CHP 15
... a. they did not count the brightest stars. b. they did not study the southern sky. c. they did not have large enough telescopes. d. they only observed stars in the disk of the galaxy and not the halo. e. they did not know about interstellar dust clouds. 2. Which of the following is not a characteris ...
... a. they did not count the brightest stars. b. they did not study the southern sky. c. they did not have large enough telescopes. d. they only observed stars in the disk of the galaxy and not the halo. e. they did not know about interstellar dust clouds. 2. Which of the following is not a characteris ...
Galaxy Questions Info
... ellipticals. A spiral galaxy consists of a flattened disk containing spiral (pinwheel-shaped) arms, a bulge at its center, and a halo. Spiral galaxies have a variety of shapes, and they are classified according to the size of the bulge and the tightness and appearance of the arms. The spiral arms, w ...
... ellipticals. A spiral galaxy consists of a flattened disk containing spiral (pinwheel-shaped) arms, a bulge at its center, and a halo. Spiral galaxies have a variety of shapes, and they are classified according to the size of the bulge and the tightness and appearance of the arms. The spiral arms, w ...
The Star-Galaxy Era of Big History in the Light of Universal
... the Universe. In addition, there is no consensus on which galaxies should be regarded as old, and which galaxies should be considered young. The point is that within a single galaxy one can find stars and their aggregates that considerably differ in their type, age, and other parameters. For example ...
... the Universe. In addition, there is no consensus on which galaxies should be regarded as old, and which galaxies should be considered young. The point is that within a single galaxy one can find stars and their aggregates that considerably differ in their type, age, and other parameters. For example ...
A Spectroscopic Study of the RV Tauri Stars TT Oph... Guillermo Hernandez , Donald K. Walter , Jennifer Cash
... alternating deep and shallow minima. The time from one deep minima to the next deep minima is known as the formal period, while the time from one deep minima to the next shallow minima is referred to as the half period. The formal periods are typically in the range of 30 to 150 days. RV Tauri stars ...
... alternating deep and shallow minima. The time from one deep minima to the next deep minima is known as the formal period, while the time from one deep minima to the next shallow minima is referred to as the half period. The formal periods are typically in the range of 30 to 150 days. RV Tauri stars ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... where v is the velocity in km/sec, c is the speed of light (300,000 km/sec), is the rest wavelength of the radiation, and is the amount the radiation has been shifted towards longer wavelengths ( = the observed wavelength minus the rest wavelength). For these spectra, wavelengths are usually ...
... where v is the velocity in km/sec, c is the speed of light (300,000 km/sec), is the rest wavelength of the radiation, and is the amount the radiation has been shifted towards longer wavelengths ( = the observed wavelength minus the rest wavelength). For these spectra, wavelengths are usually ...
Rotating Stars and Revolving Planets: Bayesian Exploration of the
... resembling the model. A frequentist nonparametric “omnibus” test that focuses on rejection of a null appears more robust. But recent theoretical insights into the capabilities of frequentist hypothesis tests ameliorate this criticism. Imagine an omnibus goodness-of-fit test that aims to detect perio ...
... resembling the model. A frequentist nonparametric “omnibus” test that focuses on rejection of a null appears more robust. But recent theoretical insights into the capabilities of frequentist hypothesis tests ameliorate this criticism. Imagine an omnibus goodness-of-fit test that aims to detect perio ...
Distance determination for RAVE stars using stellar models
... spirals, and finally dwarf galaxies. The power spectrum is used to measure the power of density perturbations on a certain scale. The current cosmological model predicts a HarrisonZel’dovich spectrum (P (k) ∝ k, where k is the wavenumber). This power spectrum predicts more power on small scale, so t ...
... spirals, and finally dwarf galaxies. The power spectrum is used to measure the power of density perturbations on a certain scale. The current cosmological model predicts a HarrisonZel’dovich spectrum (P (k) ∝ k, where k is the wavenumber). This power spectrum predicts more power on small scale, so t ...
