Why Star Positions?
... celestial cartography by conducting its survey of the night sky from high above the Earth’s atmosphere. T HE HUMAN EYE imposes its own limit to measuring angles of about one minute of arc—you can see two distinct car headlights at night up to about a kilometer distance, but much beyond that they mer ...
... celestial cartography by conducting its survey of the night sky from high above the Earth’s atmosphere. T HE HUMAN EYE imposes its own limit to measuring angles of about one minute of arc—you can see two distinct car headlights at night up to about a kilometer distance, but much beyond that they mer ...
Birth - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Where are new stars being created? Are planets a natural result of star formation, or is our solar system unique in the universe? How can we observe planets around distant stars? ...
... Where are new stars being created? Are planets a natural result of star formation, or is our solar system unique in the universe? How can we observe planets around distant stars? ...
2.4 Statistical properties of radial velocity planets
... About 10 % of the detected systems with RV-planets have more than 1 known planet. A few examples of these multi-planet systems are shown in one of the slides. In many cases the additional planets were found because the RV fit solution for the first planet showed systematic deviations. The statistica ...
... About 10 % of the detected systems with RV-planets have more than 1 known planet. A few examples of these multi-planet systems are shown in one of the slides. In many cases the additional planets were found because the RV fit solution for the first planet showed systematic deviations. The statistica ...
Lecture8_2014_v2 - UCO/Lick Observatory
... Gravitational Tugs • The Sun’s motion around the solar system’s center of mass depends on tugs from all the planets. • Astronomers around other stars that measured this motion could determine the masses and orbits ...
... Gravitational Tugs • The Sun’s motion around the solar system’s center of mass depends on tugs from all the planets. • Astronomers around other stars that measured this motion could determine the masses and orbits ...
Reconnaissance of the TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet system in the Lyman
... et al. 2017) and the sustained activity of M dwarfs over approximately one billion years could however impact the putative atmospheres of the TRAPPIST-1 planets and their habitability (Miguel et al. 2015, Bolmont et al. 2017). The system proximity (12 pc), its large planet-to-star radii ratios, and ...
... et al. 2017) and the sustained activity of M dwarfs over approximately one billion years could however impact the putative atmospheres of the TRAPPIST-1 planets and their habitability (Miguel et al. 2015, Bolmont et al. 2017). The system proximity (12 pc), its large planet-to-star radii ratios, and ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
Astronomy - Boy Scouts of America
... c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North Star and the horizon. Record the date and time each sketch was made. d. Explain what we see wh ...
... c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North Star and the horizon. Record the date and time each sketch was made. d. Explain what we see wh ...
James Webb Space Telescope
... The Ball Aerospace approach is also based on enhancing technologies that have the potential to improve scientific capabilities, to reduce the development difficulty, to reduce life-cycle costs, and improve the prospects for long-term performance and productivity. Once JWST reaches its destination — ...
... The Ball Aerospace approach is also based on enhancing technologies that have the potential to improve scientific capabilities, to reduce the development difficulty, to reduce life-cycle costs, and improve the prospects for long-term performance and productivity. Once JWST reaches its destination — ...
strolympics - Chandra X
... our clocks, phones, or other devices. In the Olympic Games, we use time to dictate how long events are held and to measure how fast athletes perform. Time plays such a crucial role that we have developed many sayings involving time, like “time is running out” or it’s “crunch time.” But how do you ac ...
... our clocks, phones, or other devices. In the Olympic Games, we use time to dictate how long events are held and to measure how fast athletes perform. Time plays such a crucial role that we have developed many sayings involving time, like “time is running out” or it’s “crunch time.” But how do you ac ...
Staring Back to Cosmic Dawn - UC-HiPACC
... areas were away from our Milky Way’s star-studded plane. Much as pollsters and medical researchers learn about the human population as a whole by studying carefully selected samples of a small number of individuals, we chose the five target areas because they’re physically representative of the univ ...
... areas were away from our Milky Way’s star-studded plane. Much as pollsters and medical researchers learn about the human population as a whole by studying carefully selected samples of a small number of individuals, we chose the five target areas because they’re physically representative of the univ ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... Z=0.0005 filled triangles Z=0.001 empty triangles Z=0.004 filled squares Z=0.008 filled squares ...
... Z=0.0005 filled triangles Z=0.001 empty triangles Z=0.004 filled squares Z=0.008 filled squares ...
A Question of Planets - Vanderbilt University
... stars haven’t lost their disks at all: The disk material has simply changed into a form that is virtually invisible to Earth-based telescopes. They published a key observation supporting their hypothesis in the September 1 issue of the Astrophysical Journal Letter that was highlighted by the editors ...
... stars haven’t lost their disks at all: The disk material has simply changed into a form that is virtually invisible to Earth-based telescopes. They published a key observation supporting their hypothesis in the September 1 issue of the Astrophysical Journal Letter that was highlighted by the editors ...
slides - Indico
... CS 31082-001: So LITTLE Lead! • 13 exposures of 90min each needed to obtain more than an upper limit for lead. • Abundance (LTE) found : log(Pb/H) = -12.55 ±0.15 (or -0.55 ± 0.15 on the scale log(nH)=12). ...
