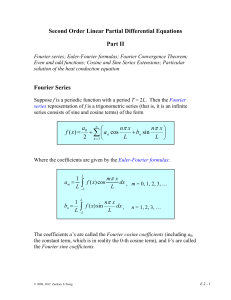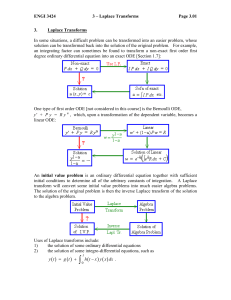
EFFICIENT ITERATIVE SOLVERS FOR STOCHASTIC GALERKIN
... m=1 are the eigenpairs of the covariance integral operator defined as in (2.3) with the covariance function of exp(a) as the kernel function. If the sum in f terms, the resulting approximate diffusion coefficient (2.17) is approximated using M f f basic random variables {ηm }M is a linear function o ...
... m=1 are the eigenpairs of the covariance integral operator defined as in (2.3) with the covariance function of exp(a) as the kernel function. If the sum in f terms, the resulting approximate diffusion coefficient (2.17) is approximated using M f f basic random variables {ηm }M is a linear function o ...
Math 115–Test 1 Sample Problems for Dr. Hukle’s Class
... 3. Market research has shown that the price people are willing to pay for gourmet chocolates is given by the demand function p = 20 − x. Find the marginal revenue function M R(x). 4. The mathematics office sells sample midterms for 50 cents each. The cost of producing x tests (in cents) is given by ...
... 3. Market research has shown that the price people are willing to pay for gourmet chocolates is given by the demand function p = 20 − x. Find the marginal revenue function M R(x). 4. The mathematics office sells sample midterms for 50 cents each. The cost of producing x tests (in cents) is given by ...
SOME DISCRETE EXTREME PROBLEMS
... As a result after all iterations the record value of power and the corresponding solution x are remembered. By this solution is restored maximum ESS, which is considered as the approximation for MSS of system S. Let us describe now the procedures, mentioned in the general work scheme of algorithm. ...
... As a result after all iterations the record value of power and the corresponding solution x are remembered. By this solution is restored maximum ESS, which is considered as the approximation for MSS of system S. Let us describe now the procedures, mentioned in the general work scheme of algorithm. ...
01 Descriptive Statistics
... Experimental vs Correlational Research • Experimental study: – Researcher controls the independent variable. – Seek to detect effects on the dependent variable. – Direction of causation may be inferred (but may be indirect). ...
... Experimental vs Correlational Research • Experimental study: – Researcher controls the independent variable. – Seek to detect effects on the dependent variable. – Direction of causation may be inferred (but may be indirect). ...