Toward a revival of Stellar Intensity Interferometry
... (Labeyrie et al. 2006). The important point is that the correlation is a function of the difference in phase between the low frequency beats at the two detectors. This correlation does not depend on the phase difference of the light at the two detectors. The requirements for t ...
... (Labeyrie et al. 2006). The important point is that the correlation is a function of the difference in phase between the low frequency beats at the two detectors. This correlation does not depend on the phase difference of the light at the two detectors. The requirements for t ...
INTL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS
... state-of-the-art achievements in optics, electronics, computer science, precision engineering and much more. One of the most important fields of astronomical science is observational astronomy, which takes observation of celestial objects as the most important source of information about the univers ...
... state-of-the-art achievements in optics, electronics, computer science, precision engineering and much more. One of the most important fields of astronomical science is observational astronomy, which takes observation of celestial objects as the most important source of information about the univers ...
ADAS Simple Guide to Telescope Instrumentation and Operation
... relatively simple. The objective forms a real image, diminished in size and upside-down, of the object observed. The eyepiece — which, consisting of a converging lens with short focal length, is actually a magnifying lens — enlarges the image formed by the objective. The image observed is however up ...
... relatively simple. The objective forms a real image, diminished in size and upside-down, of the object observed. The eyepiece — which, consisting of a converging lens with short focal length, is actually a magnifying lens — enlarges the image formed by the objective. The image observed is however up ...
The Search for Planet X Transcript
... was able to make himself invisible. As the first two letters of its name were the initials of Percival Lowell, at whose observatory it had been discovered, this suggestion was eagerly accepted. Initially it was thought that Pluto had a significant size - even though it could only be observed as a po ...
... was able to make himself invisible. As the first two letters of its name were the initials of Percival Lowell, at whose observatory it had been discovered, this suggestion was eagerly accepted. Initially it was thought that Pluto had a significant size - even though it could only be observed as a po ...
Chapter 16
... formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative model, several separate clouds of gas merge to form than Galaxy rather than one. High-velocity atomic hydrogen clouds have been observed since 1963; t ...
... formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative model, several separate clouds of gas merge to form than Galaxy rather than one. High-velocity atomic hydrogen clouds have been observed since 1963; t ...
Chapter 10 Neutron Stars and General Relativity
... properties of neutron stars, over a microscopic scale characteristic of nuclear and other sub-atomic interactions the metric is essentially constant. • Thus the microphysics (nuclear and elementary particle interactions) of the neutron star can be described by quantum mechanics implemented in flat s ...
... properties of neutron stars, over a microscopic scale characteristic of nuclear and other sub-atomic interactions the metric is essentially constant. • Thus the microphysics (nuclear and elementary particle interactions) of the neutron star can be described by quantum mechanics implemented in flat s ...
Do We Know of Any Maunder Minimum Stars?
... log RHK < −5.1, the latter of which they considered Maunder minimum candidates. Baliunas & Jastrow (1990) suggested that the activity level of the sun during the Maunder Minimum corresponded to that of these low-activity stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the ...
... log RHK < −5.1, the latter of which they considered Maunder minimum candidates. Baliunas & Jastrow (1990) suggested that the activity level of the sun during the Maunder Minimum corresponded to that of these low-activity stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the ...
The Sky
... • As you read this chapter, keep in mind that you live on a planet. – Stars are scattered in the void all around you, most very distant and some closer. – Earth rotates on its axis once a day. So, from your viewpoint, the sky appears to rotate once around you each day. – Not only does the sun rise i ...
... • As you read this chapter, keep in mind that you live on a planet. – Stars are scattered in the void all around you, most very distant and some closer. – Earth rotates on its axis once a day. So, from your viewpoint, the sky appears to rotate once around you each day. – Not only does the sun rise i ...
