The eleventh annual AST poster session - Home
... 3. Devin Kochanasz, North Seattle Community College Globular Clusters & the Oldest Stars in the Universe The size of our galaxy is commonly estimated by astronomers by a variety of methods. However, the discovery and understanding of globular clusters can tell us the true size and extent of our gala ...
... 3. Devin Kochanasz, North Seattle Community College Globular Clusters & the Oldest Stars in the Universe The size of our galaxy is commonly estimated by astronomers by a variety of methods. However, the discovery and understanding of globular clusters can tell us the true size and extent of our gala ...
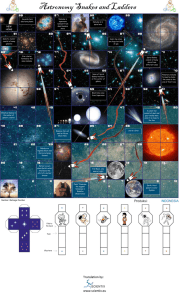
Astronomy Snakes and Ladders Earth, third planet in Solar System
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
25drake6s
... The Drake Equation In 1961, astronomer Frank Drake developed a formula to predict the number of intelligent species in our galaxy that we could communicate with right ...
... The Drake Equation In 1961, astronomer Frank Drake developed a formula to predict the number of intelligent species in our galaxy that we could communicate with right ...
25drake3s
... Observing Project Due Friday Project should be neat, organized, labeled and have all questions fully answered Telescope objects: Venus, Uranus, Neptune, Saturn, Moon ...
... Observing Project Due Friday Project should be neat, organized, labeled and have all questions fully answered Telescope objects: Venus, Uranus, Neptune, Saturn, Moon ...
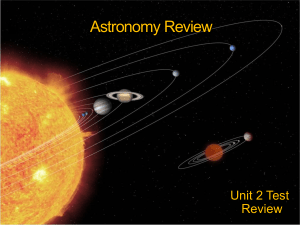
Astronomy Review fall 2013
... What is the approximate age of our Universe? 14.7 billion years old ...
... What is the approximate age of our Universe? 14.7 billion years old ...
Name____________________________________________
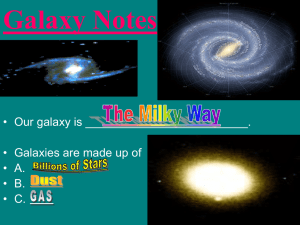
... 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. 6. Our Solar Syst ...
... 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. 6. Our Solar Syst ...
Read more about Brown`s work
... Brown has made many fundamental contributions to astronomy and astrophysics through instrument development, theory and interpretation, and observations. In the field of helioseismology—the study of the sun’s interior through the detection of subtle movements on the solar surface—he formulated a meth ...
... Brown has made many fundamental contributions to astronomy and astrophysics through instrument development, theory and interpretation, and observations. In the field of helioseismology—the study of the sun’s interior through the detection of subtle movements on the solar surface—he formulated a meth ...
Slide 1
... The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
... The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... in the middle where it has many stars. Where is the Milky Way brightest? A. in its middle B. on its edges C. It has the same brightness throughout. D. It’s not bright at all. 10. Galaxies are made up of billions of stars, all giving off light, but many galaxies can only be seen with powerful telesco ...
... in the middle where it has many stars. Where is the Milky Way brightest? A. in its middle B. on its edges C. It has the same brightness throughout. D. It’s not bright at all. 10. Galaxies are made up of billions of stars, all giving off light, but many galaxies can only be seen with powerful telesco ...
Chapter 3: the Sun
... This effect occurs when the gravitational field of a planet and its parent star act to magnify the light of a distant background star. The key advantage of gravitational microlensing is that it allows low mass (i.e. Earth-mass) planets to be detected using available ...
... This effect occurs when the gravitational field of a planet and its parent star act to magnify the light of a distant background star. The key advantage of gravitational microlensing is that it allows low mass (i.e. Earth-mass) planets to be detected using available ...
... wobbles in a star’s position caused by the gravitational tug of an orbiting planet. This method is most likely to find large planets close to their stars, however. Transits are better suited to finding something more like Earth in size and orbit. So far, 58 transiting planets have been found. The CO ...
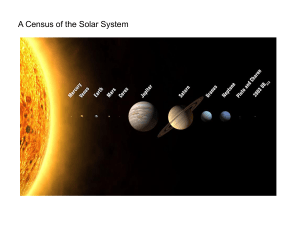
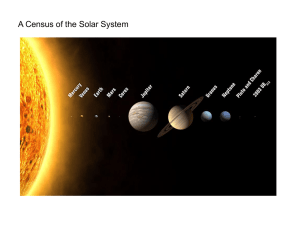
A Census of the Solar System
... The first two methods are based on the fact that a planet orbiting a star will cause the star to "wobble" in space. The first method detects the component of this wobble that is horizontal to our line of site, and is based simply on observing the position of the star ...
... The first two methods are based on the fact that a planet orbiting a star will cause the star to "wobble" in space. The first method detects the component of this wobble that is horizontal to our line of site, and is based simply on observing the position of the star ...
Extrasolar planets
... So our Sun orbits around the Sun-Jupiter centre of gravity with an orbital radius of only 1.2 solar radii. ...
... So our Sun orbits around the Sun-Jupiter centre of gravity with an orbital radius of only 1.2 solar radii. ...
File
... 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) ...
... 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is what type of galaxy? 29) ...
Slide 1
... sample powder from inside a rock target called "Telegraph Peak. This hole, with a diameter slightly smaller than a U.S. dime is the 3rd to be drilled in Curiosity’s 30 months on Mars. Current interest is the geological ratios between Si, Al and Mg which may give clues to ancient water leaching of mi ...
... sample powder from inside a rock target called "Telegraph Peak. This hole, with a diameter slightly smaller than a U.S. dime is the 3rd to be drilled in Curiosity’s 30 months on Mars. Current interest is the geological ratios between Si, Al and Mg which may give clues to ancient water leaching of mi ...
Are we Alone? The Search for Life Beyond the
... Are we Alone? - The Search for Life beyond the Earth. ...
... Are we Alone? - The Search for Life beyond the Earth. ...
Mason_Engines of Cha..
... • Combination of ESA Solar Orbiter and NASA Sentinels to probe to 0.2 AU (i.e. inside the orbit of Mercury) ...
... • Combination of ESA Solar Orbiter and NASA Sentinels to probe to 0.2 AU (i.e. inside the orbit of Mercury) ...
NOVA: Hunting the Edge of Space
... (If not in class, watch at: https://youtu.be/QkyX4C44Qwg.) As you watch the movie, please answer the following questions: 1. When was the Hubble space telescope launched? ...
... (If not in class, watch at: https://youtu.be/QkyX4C44Qwg.) As you watch the movie, please answer the following questions: 1. When was the Hubble space telescope launched? ...
What do we see in the night sky - Laureate International College
... Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have _________ that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the ____________________. ...
... Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have _________ that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the ____________________. ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
Kuiper Belt - Shades of Blue
... Exoplanet 55 Cancri e twice Earth’s Size – and made largely of diamond Oct 12, 2012 – Wired UK ...
... Exoplanet 55 Cancri e twice Earth’s Size – and made largely of diamond Oct 12, 2012 – Wired UK ...
Document
... *** The third method is based on detecting the small drop in apparent luminosity of a star as a planet transits in front of it, between the star and the Earth. ...
... *** The third method is based on detecting the small drop in apparent luminosity of a star as a planet transits in front of it, between the star and the Earth. ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.