PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
Properties of simulated galaxies at z~4-7
... Extension to lower redshift to test further the interplay between galactic winds & AGN feedback. LAEs at z ~ 3: ANGUS + CRASHα, in collaboration with Akila Jeeson-Daniel (UoM). ...
... Extension to lower redshift to test further the interplay between galactic winds & AGN feedback. LAEs at z ~ 3: ANGUS + CRASHα, in collaboration with Akila Jeeson-Daniel (UoM). ...
Thibou Page 1 of 6 Telescopic Analysis of Tomorrow: Advances in
... billion price tag was prohibitive. Of course, these telescopes will also rely on more advanced technology. For example, a 10 meter telescope only needs one guide star laser for adaptive optics; a 40 meter scope may require five. The proposed 8.4 meter Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) in Chile ...
... billion price tag was prohibitive. Of course, these telescopes will also rely on more advanced technology. For example, a 10 meter telescope only needs one guide star laser for adaptive optics; a 40 meter scope may require five. The proposed 8.4 meter Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) in Chile ...
1 A Re-appraisal of the Habitability of Planets Around M Dwarf Stars
... within the class. Colors are also used as an abbreviation for temperatures; as one might expect, blue stars are hot and red stars are cool. And astronomers use the terms ‘earlier’ and ‘later’ to refer to the spectral sequence from hotter to cooler. ‘Dwarf’ (as opposed to Supergiant, luminous and nor ...
... within the class. Colors are also used as an abbreviation for temperatures; as one might expect, blue stars are hot and red stars are cool. And astronomers use the terms ‘earlier’ and ‘later’ to refer to the spectral sequence from hotter to cooler. ‘Dwarf’ (as opposed to Supergiant, luminous and nor ...
the Local Group - Simon P Driver
... tides • the maths for distortions of extended galaxies made up of many stars are hard, but we can picture the potential wells – start with the 5 Lagrangian points, which show stable positions e.g. for satellites launched from the Earth ...
... tides • the maths for distortions of extended galaxies made up of many stars are hard, but we can picture the potential wells – start with the 5 Lagrangian points, which show stable positions e.g. for satellites launched from the Earth ...
Relativistic stellar aberration for the Space Interferometry Mission
... respect to the Sun, e.g. χ = ±π. Indeed, the light rays coming from these sources do not experience gravitational deflection at all. Thus, those observations may serve as an anchor to allow one to remove the effects of the light bending from the high accuracy astrometric catalogues. This is why, in ...
... respect to the Sun, e.g. χ = ±π. Indeed, the light rays coming from these sources do not experience gravitational deflection at all. Thus, those observations may serve as an anchor to allow one to remove the effects of the light bending from the high accuracy astrometric catalogues. This is why, in ...
PPT
... parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of standard candles – We can measure distances greater than 10 billion light years using white dwarf supernovae as stand ...
... parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of standard candles – We can measure distances greater than 10 billion light years using white dwarf supernovae as stand ...
The Extragalactic Group of MPE and USM
... • Derive masses from broadband SEDs by fitting exponential SFH + bursts (with extinction); exp. SFHs only do NOT work for large l-range (check via comparison with local SDSS+2MASS sample). • Further check: compare FDF I-selected with GOODS K-selected. ...
... • Derive masses from broadband SEDs by fitting exponential SFH + bursts (with extinction); exp. SFHs only do NOT work for large l-range (check via comparison with local SDSS+2MASS sample). • Further check: compare FDF I-selected with GOODS K-selected. ...
Globular Clusters
... to internal and external dynamical interactions, they represent an ideal workbench to study STELLAR DYNAMICS and to test most exquisite theoretical dynamical models. If studied as a global system, GCs constitute fossil tracers of the dynamical and chemical evolution of the parent galaxy and can be u ...
... to internal and external dynamical interactions, they represent an ideal workbench to study STELLAR DYNAMICS and to test most exquisite theoretical dynamical models. If studied as a global system, GCs constitute fossil tracers of the dynamical and chemical evolution of the parent galaxy and can be u ...
Introduction - Arecibo Observatory
... mass, active stars, which cannot be studied efficiently through the radial velocity method, coronography, or optical interferometry.'' Current measurement errors are limited by the number of nearby compact sources that are well above the detection threshold of their observations and which can be us ...
... mass, active stars, which cannot be studied efficiently through the radial velocity method, coronography, or optical interferometry.'' Current measurement errors are limited by the number of nearby compact sources that are well above the detection threshold of their observations and which can be us ...
Astrometric Measurements of the Visual Double Star Epsilon Lyrae
... Astrometric Measurements of the Visual Double Star Epsilon Lyrae The Celestron 8 team used a scale constant obtained in observations of STFA 43AB. Separation Because Nimbus II is a “push” Dobsonian telescope without tracking, the stars drifted across the field fairly rapidly. As a result, separation ...
... Astrometric Measurements of the Visual Double Star Epsilon Lyrae The Celestron 8 team used a scale constant obtained in observations of STFA 43AB. Separation Because Nimbus II is a “push” Dobsonian telescope without tracking, the stars drifted across the field fairly rapidly. As a result, separation ...
Terrestrial Planets
... Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. According to Einstein, when the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear fart ...
... Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. According to Einstein, when the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear fart ...
The Star-Galaxy Era of Big History in the Light of Universal
... the Universe. In addition, there is no consensus on which galaxies should be regarded as old, and which galaxies should be considered young. The point is that within a single galaxy one can find stars and their aggregates that considerably differ in their type, age, and other parameters. For example ...