1. INTRODUCTION
... as these stars often show several distinct stochastic events. We have focused our analysis on young, active stars that do not display rotationally modulated light curves and that can be considered as single X-ray sources. Some stars in the sample are detected or known binary systems, in which only o ...
... as these stars often show several distinct stochastic events. We have focused our analysis on young, active stars that do not display rotationally modulated light curves and that can be considered as single X-ray sources. Some stars in the sample are detected or known binary systems, in which only o ...
24_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... star as such a planet transited across it. Why does this technique actually miss the vast majority of planets? Answer: By searching for transits, Kepler can only detect those planets with orbits that cross our line of sight to the star. This means the orbit must be very close to edge-on. Because pla ...
... star as such a planet transited across it. Why does this technique actually miss the vast majority of planets? Answer: By searching for transits, Kepler can only detect those planets with orbits that cross our line of sight to the star. This means the orbit must be very close to edge-on. Because pla ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... Astronomy with one of its worst attributes: the magnitude scales. He sought to classify the stars by their brightness with a number scale. The first group of stars to become visible at night were called magnitude one, the next group to become visible were the magnitude two stars, and so on up to mag ...
... Astronomy with one of its worst attributes: the magnitude scales. He sought to classify the stars by their brightness with a number scale. The first group of stars to become visible at night were called magnitude one, the next group to become visible were the magnitude two stars, and so on up to mag ...
Possible climates on terrestrial exoplanets
... the planetesimals that accrete to form the bulk of the planet itself. These will be the major sources of 1) carbon compounds like CO2 or possibly CH4 , 2) water, especially if they formed beyond the “snow line” (the distance from the star in the nebula where it is cold enough for water to condense i ...
... the planetesimals that accrete to form the bulk of the planet itself. These will be the major sources of 1) carbon compounds like CO2 or possibly CH4 , 2) water, especially if they formed beyond the “snow line” (the distance from the star in the nebula where it is cold enough for water to condense i ...
1 solar and stellar abundances of the elements
... it with a real star. We must extract from our observational material both the chemical composition of the star and the physical state of its atmosphere, simultaneously ! 2. THE ATMOSPHERE OF THE SUN The sun, which is the only star close enough to appear with an appreciable disk, shows complexities e ...
... it with a real star. We must extract from our observational material both the chemical composition of the star and the physical state of its atmosphere, simultaneously ! 2. THE ATMOSPHERE OF THE SUN The sun, which is the only star close enough to appear with an appreciable disk, shows complexities e ...
Science Grade 08 Unit 11 Exemplar Lesson 02: Classifying Stars
... This unit bundles student expectations that address components and characteristics of the universe. Students learn that stars and galaxies are part of the universe and how they can be classified by their characteristics. Prior to this unit, in Grade 8, students studied the effects resulting from cyc ...
... This unit bundles student expectations that address components and characteristics of the universe. Students learn that stars and galaxies are part of the universe and how they can be classified by their characteristics. Prior to this unit, in Grade 8, students studied the effects resulting from cyc ...
Internal structure of a cold dark molecular cloud inferred
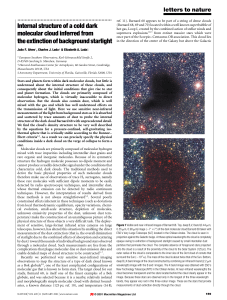
... Figure 1 Visible and near-infrared images of Barnard 68. Top, deep B,V,I band (0.44 mm, 0.55 mm, 0.90 mm) image (,79 ´ 79) of the dark molecular cloud Barnard 68 taken with ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) located in the Chilean Andes. The cloud is seen in projection against the Galactic bulge. At t ...
... Figure 1 Visible and near-infrared images of Barnard 68. Top, deep B,V,I band (0.44 mm, 0.55 mm, 0.90 mm) image (,79 ´ 79) of the dark molecular cloud Barnard 68 taken with ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) located in the Chilean Andes. The cloud is seen in projection against the Galactic bulge. At t ...