Starchtpg for PDF 2010 bw.indd
... star as it orbits). The result, one side (the dark side) of the planet remains extremely cold and any atmosphere is frozen off. Stars just 50% more massive than the Sun are too short-lived for complex life to evolve. Also, two-thirds of the stars in our region of the Galaxy are members of binary or ...
... star as it orbits). The result, one side (the dark side) of the planet remains extremely cold and any atmosphere is frozen off. Stars just 50% more massive than the Sun are too short-lived for complex life to evolve. Also, two-thirds of the stars in our region of the Galaxy are members of binary or ...
Chapter27
... Earth with the treatment of life elsewhere. This material was part of the chapter on Earth. My reason for having such a limited discussion of life in the Universe was that I thought the subject was still very speculative. For example, at that time, only a little more than 10 years ago, we didn’t yet ...
... Earth with the treatment of life elsewhere. This material was part of the chapter on Earth. My reason for having such a limited discussion of life in the Universe was that I thought the subject was still very speculative. For example, at that time, only a little more than 10 years ago, we didn’t yet ...
b. Compare the similarities and differences of planets to the stars in
... S4E1. Students will compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, star patterns, and planets. b. Compare the similarities and differences of planets to the stars in appearance, position, and number in the night sky. Multiple Choice: How is the planet Jupiter similar to the Sun? a. It is ora ...
... S4E1. Students will compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, star patterns, and planets. b. Compare the similarities and differences of planets to the stars in appearance, position, and number in the night sky. Multiple Choice: How is the planet Jupiter similar to the Sun? a. It is ora ...
pptx
... Ncivil = N* fp np fl fi fc fL Now make your best guess at each number and multiply them. What do you get? N* = the number of stars in the Milky Way = 200,000,000,000 fp = the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” = 0.5 np = the number of habitable planets per system = 2 fl = t ...
... Ncivil = N* fp np fl fi fc fL Now make your best guess at each number and multiply them. What do you get? N* = the number of stars in the Milky Way = 200,000,000,000 fp = the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” = 0.5 np = the number of habitable planets per system = 2 fl = t ...
Astrobio
... Are there other places in our solar system that might harbor life? Temperatures that allow liquid water may be very important We discussed the Goldilocks idea for Venus (too hot), Mars (too cold), Earth (just right) ...
... Are there other places in our solar system that might harbor life? Temperatures that allow liquid water may be very important We discussed the Goldilocks idea for Venus (too hot), Mars (too cold), Earth (just right) ...
HABITABLE PLANETS For every star with planets, how many of
... split on whether these are a problem. (I’ll explain in class. Your text also has a good discussion of low-mass stars.) These are clearly important points since low mass stars comprise about 70 to 80 percent of all stars: If low-mass stars can have habitable planets with life, then they are the most ...
... split on whether these are a problem. (I’ll explain in class. Your text also has a good discussion of low-mass stars.) These are clearly important points since low mass stars comprise about 70 to 80 percent of all stars: If low-mass stars can have habitable planets with life, then they are the most ...
File1 - School of Astronomy, IPM
... Before starting photosynthesis, The growth of number of genes was high where cells to find more food. After this point the rate of Complication slowed down. After Sexual production and Multicelluarity, the number of genes accelerate up the the present human. Advance organisms stared 570 million year ...
... Before starting photosynthesis, The growth of number of genes was high where cells to find more food. After this point the rate of Complication slowed down. After Sexual production and Multicelluarity, the number of genes accelerate up the the present human. Advance organisms stared 570 million year ...
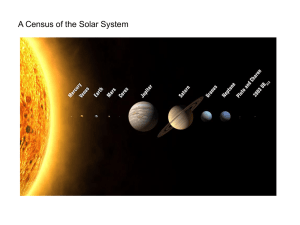
Solar System - U
... refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface ...
... refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface ...
ESSAY - First Earth-Like Exoplanet Found in Habitable Zone
... Carnegie's Alan Boss, has discovered what could be a large, rocky planet with a surface temperature of about 22 degrees Celsius (72 degrees Fahrenheit), comparable to a comfortable spring day on Earth. This landmark finding will be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The discovery team, led by W ...
... Carnegie's Alan Boss, has discovered what could be a large, rocky planet with a surface temperature of about 22 degrees Celsius (72 degrees Fahrenheit), comparable to a comfortable spring day on Earth. This landmark finding will be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The discovery team, led by W ...
31_Finding Earths
... Otherwise change in velocity of star is too small to measure. Lost in turbulence of star surface. Transit searches most sensitive to large planets orbiting close in. Otherwise unlikely to be exactly edge on and drop in brightness of star during transit will be very small. We can and have found Jupit ...
... Otherwise change in velocity of star is too small to measure. Lost in turbulence of star surface. Transit searches most sensitive to large planets orbiting close in. Otherwise unlikely to be exactly edge on and drop in brightness of star during transit will be very small. We can and have found Jupit ...
signatures of life on other worlds
... them to at least 3.8 billion years ago. Kasting notes that this interpretation of the surface morphology on Mars is not universally accepted, but it is appealing. The possibility of a liquid-water phase in the planet’s history raises the question of whether life might have had an early start there w ...
... them to at least 3.8 billion years ago. Kasting notes that this interpretation of the surface morphology on Mars is not universally accepted, but it is appealing. The possibility of a liquid-water phase in the planet’s history raises the question of whether life might have had an early start there w ...
Circumstellar habitable zone

In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the region around a star within which planetary-mass objects with sufficient atmospheric pressure can support liquid water at their surfaces. The bounds of the CHZ are calculated using the known requirements of Earth's biosphere, its position in the Solar System and the amount of radiant energy it receives from the Sun. Due to the importance of liquid water to life as it exists on Earth, the nature of the CHZ and the objects within is believed to be instrumental in determining the scope and distribution of Earth-like extraterrestrial life and intelligence.The habitable zone is also called the Goldilocks zone, a metaphor of the children's fairy tale of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, in which a little girl chooses from sets of three items, ignoring the ones that are too extreme (large or small, hot or cold, etc.), and settling on the one in the middle, which is ""just right"".Since the concept was first presented in 1953, stars have been confirmed to possess a CHZ planet, including some systems that consist of multiple CHZ planets. Most such planets, being super-Earths or gas giants, are more massive than Earth, because such planets are easier to detect. On November 4, 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs in the Milky Way. 11 billion of these may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists. The CHZ is also of particular interest to the emerging field of habitability of natural satellites, because planetary-mass moons in the CHZ might outnumber planets.In subsequent decades, the CHZ concept began to be challenged as a primary criterion for life. Since the discovery of evidence for extraterrestrial liquid water, substantial quantities of it are now believed to occur outside the circumstellar habitable zone. Sustained by other energy sources, such as tidal heating or radioactive decay or pressurized by other non-atmospheric means, the basic conditions for water-dependent life may be found even in interstellar space, on rogue planets, or their moons. In addition, other circumstellar zones, where non-water solvents favorable to hypothetical life based on alternative biochemistries could exist in liquid form at the surface, have been proposed.