, and profit Quantitative methods in practice 2. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR PROGRAMMING ...
... QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES 1. DECISION MAKING AND QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Problem solving and decision making Quantitative analysis and decision making Steps in quantitative analysis Methods of cost, revenue, and profit Quantitative methods in practice 2. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR PROGRAMMING ...
SYLLABUS for BST 621 (Statistical Methods 1)
... work indicate that the work is to be done individually, then that is what is expected. Minor violations will be dealt with on a case by case basis, with the exact repercussions dependent upon the instructor involved and the nature of the offense. In extreme cases, violations of the Honor Code will b ...
... work indicate that the work is to be done individually, then that is what is expected. Minor violations will be dealt with on a case by case basis, with the exact repercussions dependent upon the instructor involved and the nature of the offense. In extreme cases, violations of the Honor Code will b ...
Empirical cdf, quantiles, random variable generation, probability
... 5. Generating rvs using the inverse cdf method To generate N random variables from a (non-standard) cdf F(x) 1. Generate N random variables Ui from the uniform distribution on [0,1] 2. Find the inverse cdf (quantile function) F-1(p) = Q(p) 3. Compute Q(Ui) using the menu Calc/Calculator Example: Ge ...
... 5. Generating rvs using the inverse cdf method To generate N random variables from a (non-standard) cdf F(x) 1. Generate N random variables Ui from the uniform distribution on [0,1] 2. Find the inverse cdf (quantile function) F-1(p) = Q(p) 3. Compute Q(Ui) using the menu Calc/Calculator Example: Ge ...
ISyE 3104: Introduction to Supply Chain Modeling
... whether the club management should place an order at this reduced rate or not, and in case of a positive answer, what should be the optimal order size. Hint: What is the exact distribution characterizing the number of any additional attendees beyond the ones that are already bought their tickets? In ...
... whether the club management should place an order at this reduced rate or not, and in case of a positive answer, what should be the optimal order size. Hint: What is the exact distribution characterizing the number of any additional attendees beyond the ones that are already bought their tickets? In ...