Stars I - Astronomy Centre
... Distances to Stars • Early astronomers considered the stars to be located on the surface of a sphere, and hence all at the same distance • To understand most properties of stars we need to know their distance • For nearby stars distance can be measured via parallax • This works on the same principl ...
... Distances to Stars • Early astronomers considered the stars to be located on the surface of a sphere, and hence all at the same distance • To understand most properties of stars we need to know their distance • For nearby stars distance can be measured via parallax • This works on the same principl ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... The aim of this course is to explore the continuing evolution of the universe. The scales examined will range from the structure of individual galaxies up to the geometry of the universe as a whole. ...
... The aim of this course is to explore the continuing evolution of the universe. The scales examined will range from the structure of individual galaxies up to the geometry of the universe as a whole. ...
Ch 3 PPT - Blountstown Middle School
... • The sky is divided into 88 constellations. • Astronomers learn about the energy, distance, temperature, and composition of stars by studying their light. • Astronomers measure distances in space in astrological units and in light-years. They measure star brightness as apparent magnitude and as ...
... • The sky is divided into 88 constellations. • Astronomers learn about the energy, distance, temperature, and composition of stars by studying their light. • Astronomers measure distances in space in astrological units and in light-years. They measure star brightness as apparent magnitude and as ...
The first cool rocky/icy exoplanet
... the larger velocity and the larger range of inclinations for which an eclipse can occur favour closer orbits for the radial-velocity and the transit technique, respectively, the astrometric signal increases with orbit size. For all these techniques, a few orbits need to be observed, so the duration ...
... the larger velocity and the larger range of inclinations for which an eclipse can occur favour closer orbits for the radial-velocity and the transit technique, respectively, the astrometric signal increases with orbit size. For all these techniques, a few orbits need to be observed, so the duration ...
ph709-15-testrevision
... Short period giant planets in close orbits around their stars will undergo reflected light variations changes because, like the Moon, they will go through phases from full to new and back again. Since telescopes cannot resolve the planet from the star, they see only the combined light, and the brigh ...
... Short period giant planets in close orbits around their stars will undergo reflected light variations changes because, like the Moon, they will go through phases from full to new and back again. Since telescopes cannot resolve the planet from the star, they see only the combined light, and the brigh ...
Heavy Metal from Ancient Superstars
... energy by fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium, and helium into heavier nuclei ...
... energy by fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium, and helium into heavier nuclei ...
Lecture 39: Life in the Universe The Main Point Simple Life vs
... – Increased awareness of our place in the Cosmos – Answers the question "Are We Alone?" – Practical knowledge gained over time? ...
... – Increased awareness of our place in the Cosmos – Answers the question "Are We Alone?" – Practical knowledge gained over time? ...
File - Mr. Gray`s Class
... Motion of the Planets As we watch planets move across the sky, they move relative to their background “fixed” stars. – Planets normally move westward across the night sky. This is called Prograde motion. – Sometimes planets appear to begin moving “backward” or eastward across the night sky. This ...
... Motion of the Planets As we watch planets move across the sky, they move relative to their background “fixed” stars. – Planets normally move westward across the night sky. This is called Prograde motion. – Sometimes planets appear to begin moving “backward” or eastward across the night sky. This ...
ph709-15
... Small planets between the sizes of Earth and Neptune substantially outnumber Jupiter-sized planets. Super-Earths with orbital periods less than 100 days are extremely abundant around Sun-like stars. It is unlikely that these planets formed at their current locations. Rather, they likely formed at la ...
... Small planets between the sizes of Earth and Neptune substantially outnumber Jupiter-sized planets. Super-Earths with orbital periods less than 100 days are extremely abundant around Sun-like stars. It is unlikely that these planets formed at their current locations. Rather, they likely formed at la ...
Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date
... Eclipsing Binary systems serve as an effective tool for the precise determination of masses and radii of both the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter pri ...
... Eclipsing Binary systems serve as an effective tool for the precise determination of masses and radii of both the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter pri ...
color-stellar mass diagram
... constituent stars (ignoring complications such as internal absorption by dust or co-evolving binary systems): ...
... constituent stars (ignoring complications such as internal absorption by dust or co-evolving binary systems): ...
Phys 1830: Lecture 33 - University of Manitoba Physics Department
... Zone (HZ)? This zone is around each star and has a temperature such that water condenses on the planet’s surface but does not permanently freeze. That is, it is a spherical shell bound on the interior by regions with T > 100C and outside by T<0C. For example, our sun (G star) 0.85 AU < HZ < 2 AU ...
... Zone (HZ)? This zone is around each star and has a temperature such that water condenses on the planet’s surface but does not permanently freeze. That is, it is a spherical shell bound on the interior by regions with T > 100C and outside by T<0C. For example, our sun (G star) 0.85 AU < HZ < 2 AU ...
An optical/UV space coronagraph concept for the terrestrial planet finder
... Everything discussed until now has been for an ideal optical system. Unfortunately, the limiting performance of TPF will be determined by the various error sources. Our capability to achieve high contrast is limited and there will always be a residual halo of scattered starlight near the planet. A c ...
