Globular Clusters
... place. The nuclear energy production slows down and eventually stops the contraction. The star reaches a nice equilibrium, balancing energy production and transfer and global brightness, and enters into the main sequence (MS). This equilibrium holds on the MS for more than 70% of the total stellar l ...
... place. The nuclear energy production slows down and eventually stops the contraction. The star reaches a nice equilibrium, balancing energy production and transfer and global brightness, and enters into the main sequence (MS). This equilibrium holds on the MS for more than 70% of the total stellar l ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... • significant fraction of red sequence are disks, particularly at low masses • red disks are more bulge-dominated than higher z star-forming disks • a key intermediate phase in the transition to present day spheroidals Bundy et al 0912.1077 ...
... • significant fraction of red sequence are disks, particularly at low masses • red disks are more bulge-dominated than higher z star-forming disks • a key intermediate phase in the transition to present day spheroidals Bundy et al 0912.1077 ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution II
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
Understanding the H-R Diagram
... final stage of a star's life will be that of a dwarf or black hole, depending upon the star's original mass at its time of formation. In order to complete the accompanying assignment for this lesson, you must first learn about luminosity and the types of stars you will see on the H-R Diagram. (Here ...
... final stage of a star's life will be that of a dwarf or black hole, depending upon the star's original mass at its time of formation. In order to complete the accompanying assignment for this lesson, you must first learn about luminosity and the types of stars you will see on the H-R Diagram. (Here ...
Differential Rotation in A stars
... represents V = 3 km/s, M = 0 km/s. The blue line represents V=0 km/s, and M = 3 km/s. In wavelength space (left) the differences are barely noticeable. In Fourier space (right), the differences are larger. ...
... represents V = 3 km/s, M = 0 km/s. The blue line represents V=0 km/s, and M = 3 km/s. In wavelength space (left) the differences are barely noticeable. In Fourier space (right), the differences are larger. ...
The Sculptor dwarf irregular galaxy SDIG: present and past
... near-infrared (J andK) imaging at the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT). Despite the presence of many blue stars, there are at present no detectable H II regions, indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of oth ...
... near-infrared (J andK) imaging at the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT). Despite the presence of many blue stars, there are at present no detectable H II regions, indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of oth ...
PDF Full-text
... HD 20794d, Kepler-20d, and Gliese 581d, then by Mars, five more exoplanets, and Europa. Of the 637 exoplanets in the sample here considered, 10 (1.6%) have BCI values higher than for Europa, and five (0.8%) have BCI values higher than for Mars. Six of the exoplanets with the 14 highest BCI values or ...
... HD 20794d, Kepler-20d, and Gliese 581d, then by Mars, five more exoplanets, and Europa. Of the 637 exoplanets in the sample here considered, 10 (1.6%) have BCI values higher than for Europa, and five (0.8%) have BCI values higher than for Mars. Six of the exoplanets with the 14 highest BCI values or ...
Assessing the Possibility of Biological Complexity on Other
... HD 20794d, Kepler-20d, and Gliese 581d, then by Mars, five more exoplanets, and Europa. Of the 637 exoplanets in the sample here considered, 10 (1.6%) have BCI values higher than for Europa, and five (0.8%) have BCI values higher than for Mars. Six of the exoplanets with the 14 highest BCI values or ...
... HD 20794d, Kepler-20d, and Gliese 581d, then by Mars, five more exoplanets, and Europa. Of the 637 exoplanets in the sample here considered, 10 (1.6%) have BCI values higher than for Europa, and five (0.8%) have BCI values higher than for Mars. Six of the exoplanets with the 14 highest BCI values or ...
2P24.pdf
... spectroscopy of local star-forming galaxies in order to study their properties with spatial resolution. This data, in combination with optical and near-infrared imaging will be used to separate the regions where there is active star formation from the zones where the older underlying population domi ...
... spectroscopy of local star-forming galaxies in order to study their properties with spatial resolution. This data, in combination with optical and near-infrared imaging will be used to separate the regions where there is active star formation from the zones where the older underlying population domi ...