... CS 31082-001: So LITTLE Lead! • 13 exposures of 90min each needed to obtain more than an upper limit for lead. • Abundance (LTE) found : log(Pb/H) = -12.55 ±0.15 (or -0.55 ± 0.15 on the scale log(nH)=12). ...
Earth - Harding University
... The lightest and simplest elements, hydrogen and helium, are abundant in the universe. Heavier elements, such as iron and silicon, are created by thermonuclear reactions in the interiors of stars, and then ejected into space by those stars. Ejection of Matter from Stars ...
... The lightest and simplest elements, hydrogen and helium, are abundant in the universe. Heavier elements, such as iron and silicon, are created by thermonuclear reactions in the interiors of stars, and then ejected into space by those stars. Ejection of Matter from Stars ...
Powerpoint file
... the end of 2013 • On 7 March 2009 CoRoT lost DPU1 (Data Processing Unit) that controlled one Exoplanet and one Seismo CCD. CoRoT continues to work well, but only getting data on ½ the original number of stars On 6 March 2009 NASA Launched Kepler ...
... the end of 2013 • On 7 March 2009 CoRoT lost DPU1 (Data Processing Unit) that controlled one Exoplanet and one Seismo CCD. CoRoT continues to work well, but only getting data on ½ the original number of stars On 6 March 2009 NASA Launched Kepler ...
Characteristics of Our Galaxy
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
Searching for stars in high-velocity clouds
... et al. (2002) have measured a metallicity of ≈0.5 solar for one compact HVC. They say that such a low metallicity is inconsistent with an origin for the gas inside the Milky Way. They suggest that it is associated with the Magellanic Clouds or Stream. If stars are associated with some HVCs then ther ...
... et al. (2002) have measured a metallicity of ≈0.5 solar for one compact HVC. They say that such a low metallicity is inconsistent with an origin for the gas inside the Milky Way. They suggest that it is associated with the Magellanic Clouds or Stream. If stars are associated with some HVCs then ther ...
Study of the X-ray Source Population and the Dark Matter
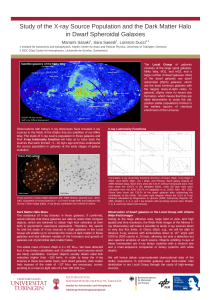
... The existence of X-ray binaries in these galaxies, if confirmed, would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources ...
... The existence of X-ray binaries in these galaxies, if confirmed, would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources ...
Galaxies - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
Nulling Interferometry A technique for blocking the light of a bright
... • Reflection from cat’s eye mirror introduces achromatic half-wave phase shift (n2 > n1) are ...
... • Reflection from cat’s eye mirror introduces achromatic half-wave phase shift (n2 > n1) are ...
15.6 Planets Beyond the Solar System
... luminosity may be observed as a function of time. This is called a transit. Notice a transit requires a planetary orbit almost perfectly in the line of sight of an observer on Earth. So transits will be found in only a tiny fraction of stars, even if all have planets. The time to enter and exit the ...
... luminosity may be observed as a function of time. This is called a transit. Notice a transit requires a planetary orbit almost perfectly in the line of sight of an observer on Earth. So transits will be found in only a tiny fraction of stars, even if all have planets. The time to enter and exit the ...
The H-R Diagram
... • It’s heavily skewed toward the most luminous stars, which you can see from much farther away and hence sampling a much bigger volume of space • HR diagram dominated by the Main Sequence ...
... • It’s heavily skewed toward the most luminous stars, which you can see from much farther away and hence sampling a much bigger volume of space • HR diagram dominated by the Main Sequence ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... Only one direct method of mass determination: study dynamics of binary systems. By Kepler’s third law: (M1 + M2)/M¯ = a3/P2 a = semi-major axis of apparent orbit in astronomical units; P = period in years. a) Visual binary stars: ...
... Only one direct method of mass determination: study dynamics of binary systems. By Kepler’s third law: (M1 + M2)/M¯ = a3/P2 a = semi-major axis of apparent orbit in astronomical units; P = period in years. a) Visual binary stars: ...
colour
... Only one direct method of mass determination: study dynamics of binary systems. By Kepler’s third law: (M1 + M2)/M¯ = a3/P2 a = semi-major axis of apparent orbit in astronomical units; P = period in years. a) Visual binary stars: ...
... Only one direct method of mass determination: study dynamics of binary systems. By Kepler’s third law: (M1 + M2)/M¯ = a3/P2 a = semi-major axis of apparent orbit in astronomical units; P = period in years. a) Visual binary stars: ...
Surveying the Stars
... • It’s heavily skewed toward the most luminous stars, which you can see from much farther away and hence sampling a much bigger volume of space • HR diagram dominated by the Main Sequence ...
... • It’s heavily skewed toward the most luminous stars, which you can see from much farther away and hence sampling a much bigger volume of space • HR diagram dominated by the Main Sequence ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.