... Everything discussed until now has been for an ideal optical system. Unfortunately, the limiting performance of TPF will be determined by the various error sources. Our capability to achieve high contrast is limited and there will always be a residual halo of scattered starlight near the planet. A c ...
exo planets
... Before 1990, no planets were known outside of our solar system. We did not have the methods to discover these planets yet. But in the nearly 25 years since then, we have discovered at least 1800 planets outside of our system – and the count seems to be increasing almost every day. We call these worl ...
... Before 1990, no planets were known outside of our solar system. We did not have the methods to discover these planets yet. But in the nearly 25 years since then, we have discovered at least 1800 planets outside of our system – and the count seems to be increasing almost every day. We call these worl ...
Astronomy - Career Account Web Pages
... The dim object is a compact galaxy of blue stars that existed 480 million years after the Big Bang, only four percent of the universe's current age. It is tiny and considered a building block of today's giant galaxies. Over one hundred such mini-galaxies would be needed to make up our Milky Way gala ...
... The dim object is a compact galaxy of blue stars that existed 480 million years after the Big Bang, only four percent of the universe's current age. It is tiny and considered a building block of today's giant galaxies. Over one hundred such mini-galaxies would be needed to make up our Milky Way gala ...
A Spyglass Telescope
... Would we ever – even in our wildest dreams – have been able to imagine the universe as we know it today if we had not had any tele- in 1946. Today we are blessed to have telscopes? We owe the telescope the most hon- escopes of different kinds in space, opening orary position in relation to the stars ...
... Would we ever – even in our wildest dreams – have been able to imagine the universe as we know it today if we had not had any tele- in 1946. Today we are blessed to have telscopes? We owe the telescope the most hon- escopes of different kinds in space, opening orary position in relation to the stars ...
Study Guide for 3RD Astronomy Exam
... Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in the “adult” phase or the “nursing home” phase of its evolution. Describe or identify how a parsec is defined. Convert stellar distances between parsecs and light years. Write or identify the def ...
... Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in the “adult” phase or the “nursing home” phase of its evolution. Describe or identify how a parsec is defined. Convert stellar distances between parsecs and light years. Write or identify the def ...
Hubble Offers a Dazzling View of Necklace Nebula
... miles wide and dotted with pearls of glowing gas. The object is the glowing remains of an ordinary, Sun-like star, called a planetary nebula. What’s in a name? The planetary nebula name is a misnomer because these objects have nothing to do with planets. They acquired their name more than 100 years ...
... miles wide and dotted with pearls of glowing gas. The object is the glowing remains of an ordinary, Sun-like star, called a planetary nebula. What’s in a name? The planetary nebula name is a misnomer because these objects have nothing to do with planets. They acquired their name more than 100 years ...
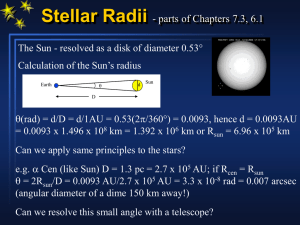
v A v A
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
SCIN 293-PL-New Course
... Explain the evolution of stars and how it applies to the Sun. Describe the theories of formation of galaxies. Determine the structure of the Milky Way, Local Group galaxies and other galaxies. Summarize the history of formation of the universe and its future ...
... Explain the evolution of stars and how it applies to the Sun. Describe the theories of formation of galaxies. Determine the structure of the Milky Way, Local Group galaxies and other galaxies. Summarize the history of formation of the universe and its future ...
Publication - Centre for Star and Planet Formation
... respectively. The binary star consists of a Sun-like star and a companion roughly one-third its size, orbiting each other every 7.45 days. With an orbital period of 49.5 days, 18 transits of the inner planet have been observed, allowing a detailed characterization of its orbit and those of the stars ...
... respectively. The binary star consists of a Sun-like star and a companion roughly one-third its size, orbiting each other every 7.45 days. With an orbital period of 49.5 days, 18 transits of the inner planet have been observed, allowing a detailed characterization of its orbit and those of the stars ...
PPT - Yale University
... rotation periods) because disks are fragile and cannot sustain a large torque. Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
... rotation periods) because disks are fragile and cannot sustain a large torque. Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
student instruction and answer sheet
... temperature for liquid water to exist (i.e. in the habitable zone). Recent discoveries suggest that we should also consider including moons around gas giant planets that are orbiting their central star in the habitable zone. A reasonable estimate for this number is difficult to imagine. In our solar ...
... temperature for liquid water to exist (i.e. in the habitable zone). Recent discoveries suggest that we should also consider including moons around gas giant planets that are orbiting their central star in the habitable zone. A reasonable estimate for this number is difficult to imagine. In our solar ...
Stellar Lives (continued). Galaxies.
... Virtually all elements besides H and He were created inside stars. The battle between gravity and pressure determines how stars behave during their lives. Low-mass stars live longer than high-mass stars. High-mass stars dramatically explode as supernovae. They create the entire variety of elements t ...
... Virtually all elements besides H and He were created inside stars. The battle between gravity and pressure determines how stars behave during their lives. Low-mass stars live longer than high-mass stars. High-mass stars dramatically explode as supernovae. They create the entire variety of elements t ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.









![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)