Measuring Distances
... Measuring Distances This apparent shift in position is called parallax. Because we are riding on Earth as it orbits the Sun we see the same effect for faraway objects like planets or stars. To the ancient astronomers of Greece, their failure to see stellar parallax meant that Earth must not be movi ...
... Measuring Distances This apparent shift in position is called parallax. Because we are riding on Earth as it orbits the Sun we see the same effect for faraway objects like planets or stars. To the ancient astronomers of Greece, their failure to see stellar parallax meant that Earth must not be movi ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... light-years. The sun is in a galaxy called the Milky Way that contains more than 100 billion stars. There are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe, and the average number of stars per galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the nig ...
... light-years. The sun is in a galaxy called the Milky Way that contains more than 100 billion stars. There are more than 100 billion galaxies in the universe, and the average number of stars per galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the nig ...
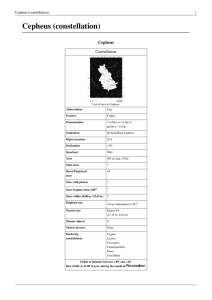
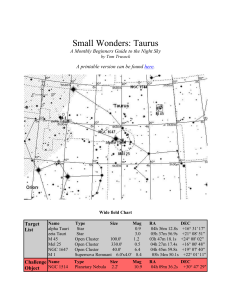
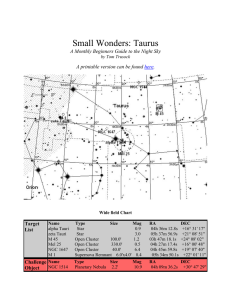
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
Science and the Universe
... size that orbits a star and does not produce its own light • A star is large body which (at some point during its life) produces light by nuclear reactions ...
... size that orbits a star and does not produce its own light • A star is large body which (at some point during its life) produces light by nuclear reactions ...
STELLAR FORMATION AND EVOLUTION
... The central region is denser and forms the protostar. The nebular disk forms slower to become a planetary system. As the temperature and pressure in the center begin to increase, the pressure from the core stops the infalling of gas into the core and the object becomes stable as a protostar. If a pr ...
... The central region is denser and forms the protostar. The nebular disk forms slower to become a planetary system. As the temperature and pressure in the center begin to increase, the pressure from the core stops the infalling of gas into the core and the object becomes stable as a protostar. If a pr ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B pre-main
... Blum et al. 2004), where the blue shoulder would imply a relatively high inclination angle of the disk (“edge-on”). Blum et al. (2004) model the CO 2−0 first-overtone ro-vibrational bandhead at 2294 nm of B275 resulting in v sin i = 109.7 ± 0.6 km s−1 (at the inner edge of the CO emission zone) and ...
... Blum et al. 2004), where the blue shoulder would imply a relatively high inclination angle of the disk (“edge-on”). Blum et al. (2004) model the CO 2−0 first-overtone ro-vibrational bandhead at 2294 nm of B275 resulting in v sin i = 109.7 ± 0.6 km s−1 (at the inner edge of the CO emission zone) and ...
H-Band spectroscopic classification of OB stars
... be confined to regions relatively close to their birthplaces and will be found close to the Galactic plane. The youngest massive stars will also still be in or near their dusty star forming environment. Due to the strong extinction from interstellar dust at optical wavelengths, OB stars at large dis ...
... be confined to regions relatively close to their birthplaces and will be found close to the Galactic plane. The youngest massive stars will also still be in or near their dusty star forming environment. Due to the strong extinction from interstellar dust at optical wavelengths, OB stars at large dis ...
10. The Lives of the Stars
... Disks and Jets Rotation presents a barrier to star formation; unless most of the original angular momentum is lost, gas can’t reach the center! It seems that jets — possibly driven by magnetic fields — may slow disk rotation and allow gas to flow in. Wikipedia: Protoplanetary disk ...
... Disks and Jets Rotation presents a barrier to star formation; unless most of the original angular momentum is lost, gas can’t reach the center! It seems that jets — possibly driven by magnetic fields — may slow disk rotation and allow gas to flow in. Wikipedia: Protoplanetary disk ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...