The Solar Nebula Theory
... The planets formed in a dust-filled disk of gas surrounding the very young Sun ...
... The planets formed in a dust-filled disk of gas surrounding the very young Sun ...
Magnitudes - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer, devised a method of measuring the brightness of stars. A bright star would be said to have an apparent magnitude of 1. A faint star has an apparent magnitude of 6. A few stars, planets and of course our own Sun have been recategorised so they appear brighter than 1. S ...
... Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer, devised a method of measuring the brightness of stars. A bright star would be said to have an apparent magnitude of 1. A faint star has an apparent magnitude of 6. A few stars, planets and of course our own Sun have been recategorised so they appear brighter than 1. S ...
12 Stellar Evolution
... If the white dwarf’s mass exceeds 1.4 solar masses, electron degeneracy can no longer keep the core from collapsing. Carbon fusion begins throughout the star almost simultaneously, resulting in a carbon ...
... If the white dwarf’s mass exceeds 1.4 solar masses, electron degeneracy can no longer keep the core from collapsing. Carbon fusion begins throughout the star almost simultaneously, resulting in a carbon ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... Body and Star fill the listbox with Bodies and Stars respectively. If you have selected a body in the star chart it will be displayed by default. Now sets the time fields to the current time. Last sets the time fields to the last calculated LOP. UTC when checked indicates that time values are in Coo ...
... Body and Star fill the listbox with Bodies and Stars respectively. If you have selected a body in the star chart it will be displayed by default. Now sets the time fields to the current time. Last sets the time fields to the last calculated LOP. UTC when checked indicates that time values are in Coo ...
01-Star Atlas Project - Mapping the Heavens
... A two-dimensional surface (like a sheet of graph paper) requires two number axes (axes is the plural of axis) oriented perpendicular to each other (Figure 1-7). The coordinates for any point on the sheet is just an ordered pair of numbers — the horizontal (left/right) coordinate followed by the vert ...
... A two-dimensional surface (like a sheet of graph paper) requires two number axes (axes is the plural of axis) oriented perpendicular to each other (Figure 1-7). The coordinates for any point on the sheet is just an ordered pair of numbers — the horizontal (left/right) coordinate followed by the vert ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... You will encounter the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram on several occations during this course. Here you will only get a short introduction and just enough information in order to be able to use it for the estimation of distances. In the lectures on stellar evolution, you will get more details. The ...
... You will encounter the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram on several occations during this course. Here you will only get a short introduction and just enough information in order to be able to use it for the estimation of distances. In the lectures on stellar evolution, you will get more details. The ...
$doc.title
... The astronomers soon determined that shifting the spectrum of SCP 06F6 similarly aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have ...
... The astronomers soon determined that shifting the spectrum of SCP 06F6 similarly aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have ...
Magnetic cycles of Sun-like stars with different levels of coronal and
... For the HK-project, stars were carefully chosen according to those physical parameters, which are most close to the Sun: cold, single stars – dwarfs, belonging to the main sequence. Close binary systems are excluded. Results of joint observations of the HK-project radiation fluxes and periods of rot ...
... For the HK-project, stars were carefully chosen according to those physical parameters, which are most close to the Sun: cold, single stars – dwarfs, belonging to the main sequence. Close binary systems are excluded. Results of joint observations of the HK-project radiation fluxes and periods of rot ...
Heavy Element Abundances in Late-B and Early
... peculiar stars of the upper main sequence by up to a million times the solar system levels. Such enhancements are believed to result from atmospheric dynamics (i.e., diffusion) rather than scenarios that dredge up nuclearprocessed material to the surface or transfer processed material between binary ...
... peculiar stars of the upper main sequence by up to a million times the solar system levels. Such enhancements are believed to result from atmospheric dynamics (i.e., diffusion) rather than scenarios that dredge up nuclearprocessed material to the surface or transfer processed material between binary ...
Moitinho et al. - Wiley Online Library
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
Larger, high-res file, best for printing
... Is it possible Cas A’s supernovae was unusually dim? Model calculations indicate that a delayed explosion after core collapse can result in gravitationally bound ejecta — within minutes of the explosion, much of the ejecta falls back onto the core. Since supernovae luminosity is proportional to the ...
... Is it possible Cas A’s supernovae was unusually dim? Model calculations indicate that a delayed explosion after core collapse can result in gravitationally bound ejecta — within minutes of the explosion, much of the ejecta falls back onto the core. Since supernovae luminosity is proportional to the ...
Journey through the cosmos
... and not in perfect circular orbits. This was a discovery by Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) as a result of mathematical calculations using data from accurate night sky observations made by Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). Kepler also developed laws that state how: ...
... and not in perfect circular orbits. This was a discovery by Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) as a result of mathematical calculations using data from accurate night sky observations made by Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). Kepler also developed laws that state how: ...
Full Poster - Cool Cosmos
... Almost everything that we know about the Universe comes from studying the light that is emitted or reflected by objects in space. Apart from a few exceptions, such as the collection of moon rocks, astronomers must rely on collecting and analyzing the faint light from distant objects in order to stud ...
... Almost everything that we know about the Universe comes from studying the light that is emitted or reflected by objects in space. Apart from a few exceptions, such as the collection of moon rocks, astronomers must rely on collecting and analyzing the faint light from distant objects in order to stud ...
Stellar Magnitudes & Distances
... beyond the 1 to 6 range. • For example, the sun appears much brighter than any other star in the sky. It has an (apparent) magnitude of -26.73. • The full moon, at its brightest, has an (apparent) magnitude of -12.6 and Venus can be as bright as -4.4. • On the other end, the Hubble Space Telescope c ...
... beyond the 1 to 6 range. • For example, the sun appears much brighter than any other star in the sky. It has an (apparent) magnitude of -26.73. • The full moon, at its brightest, has an (apparent) magnitude of -12.6 and Venus can be as bright as -4.4. • On the other end, the Hubble Space Telescope c ...
The Relationship Between a Star`s Brightness and its Distance
... beyond the 1 to 6 range. • For example, the sun appears much brighter than any other star in the sky. It has an (apparent) magnitude of -26.73. • The full moon, at its brightest, has an (apparent) magnitude of -12.6 and Venus can be as bright as -4.4. • On the other end, the Hubble Space Telescope c ...
... beyond the 1 to 6 range. • For example, the sun appears much brighter than any other star in the sky. It has an (apparent) magnitude of -26.73. • The full moon, at its brightest, has an (apparent) magnitude of -12.6 and Venus can be as bright as -4.4. • On the other end, the Hubble Space Telescope c ...
Constellation
... announced the discovery in his Monthly Correspondence summer of 1801. Piazzi tried to predict Ceres’ orbit. This was needed so other astronomers could find it. He observed Ceres for six weeks. He didn’t have enough information to determine Ceres’ orbit. After that, others searched for Ceres in vain. ...
... announced the discovery in his Monthly Correspondence summer of 1801. Piazzi tried to predict Ceres’ orbit. This was needed so other astronomers could find it. He observed Ceres for six weeks. He didn’t have enough information to determine Ceres’ orbit. After that, others searched for Ceres in vain. ...
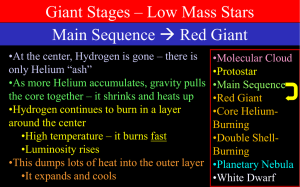
Giant Stars
... plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
... plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...