... the Universe. In addition, there is no consensus on which galaxies should be regarded as old, and which galaxies should be considered young. The point is that within a single galaxy one can find stars and their aggregates that considerably differ in their type, age, and other parameters. For example ...
Astronomy (ASTR)
... ASTR 390 Topics in Astronomy 3 Credit Hours A lecture in a topic of current interest in astronomy. Topics vary and are announced in the current Schedule of Classes. Three hours lecture. Prerequisite(s): ASTR 130 or PHYS 130 ASTR 390A Topics in Astronomy 3 Credit Hours Topic: Dark Mat ...
... ASTR 390 Topics in Astronomy 3 Credit Hours A lecture in a topic of current interest in astronomy. Topics vary and are announced in the current Schedule of Classes. Three hours lecture. Prerequisite(s): ASTR 130 or PHYS 130 ASTR 390A Topics in Astronomy 3 Credit Hours Topic: Dark Mat ...
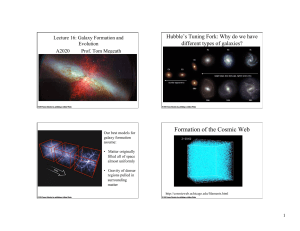
Lecture 16
... – Observations of stars and gas clouds orbiting at the centers of galaxies indicate that many galaxies, and perhaps all of them, have supermassive black holes • Are black holes important in galaxy formation – There is a relationships between bulge size and black holes size ...
... – Observations of stars and gas clouds orbiting at the centers of galaxies indicate that many galaxies, and perhaps all of them, have supermassive black holes • Are black holes important in galaxy formation – There is a relationships between bulge size and black holes size ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Letter to the Editor Low
... subsequent exposures per waveband and night, and careful eyeinspection showed that all sources have been efficiently removed using our modified median filtering technique which returns the lower 1/3 instead of the mean (1/2) value. We subtracted the sky-background and flat-fielded each exposure usin ...
... subsequent exposures per waveband and night, and careful eyeinspection showed that all sources have been efficiently removed using our modified median filtering technique which returns the lower 1/3 instead of the mean (1/2) value. We subtracted the sky-background and flat-fielded each exposure usin ...
Active Galactic Nuclei
... from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
... from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
Direct Detection of Galactic Halo Dark Matter
... predicted from the subdwarf star counts and a standard initial mass function is 1.3 ⫻ 10⫺5 MJ pc⫺3 (29), which is 10 times smaller than the value we calculate. This means that star formation in the early galaxy must have favored higher-mass stars that would evolve into the white dwarfs we are detect ...
... predicted from the subdwarf star counts and a standard initial mass function is 1.3 ⫻ 10⫺5 MJ pc⫺3 (29), which is 10 times smaller than the value we calculate. This means that star formation in the early galaxy must have favored higher-mass stars that would evolve into the white dwarfs we are detect ...
Lowell Observer, Winter 2006, Issue 69
... Observation of these double exponentials motivated my collaborator Bruce Elmegreen at IBM T. J. Watson Research Center to construct a new model of star formation that reproduces the observed double exponential profile. The model is based on the concept that both gravitational instabilities, as in th ...
... Observation of these double exponentials motivated my collaborator Bruce Elmegreen at IBM T. J. Watson Research Center to construct a new model of star formation that reproduces the observed double exponential profile. The model is based on the concept that both gravitational instabilities, as in th ...
MEarth
... single enclosure on Mount Hopkins, Arizona. Multiple sites spread in longitude would be observationally favorable, but would unfortunately be a cost-prohibitive arrangement. The number of targets is selected to ensure that even a null result is astrophysically interesting, while the sensitivity goal ...
... single enclosure on Mount Hopkins, Arizona. Multiple sites spread in longitude would be observationally favorable, but would unfortunately be a cost-prohibitive arrangement. The number of targets is selected to ensure that even a null result is astrophysically interesting, while the sensitivity goal ...
J: Chapter 4: Stars and Galaxies
... Measurement in Space How do scientists determine distance to stars from the solar system that Earth is part of? One way is to measure its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left ey ...
... Measurement in Space How do scientists determine distance to stars from the solar system that Earth is part of? One way is to measure its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left ey ...
Lecture 12
... Future missions • Space Interferometry Mission (SIM) – Launch in about 2013 – Goal of 4 microarcseconds • Direct parallax to any star in our Galaxy ...
... Future missions • Space Interferometry Mission (SIM) – Launch in about 2013 – Goal of 4 microarcseconds • Direct parallax to any star in our Galaxy ...
Stellar Evolution
... appear as a single point of light). Where does the binary appear: A: on the main sequence B: above the main sequence C: below the main sequence D: as a supergiant ...
... appear as a single point of light). Where does the binary appear: A: on the main sequence B: above the main sequence C: below the main sequence D: as a supergiant ...
15.1 Introduction
... ∼15 M% exceed Revol in Equation 1 by significant factors if mass loss is neglected, owing to their proximity to the Eddington limit, !e = 1. Here, the Eddington parameter, !e , is the ratio of radiative acceleration owing to Thomson (electron) scattering to surface gravity and may be written as ...
... ∼15 M% exceed Revol in Equation 1 by significant factors if mass loss is neglected, owing to their proximity to the Eddington limit, !e = 1. Here, the Eddington parameter, !e , is the ratio of radiative acceleration owing to Thomson (electron) scattering to surface gravity and may be written as ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.